An autochthon in structural geology is a large block or mass of rock which is in the place of its original formation relative to its basement or foundation rock. It can be described as rooted to its basement rock as opposed to an allochthonous block or nappe which has been relocated from its site of formation usually by low angle thrust faulting. For other possible mechanisms see obduction. Autochthonous sediment is sediment found at or very close to its site of deposition. The etymology of the term is from Greek: ‘autos’ means self, and ‘chthon’ means earth.
- Dictionary of Geological Terms: Third Edition, p. 35, at Google Books ISBN 9780385181013
- DiPietro, Joseph A. (December 21, 2012). Landscape Evolution in the United States: An Introduction to the Geography, Geology, and Natural History. Newnes. p. 343. ISBN 9780123978066. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
- Obduction is a geological process whereby denser oceanic crust (and even upper mantle) is scraped off a descending ocean plate at a convergent plate boundary and thrust on top of an adjacent plate. When oceanic and continental plates converge, normally the denser oceanic crust sinks under the continental crust in the process of subduction. Obduction, which is less common, normally occurs in plate collisions at orogenic belts (where an oceanic plate that is subducting scrapes some of its material onto the continental plate) or back-arc basins (places where the edge of a continent is pulled away from the rest of the continent due to the stress of plate collision). Obduction of oceanic lithosphere produces a characteristic set of rock types called an ophiolite
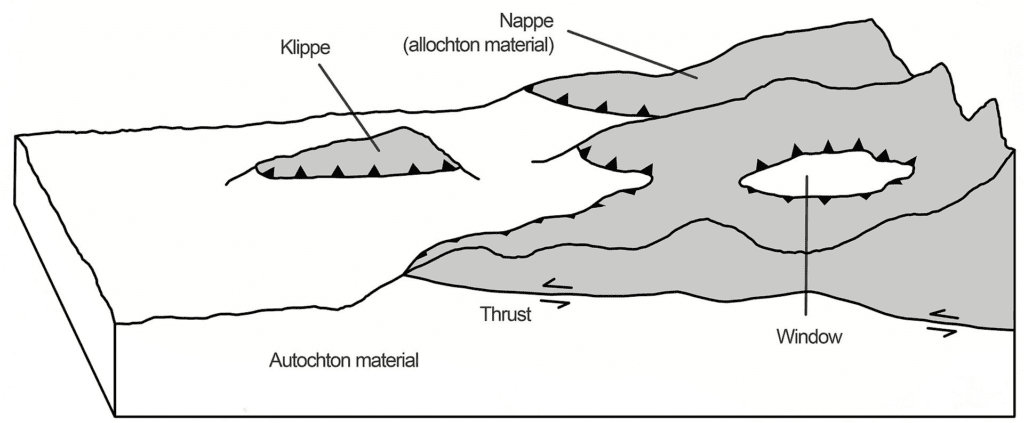
Areas with a nappe structure often contain two types of geological features:
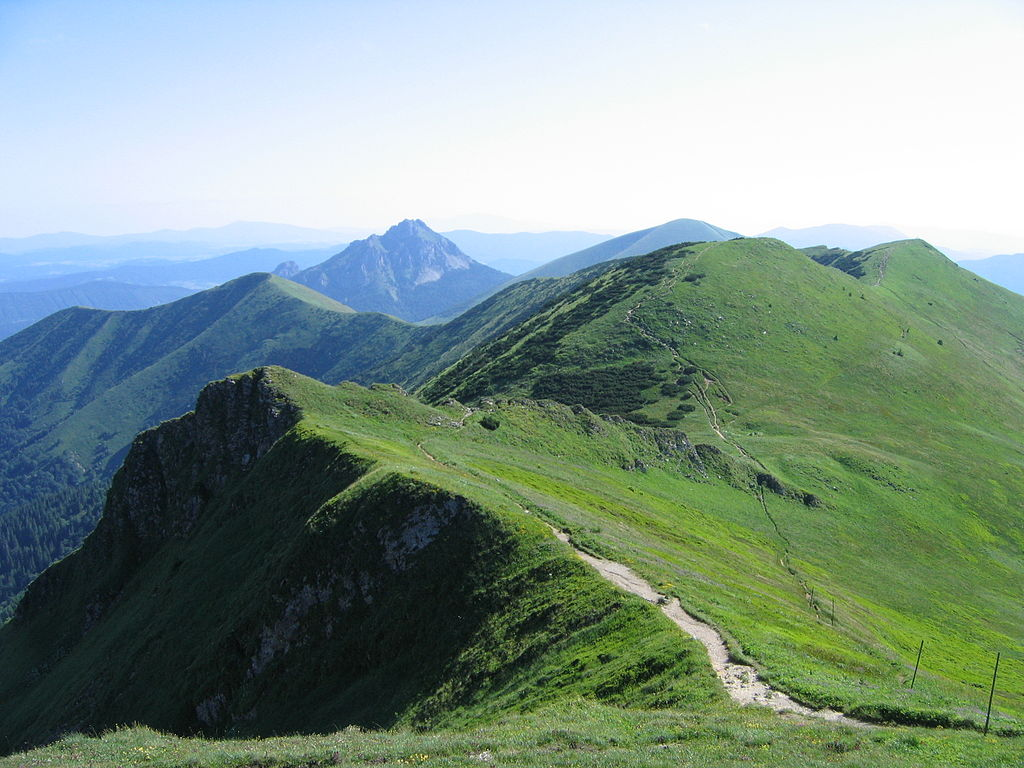

A nappe outlier or klippe is a small area isolated from the main body of the nappe by erosion that lies on the autochthonous base; the summit of Veľký Rozsutec in the Western Carpathians is a typical example. The term stems from the French word for tablecloth in allusion to a rumpled tablecloth being pushed across a table.
- Twiss, Robert J. and Eldridge M. Moores, Structural Geology, W. H. Freeman, 1992, p. 236 ISBN 978-0716722526
A fault inlier, fenster, or window is an area of the autochthonous basement uncovered by erosion, but entirely surrounded by the body of the nappe; the Hohe Tauern window in the Alps is a typical example.

Allochthon
In the United States there are three notable allochthons; all of which were displaced nearly 50 km (31 miles) along thrust faults. The Golconda and Robert Mountains allochthons are both found in Nevada, a product of the Antler Orogeny in the Late-Devonian period. The third is the Taconic allochthons found in New York, Massachusetts and Vermont formed from the collision of the Taconic magmatic arc with the super-continent Laurentia in the Late-Cambrian period.
- DiPietro, Joseph A. (December 21, 2012). Landscape Evolution in the United States: An Introduction to the Geography, Geology, and Natural History. Newnes. p. 416. ISBN 9780123978066. Retrieved 18 April 2021.
While an autochthon may have experienced some minor shifting, an allochthonous block will have moved at least a few kilometres. If an allochthon has a “hole” in it so that one can view the autochthon beneath the allochthon, the hole is called a “window” (or Fenster). Etymology: Greek; ‘allo’ = other, and ‘chthon’ = earth. In generalized terms, the term is applied to any geologic units that originated at a distance from their present location. An allochthon which is isolated from the rock that pushed it into position is called a klippe.
- Allaby, Michael. A Dictionary of Geology and Earth Sciences (Oxford Quick Reference) (p. 353). OUP Oxford. Kindle Edition.
- Howell, J.V. (Editor) 1960: Glossary of geology and related sciences. American Geological Institute, Washington D.C., 325 p.
- Marko, F., Jacko, S., 1999: Structural geology (General and systematic). Archived 2011-07-19 at the Wayback Machine ISBN 80-88896-36-3 Vydavateľstvo Harlequin, Košice, p. 81 – 93 (in Slovak)
See also
- Tectonics
- Accretion (geology)
- Continental collision
- Orogeny
- List of tectonic plate interactions – Movements of the earth’s lithosphere
- For the Dutch demographical term, see Allochtoon.
References
- Dictionary of Geological Terms: Third Edition, p. 35, at Google Books ISBN 9780385181013
- Howell, J.V. (Editor) 1960: Glossary of geology and related sciences. American Geological Institute, Washington D.C., 325 p.
- Marko, F., Jacko, S., 1999: Structural geology (General and systematic). Archived 2011-07-19 at the Wayback Machine ISBN 80-88896-36-3 Vydavateľstvo Harlequin, Košice, p. 81 – 93 (in Slovak)
- DiPietro, Joseph A. (December 21, 2012). Landscape Evolution in the United States: An Introduction to the Geography, Geology, and Natural History. Newnes. p. 343. ISBN 9780123978066. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
External links
- The dictionary definition of autochthon at Wiktionary