Medical uses of adrenaline
Main article: Epinephrine (medication) As a medication, it is used to treat several conditions, including allergic reaction anaphylaxis, cardiac arrest, and superficial bleeding. Inhaled adrenaline may be used to improve the symptoms of croup. It may…
Adrenaline has been isolated from the plant Scoparia dulcis found in Northern Vietnam
Scoparia dulcis is a species of flowering plant in the plantain family. Plantaginaceae, the plantain family, is a large, diverse family of flowering plants in the order Lamiales that includes common flowers such as snapdragon and foxglove. It is unrelated…
Adrenaline, aka epinephrine, is a hormone and medication involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration)
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and by a…
CBP and p300 are critical for normal embryonic development
Mouse models CBP and p300 are critical for normal embryonic development, as mice completely lacking either CBP or p300 protein, die at an early embryonic stage. In addition, mice which lack…
p300-CBP coactivator family – clinical significance
Mutations in CBP, and to a lesser extent p300, are the cause of Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome, which is characterized by severe mental retardation. These mutations result in the loss of one copy of…
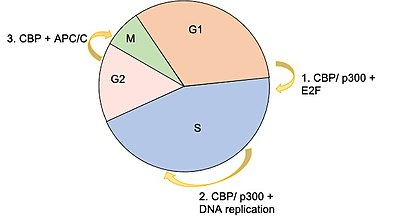
An example of a process involving p300 and CBP is G protein signaling
Function in G protein signaling Some G proteins stimulate adenylate cyclase that results in elevation of cAMP. cAMP stimulates PKA, which consists of four subunits, two regulatory and two catalytic. Binding of cAMP to…
p300 and CBP are thought to increase gene expression in three ways
Regulation of gene expression p300 and CBP are thought to increase gene expression in three ways: p300 regulates transcription by directly binding to transcription factors (see external reference for explanatory image). This…
p300-CBP coactivator family
The p300-CBP coactivator family in humans is composed of two closely related transcriptional co-activating proteins (or coactivators): Both p300 and CBP interact with numerous transcription factors and act to increase the expression of their target genes.…
Histone acetyltransferase p300
Histone acetyltransferase p300 also known as p300 HAT or E1A-associated protein p300 (where E1A = adenovirus early region 1A) also known as EP300 or p300 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the EP300 gene. It functions as histone acetyltransferase that regulates transcription of genes…
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome (RTS) is a rare genetic disorder that is the result of genetic mutations in either CBP or p300
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome (RTS) Type 1, which is caused by CBP mutations, for which over 500 different variations have been documented, accounts for approximately 55% of all cases, whereas RTS Type 2,…
CBP has two critical mechanisms by which it is able to regulate gene expression: as an acetyltransferase, and as a protein scaffold
This gene is ubiquitously expressed and is involved in the transcriptional coactivation of many different transcription factors. CBP has two critical mechanisms by which it is able to regulate gene expression: as an…