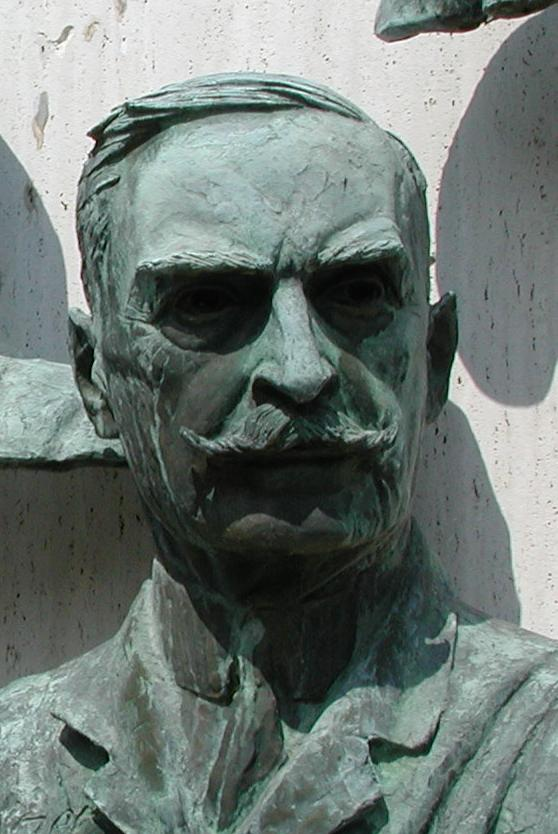
Karl Landsteiner ForMemRS (14 June 1868 – 26 June 1943) was an Austrian-born American biologist, physician, and immunologist. He distinguished the main blood groups in 1900, having developed the modern system of classification of blood groups from his identification of the presence of agglutinins in the blood, and in 1937 identified, with Alexander S. Wiener, the Rhesus factor, thus enabling physicians to transfuse blood without endangering the patient’s life. With Constantin Levaditi and Erwin Popper, he discovered the polio virus in 1909. He received the Aronson Prize in 1926. In 1930, he received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. He was posthumously awarded the Lasker Award in 1946, and has been described as the father of transfusion medicine.
Rous, P. (1947). “Karl Landsteiner. 1868–1943”. Obituary Notices of Fellows of the Royal Society. 5 (15): 294–324. doi:10.1098/rsbm.1947.0002. JSTOR 769085. S2CID 161789667. “Karl Landsteiner”. Nobel Lectures, Physiology or Medicine 1922–1941. Amsterdam: Elsevier Publishing Company. 1965. Retrieved 12 June 2018. “Karl Landsteiner”, Jewish Virtual Library Speiser, Paul; Smekal, Ferdinand G. (1990). Karl Landsteiner: Entdecker der Blutgruppen und Pionier der Immunologie (3rd ed.). Berlin. ISBN 9783894120849.
Early life and education
Born into a Jewish family, Landsteiner’s father, Leopold (1818–1875), a renowned Viennese journalist who was editor-in-chief of Die Presse, died at age 56, when Karl was only 6. This led to a close relationship between him and his mother Fanny (née Hess; 1837–1908). After graduating with the Matura exam from a Vienna secondary school, he took up the study of medicine at the University of Vienna and wrote his doctoral thesis in 1891. While still a student he published an essay on the influence of diets on the composition of blood.
“Karl Landsteiner”. Nobel Lectures, Physiology or Medicine 1922–1941. Amsterdam: Elsevier Publishing Company. 1965. Retrieved 12 June 2018.
From 1891 to 1893, Landsteiner studied chemistry in Würzburg under Hermann Emil Fischer, in München, Eugen Bamberger and in Zürich under Arthur Rudolf Hantzsch. He had a number of publications from that period, some of them in co-operation with his professors.
Speiser & Smekal 1990, p. 24.
Research work in Vienna; discovery of the polio virus
After returning to Vienna he became an assistant to Max von Gruber at the Hygienic Institute. As a leading racial hygienist, when von Gruber first met the Nazi dictator Adolf Hitler he described him as:
It was the first time I had seen Hitler close at hand. Face and head of inferior type, cross-breed; low receding forehead, ugly nose, broad cheekbones, little eyes, dark hair. Expression not of a man exercising authority in perfect self-command, but of raving excitement. At the end an expression of satisfied egotism.
— Max von Gruber, Description as a witness at court in 1923
OSS Psychological Profile of Hitler, Part Two. Nizkor.org. Retrieved on 2014-06-30.

In his studies Landsteiner concentrated on the mechanism of immunity and the nature of antibodies. From November 1897 to 1908 Landsteiner was an assistant at the pathological-anatomical institute of the University of Vienna under Anton Weichselbaum, where he published 75 papers, dealing with issues in serology, bacteriology, virology and pathological anatomy. In addition he did some 3,600 autopsies in those ten years. Weichselbaum was Landsteiner’s tutor for his postdoctoral lecture qualification in 1903. From 1908 to 1920 Landsteiner was prosector at the Wilhelminenspital in Vienna and in 1911 he was sworn in as an associate professor of pathological anatomy. During that time he discovered – in co-operation with Erwin Popper – the infectious character of poliomyelitis and isolated the polio virus. In recognition of this groundbreaking discovery, which proved to be the basis for the fight against polio, he was posthumously inducted into the Polio Hall of Fame at Warm Springs, Georgia, which was dedicated in January 1958.
Speiser & Smekal 1990, p. 33. Landsteiner, K.; Popper, E. (1909). “Übertragung der Poliomyelitis acuta auf Affen” [Transmission of Poliomyelitis acuta to monkeys]. Zeitschrift für Immunitätsforschung und experimentelle Therapie [Journal for Research on Immunity and Experimental Therapy] (in German). 2: 377–390.
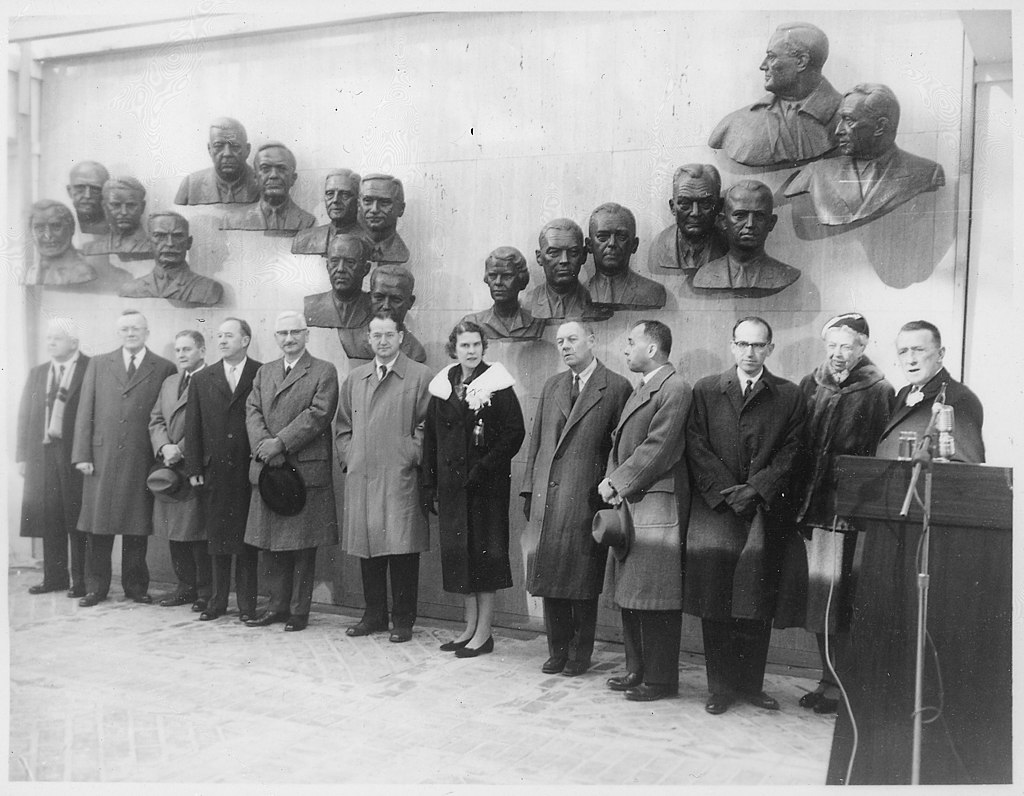


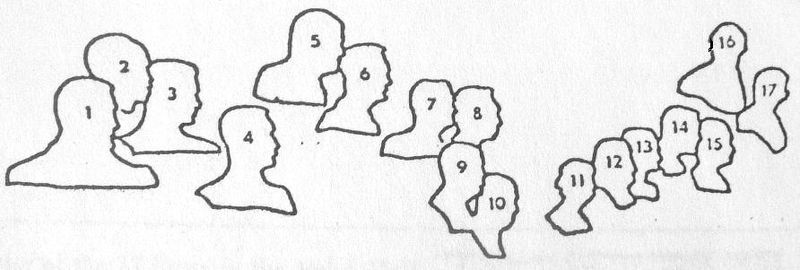
| # | Name | Achievement |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jakob Heine (1800 – 1879) | Discovered and described infantile paralysis in 1840. Jakob Heine – remembered and honoured in the USA |
| 2 | Karl Oskar Medin (1847 – 1927) | Recognized and described polio as an acute infection (1890). |
| 3 | Ivar Wickman (1872 – 1914) | Discovered the epidemic character of polio (1907) and coined the term Heine–Medin disease; also showed a high prevalence of non-paralytic polio. |
| 4 | Karl Landsteiner (1868 – 1943) | Discovered poliovirus and demonstrated transmission to monkeys. |
| 5 | Thomas Milton Rivers (1888 – 1962) | Chairman of the National Foundation committee on vaccination, which planned the successful 1954 vaccine field trials. |
| 6 | Charles Armstrong (1886 – 1967) | A Public Health Service physician, Armstrong discovered in 1939 that poliovirus can be transmitted to cotton rats, and started self-tests with nasal spray vaccination. Armstrong Biography |
| 7 | John R. Paul (1893 – 1972) | Made essential contributions to the knowledge of how polio is spread. John R. Paul: A History of Poliomyelitis (Yale University,1971 and http://edoc.hu-berlin.de/habilitationen/kunz-regina-agnes-2003-10-23/HTML/chapter1.html |
| 8 | Albert Sabin (1906 – 1993) | A leader in the search for a live virus vaccine for polio, Sabin helped show how the virus reached the central nervous system; developed the oral vaccine, which was cheaper and easier to distribute. |
| 9 | Thomas Francis, Jr. (1900 – 1969) | An epidemiologist at the University of Michigan and Salk’s (No. 15) tutor; recognized the effectiveness of the Salk vaccine. Thomas Francis, Jr., MD | 50th Anniversary of the Polio Vaccine Archived May 15, 2009, at the Wayback Machine |
| 10 | Joseph L. Melnick (1914 – 2001) | Developed immunity measures for populations exposed to the virus. |
| 11 | Isabel Morgan (1911 – 1996) | Prepared an experimental vaccine from virus inactivated with formaldehyde which protected monkeys against paralytic polio. |
| 12 | Howard A. Howe (1901 – 1976) | The first to show that chimpanzees can acquire polio infection by mouth; carried out small-scale experiments in humans with a formalin– treated vaccine. Howe, Howard A.: Antibody response of chimpanzees and human beings to formalin-inactivated trivalent poliomyelitis vaccine in American Journal of Hygiene, 1952 Nov;56(3)pp.265–286. |
| 13 | David Bodian (1910 – 1992) | Showed that the virus gets into the blood stream before reaching the central nervous system and therefore could be blocked by antibodies in the blood. David Bodian Archived 2007-05-09 at the Wayback Machine |
| 14 | John F. Enders (1897 – 1985) | Led the way in finding how to grow polio viruses in cultures of non-nervous tissue, which made possible the production of a safe and effective vaccine in quantity. |
| 15 | Jonas E. Salk (1914 – 1995) | Developed the vaccine which bears his name. |
| 16 | Franklin D. Roosevelt (1882 – 1945) | Founded the Warm Springs Foundation in 1927 and the “National Foundation for Infantile Paralysis (NFIP)” in 1938. |
| 17 | Basil O’Connor (1892 – 1972) | The architect of the fight against polio, O’Connor was president of the NFIP from its outset in 1938 and of the “Georgia Warm Springs Foundation” after 1945. |
Research of the blood groups
In 1900 Landsteiner found out that the blood of two people under contact agglutinates, and in 1901 he found that this effect was due to contact of blood with blood serum. As a result, he succeeded in identifying the three blood groups A, B and O, which he labelled C, of human blood. Landsteiner also found out that blood transfusion between persons with the same blood group did not lead to the destruction of blood cells, whereas this occurred between persons of different blood groups. Based on his findings, the first successful blood transfusion was performed by Reuben Ottenberg at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York in 1907.
Landsteiner, Karl (1900). “Zur Kenntnis der antifermentativen, lytischen und agglutinierenden Wirkungen des Blutserums und der Lymphe”. Centralblatt F. Bakteriologie, Parasitenkunde U. Infektionskrankheiten. 27: 357–362.

Karl Landsteiner depicted on a medal awarded by the Netherlands Red Cross
Today, whole blood transfusions are rare. It is now well known that persons with blood group AB can accept red blood cell donations of the other blood groups, and that persons with blood group O-negative can donate red blood cells to all other groups. Individuals with blood group AB are referred to as universal recipients and those with blood group O-negative are known as universal donors. These donor-recipient relationships arise due to the fact that type O-negative blood possesses neither antigens of blood group A nor of blood group B. Therefore, the immune systems of persons with blood group A, B or AB do not refuse the donation. Further, because persons with blood group AB do not form antibodies against either the antigens of blood group A or B, they can accept red blood cells from persons with these blood groups, as well as from persons with blood group O-negative.
In 1930 Landsteiner was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in recognition of these achievements. For his pioneering work, he is recognized as the father of transfusion medicine.
“Homage to scientist on Blood Donor’s Day”. The Tribune. 15 June 2006. Retrieved 14 January 2012.
Research work in the Netherlands and the United States
After World War I, Vienna and the new republic of Austria as a whole was in a desolate economic state, a situation in which Landsteiner did not see any possibilities to carry on with his research work. He decided to move to the Netherlands and accepted a post as prosector in the small Catholic St. Joannes de Deo hospital (now MCH Westeinde) in The Hague and, in order to improve his financial situation also took a job in a small factory, producing old tuberculin (tuberculinum pristinum). He also published a number of papers, five of them being published in Dutch by the Royal Academy of Sciences. Yet working conditions proved to be not much better than in post-war Vienna.
“Wie was Karl Landsteiner?” [Who was Karl Landsteiner?]. Landsteiner Instituut (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 16 December 2018. Retrieved 13 December 2018. Speiser & Smekal 1990, p. 63.
So Landsteiner accepted the invitation that reached him from New York, initiated by Simon Flexner, who was familiar with Landsteiner’s work, to work for the Rockefeller Institute. He arrived there with his family in the spring of 1923. Throughout the 1920s Landsteiner worked on the problems of immunity and allergy. In 1927 he discovered new blood groups: M, N and P, refining the work he had begun 20 years before. Shortly thereafter, Landsteiner and his collaborator, Philip Levine, published the work and, later that same year, the types began to be used in paternity suits.
“Karl Landsteiner”. Nobel Lectures, Physiology or Medicine 1922–1941. Amsterdam: Elsevier Publishing Company. 1965. Retrieved 12 June 2018.
Awards and honours
Landsteiner was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 1932 and awarded the Cameron Prize for Therapeutics of the University of Edinburgh in 1937. He was elected a Foreign Member of the Royal Society (ForMemRS) in 1941. In 1946, he was posthumously awarded the Lasker-DeBakey Clinical Medical Research Award.
Since 2005, World Blood Donor Day is celebrated on Landsteiner’s birthday anniversary.
Personal life
Landsteiner converted from Judaism to Christianity in 1890, as he baptised into the Catholic Church. In 1916, he married Leopoldine Helene Wlasto, a Greek Orthodox woman who converted to her husband’s Catholic faith. In 1937, Landsteiner unsuccessfully initiated legal action against an American publisher who had included him in the book Who’s Who in American Jewry, stating that “it will be detrimental to me to emphasize publicly the religion of my ancestors.”
Staudacher, Anna L. (2009) “… meldet den Austritt aus dem mosaischen Glauben”. 18000 Austritte aus dem Judentum in Wien, 1868–1914: Namen – Quellen – Daten. Peter Lang, Frankfurt, ISBN 978-3-631-55832-4, p. 349 “Concise Dictionary of American Jewish Biography”. The Jacob Rader Marcus Center of the American Jewish Archives.[page needed] “Dr. Landsteiner Sues to Escape Being Labelled Jew”. Jewish Telegraphic Agency. 6 April 1937.
References[edit]
- ^ Dorner, Friedrich; Schwarz, Hans Peter (2003). “Karl Landsteiner and his major contributions to haematology”. British Journal of Haematology. 121 (4): 556–565. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.2003.04295.x. PMID 12752096. S2CID 36393411.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c Rous, P. (1947). “Karl Landsteiner. 1868–1943”. Obituary Notices of Fellows of the Royal Society. 5 (15): 294–324. doi:10.1098/rsbm.1947.0002. JSTOR 769085. S2CID 161789667.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c “Karl Landsteiner”. Nobel Lectures, Physiology or Medicine 1922–1941. Amsterdam: Elsevier Publishing Company. 1965. Retrieved 12 June 2018.
- ^ “Karl Landsteiner”, Jewish Virtual Library
- ^ Speiser, Paul; Smekal, Ferdinand G. (1990). Karl Landsteiner: Entdecker der Blutgruppen und Pionier der Immunologie (3rd ed.). Berlin. ISBN 9783894120849.[page needed]
- ^ Speiser & Smekal 1990, p. 24.
- ^ Speiser & Smekal 1990, p. 33.
- ^ Landsteiner, K.; Popper, E. (1909). “Übertragung der Poliomyelitis acuta auf Affen” [Transmission of Poliomyelitis acuta to monkeys]. Zeitschrift für Immunitätsforschung und experimentelle Therapie [Journal for Research on Immunity and Experimental Therapy] (in German). 2: 377–390.
- ^ Landsteiner, Karl (1900). “Zur Kenntnis der antifermentativen, lytischen und agglutinierenden Wirkungen des Blutserums und der Lymphe”. Centralblatt F. Bakteriologie, Parasitenkunde U. Infektionskrankheiten. 27: 357–362.
- ^ “Homage to scientist on Blood Donor’s Day”. The Tribune. 15 June 2006. Retrieved 14 January 2012.
- ^ “Wie was Karl Landsteiner?” [Who was Karl Landsteiner?]. Landsteiner Instituut (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 16 December 2018. Retrieved 13 December 2018.
- ^ Speiser & Smekal 1990, p. 63.
- ^ Staudacher, Anna L. (2009) “… meldet den Austritt aus dem mosaischen Glauben”. 18000 Austritte aus dem Judentum in Wien, 1868–1914: Namen – Quellen – Daten. Peter Lang, Frankfurt, ISBN 978-3-631-55832-4, p. 349
- ^ “Concise Dictionary of American Jewish Biography”. The Jacob Rader Marcus Center of the American Jewish Archives.[page needed]
- ^ “Dr. Landsteiner Sues to Escape Being Labelled Jew”. Jewish Telegraphic Agency. 6 April 1937.
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Karl Landsteiner.
- Karl Landsteiner on Nobelprize.org including the Nobel Lecture, 11 December 1930 On Individual Differences in Human Blood
- Karl Landsteiner 1868—1943 A Biographical Memoir by Michael Heidelberger
- 1946 Lasker award for clinical medicine
- Key Participants: Karl Landsteiner – It’s in the Blood! A Documentary History of Linus Pauling, Hemoglobin, and Sickle Cell Anemia
- National Academy of Sciences Biographical Memoir
| 1930 Nobel Prize laureates |
|---|