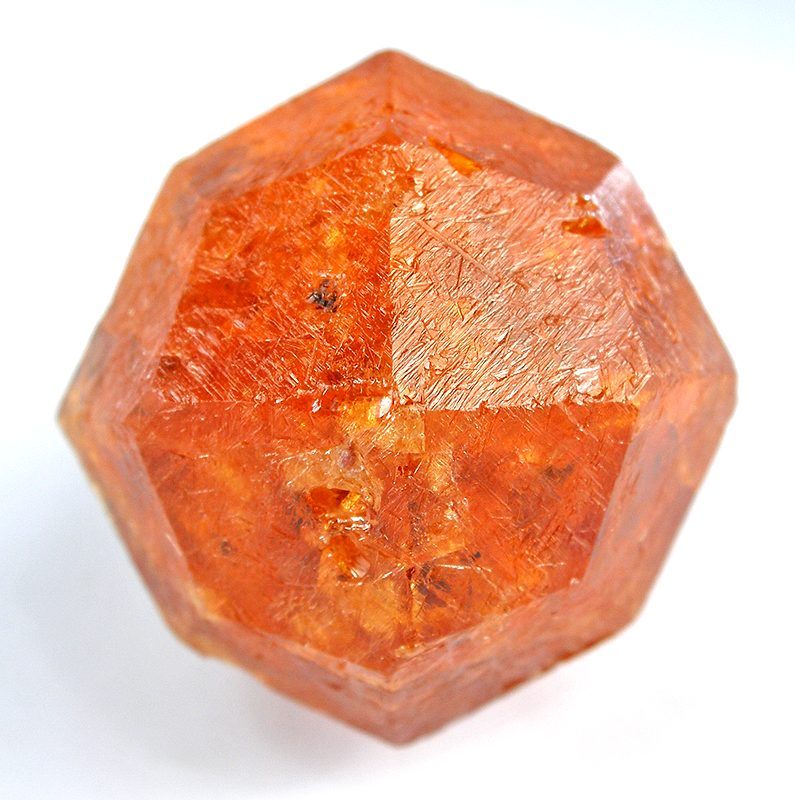
Icositetrahedral – Icositetrahedron-shaped, 24-faced
Common examples include: spessartine
Hexagonal – Hexagonal prism (six-sided)
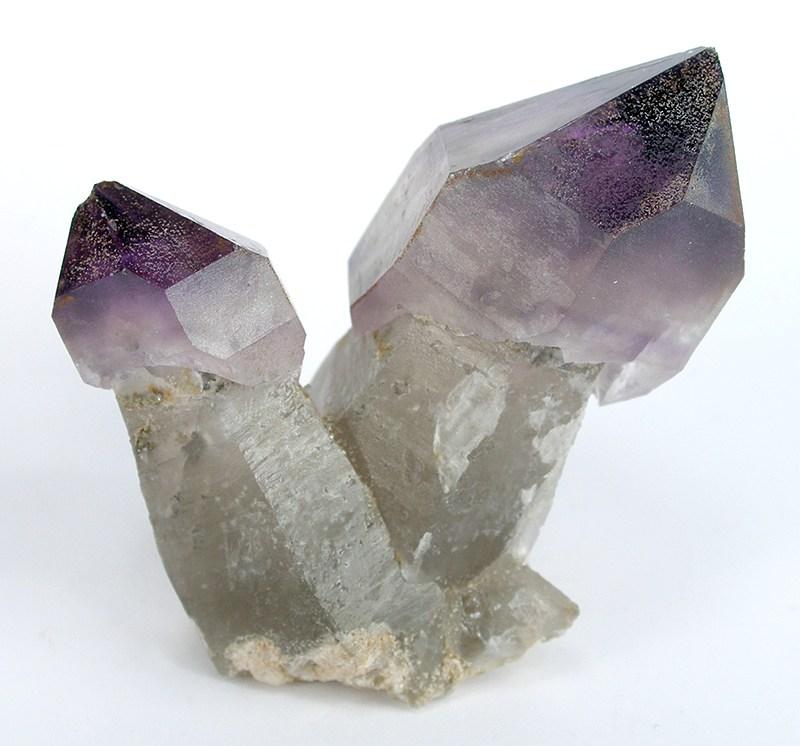
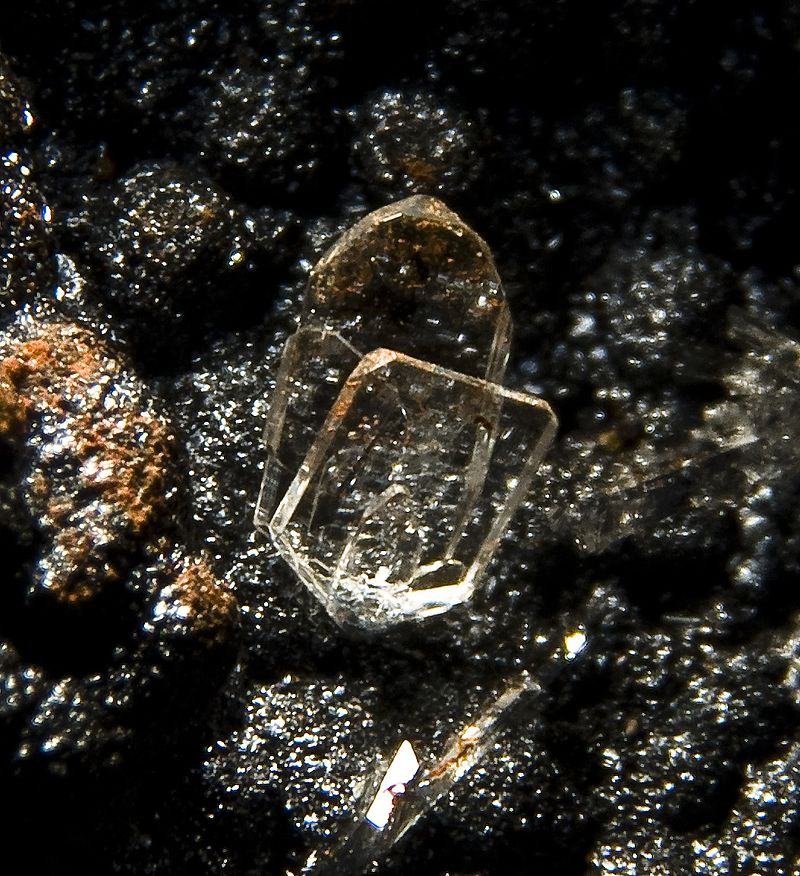
Common examples include: emerald, galena, quartz, hanksite, vanadinite
Equant/Stout – Length, width, and breadth roughly equal
Common examples include: apophyllite, olivine, garnet
Enantiomorphic – Mirror-image habit (i.e. crystal twinning) and optical characteristics; right- and left-handed crystals
Common examples include: gypsum, quartz, plagioclase, staurolite
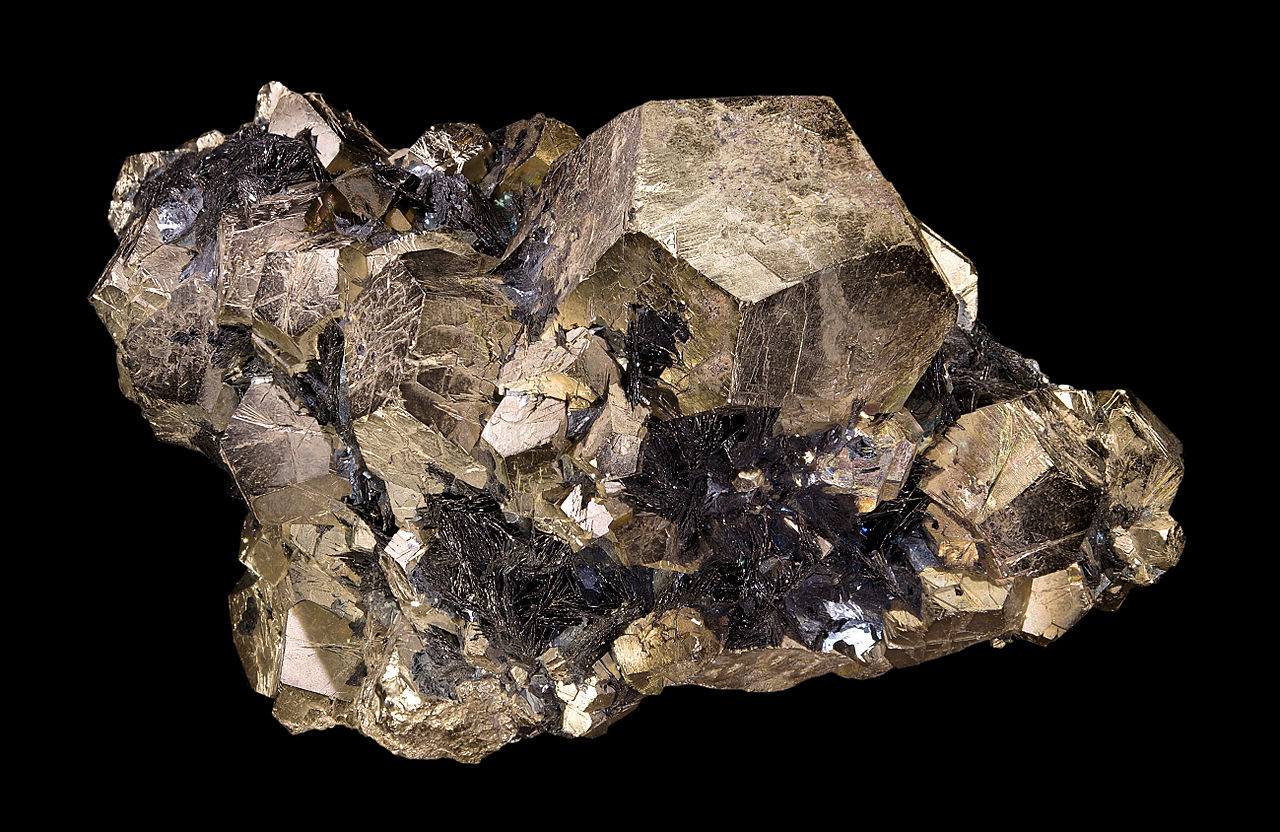
Dodecahedral – Dodecahedron-shaped, 12-sided
Common examples include: garnet, pyrite
Sceptered – Crystal growth stops and continues at the top of the crystal, but not at the bottom
Common examples include: hedenbergite, quartz
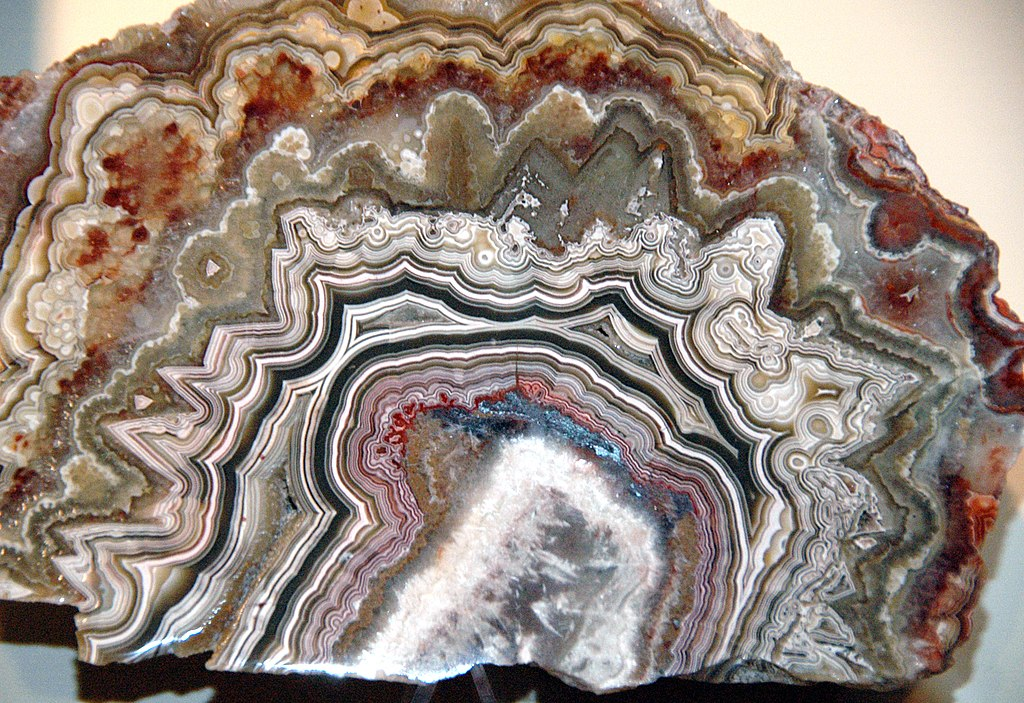
Nodular/Tuberose – Deposit of roughly spherical form with irregular protuberances
Common examples include: agate (and other chalcedony)
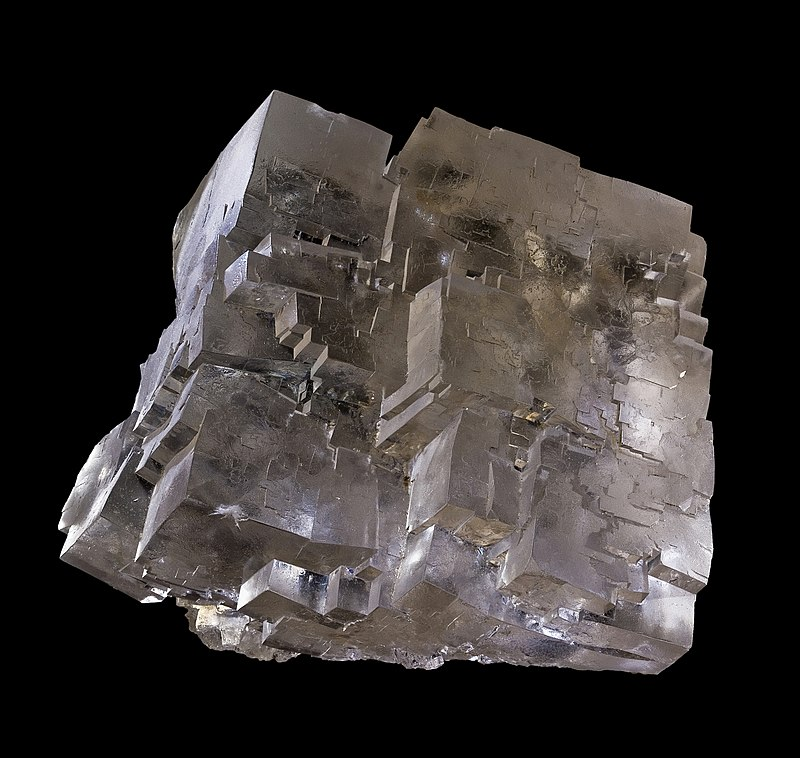
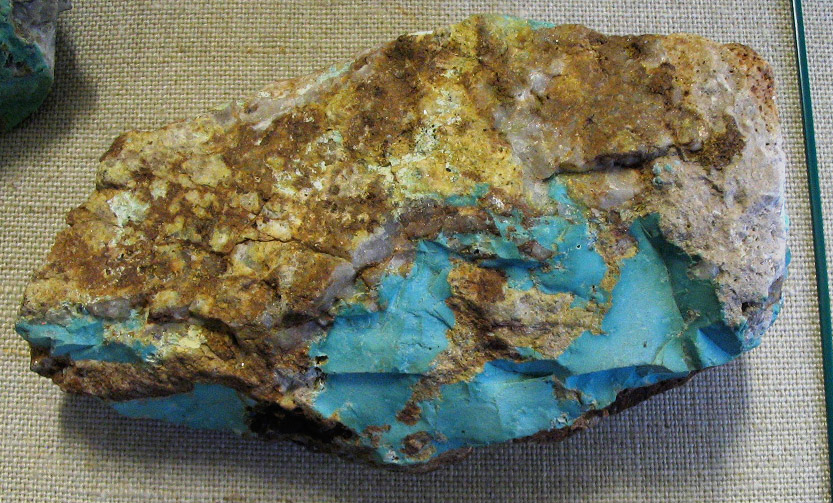
Massive/Compact – Shapeless, no distinctive external crystal shape
Common examples include: limonite, turquoise, cinnabar, quartz, realgar, lazurite
Hemimorphic – Doubly terminated crystal with two differently shaped ends
Common examples include: hemimorphite, elbaite
Amygdaloidal – Like embedded almonds
Common examples include: heulandite, subhedral zircon Amygdules or amygdales (/əˈmɪɡdjuːlz, -deɪlz/) form when the vesicles (pores from gas bubbles in lava) of a volcanic rock or other extrusive igneous rock are infilled with a secondary mineral, such as calcite, quartz, chlorite, or one of the zeolites. Amygdules usually…
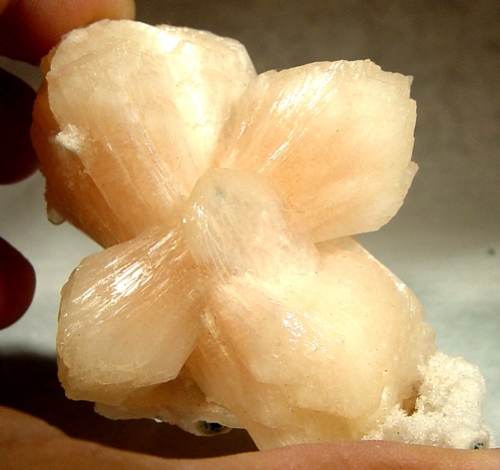
Wheat Sheaf – Aggregates resembling hand-reaped wheat sheaves
Common examples include: stilbite
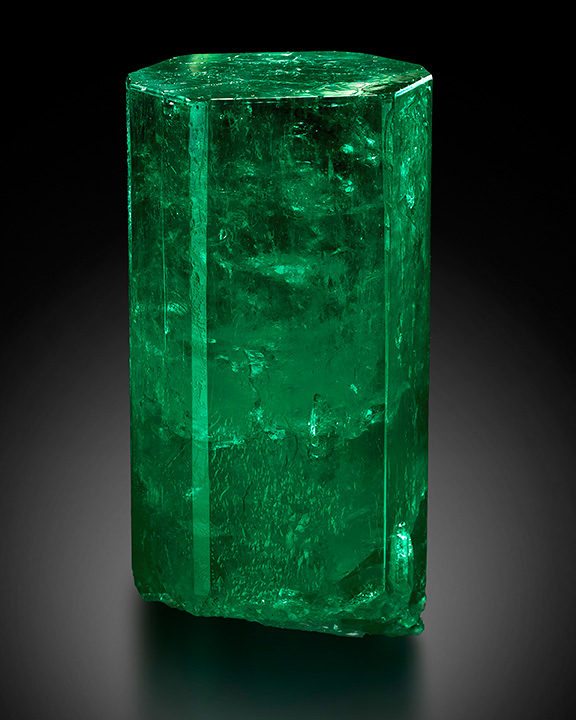


 Hexagonal prism (six-sided)">
Hexagonal prism (six-sided)">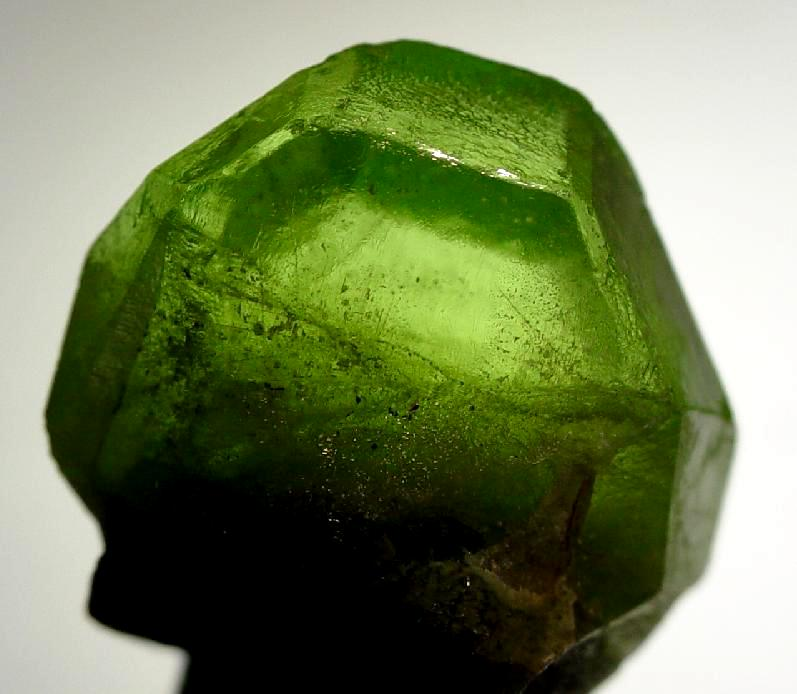







 wheat sheaves">
wheat sheaves">