Gastric inhibitory peptide aka GIP and receptors
Gastric inhibitory polypeptide or gastric inhibitory peptide also known as glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide abbreviated as GIP, is an inhibiting hormone of the secretin family of hormones. While it is a weak inhibitor of gastric acid secretion, its main role is to stimulate insulin secretion. GIP,…
Gastrin-releasing peptide aka GRP
Gastrin-releasing peptide, also known as GRP, is a neuropeptide, a regulatory molecule that has been implicated in a number of physiological and pathophysiological processes. Most notably, GRP stimulates the release of gastrin from the G…
Neuromedin U
Neuromedin U (or NmU) is a neuropeptide found in the brain of humans and other mammals, which has a number of diverse functions including contraction of smooth muscle, regulation of blood pressure, pain perception,…
Neuromedin S
Neuromedin S is a 36-amino acid neuropeptide found in the brain of humans and other mammals. It is produced in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus and is related to neuromedin U. It is thought to be involved…
Neuromedin N
Neuromedin N is a neuropeptide derived from the same precursor polypeptide as neurotensin, and with similar but subtly distinct expression and effects. References Peptides: neuropeptides Categories:
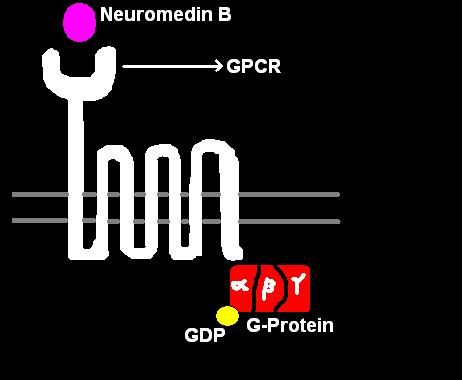
Neuromedin B
Neuromedin B (NMB) is a bombesin-related peptide in mammals. It was originally purified from pig spinal cord, and later shown to be present in human central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract. Sequence The sequence of the C-terminal…
Bombesin (and a wee bit of ranatensin)
Bombesin is a 14-amino acid peptide originally isolated from the skin of the European fire-bellied toad (Bombina bombina) by Vittorio Erspamer et al. and named after its source. It has two known homologs in mammals called neuromedin B and gastrin-releasing peptide. It stimulates gastrin release from G cells. It activates three…