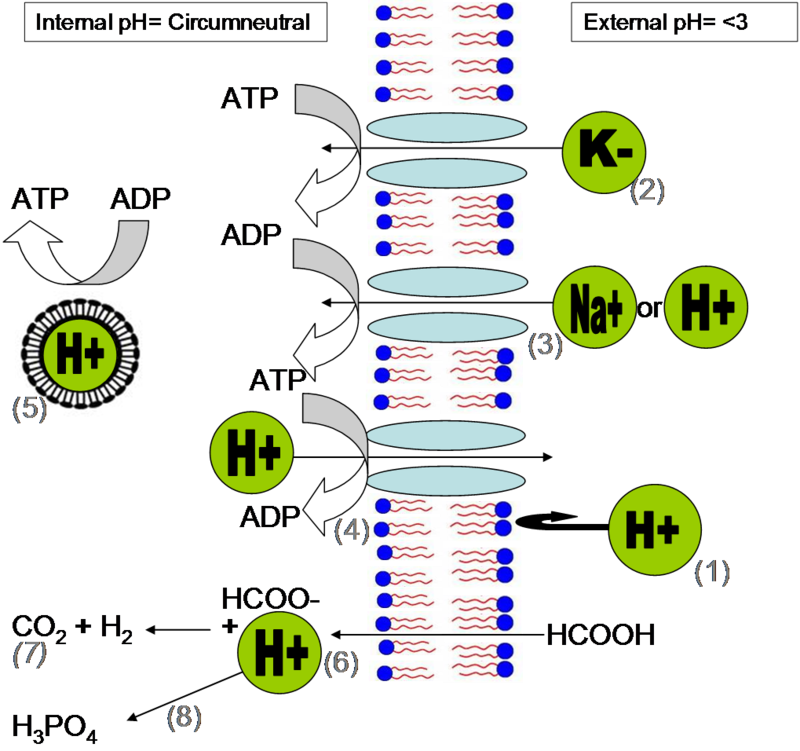
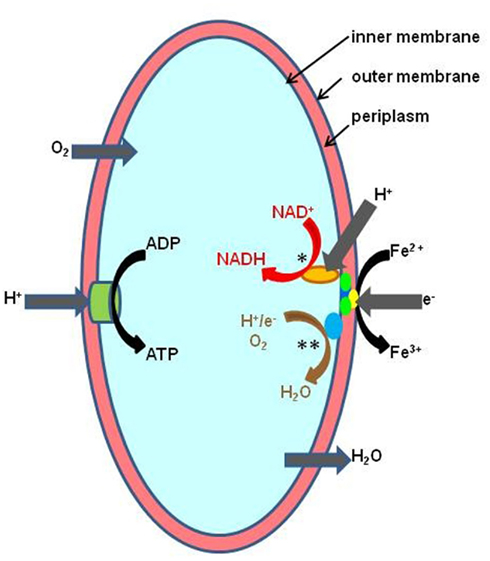
Acidophiles in acid mine drainage
The outflow of acidic liquids and other pollutants from mines is often catalysed by acid-loving microorganisms; these are the acidophiles in acid mine drainage. Acidophiles are not just present in exotic environments such as Yellowstone National Park or deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Genera su
Biomining or what I suspect “healthcare” (and much of the “food” industry) has been up to for a very, very long time
Biomining is the technique of extracting metals from ores and other solid materials typically using prokaryotes, fungi or plants (phytoextraction also known as phytomining or biomining). These organisms secrete different organic compounds that chelate metals from t
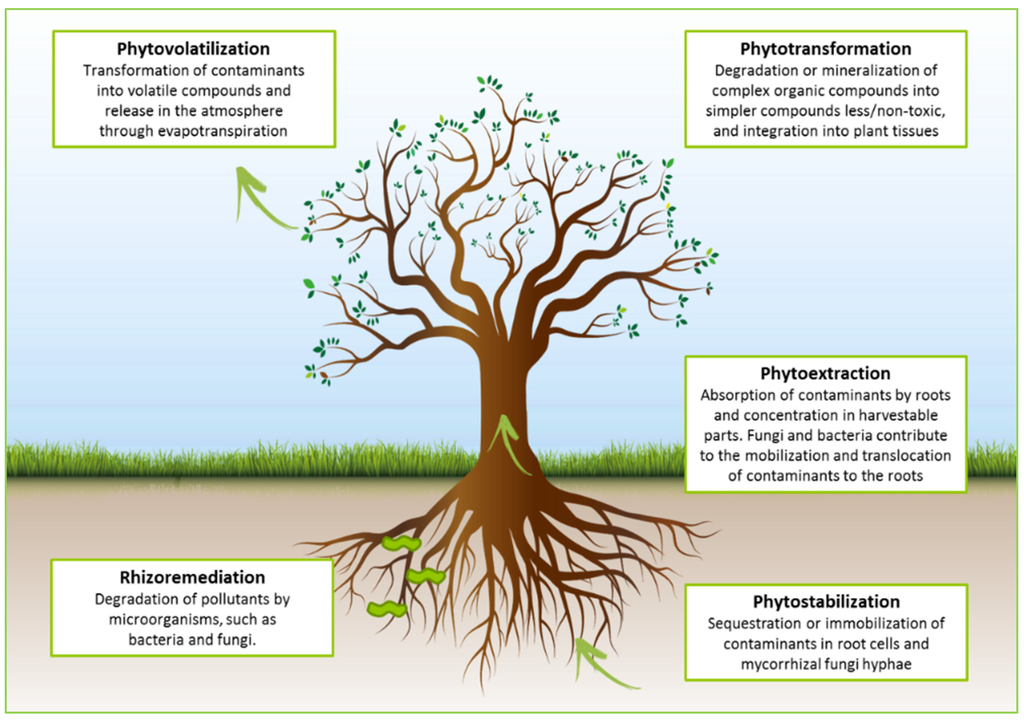
Phytoremediation is the use of green plants and the associated microorganisms to remove or render harmless toxic environmental contaminants
Phytoremediation technologies use living plants to clean up soil, air and water contaminated with hazardous contaminants. It is defined as “the use of green plants and the associated microorganisms, along with proper soil amendments and agronomic techniques to either contain, remove or ren
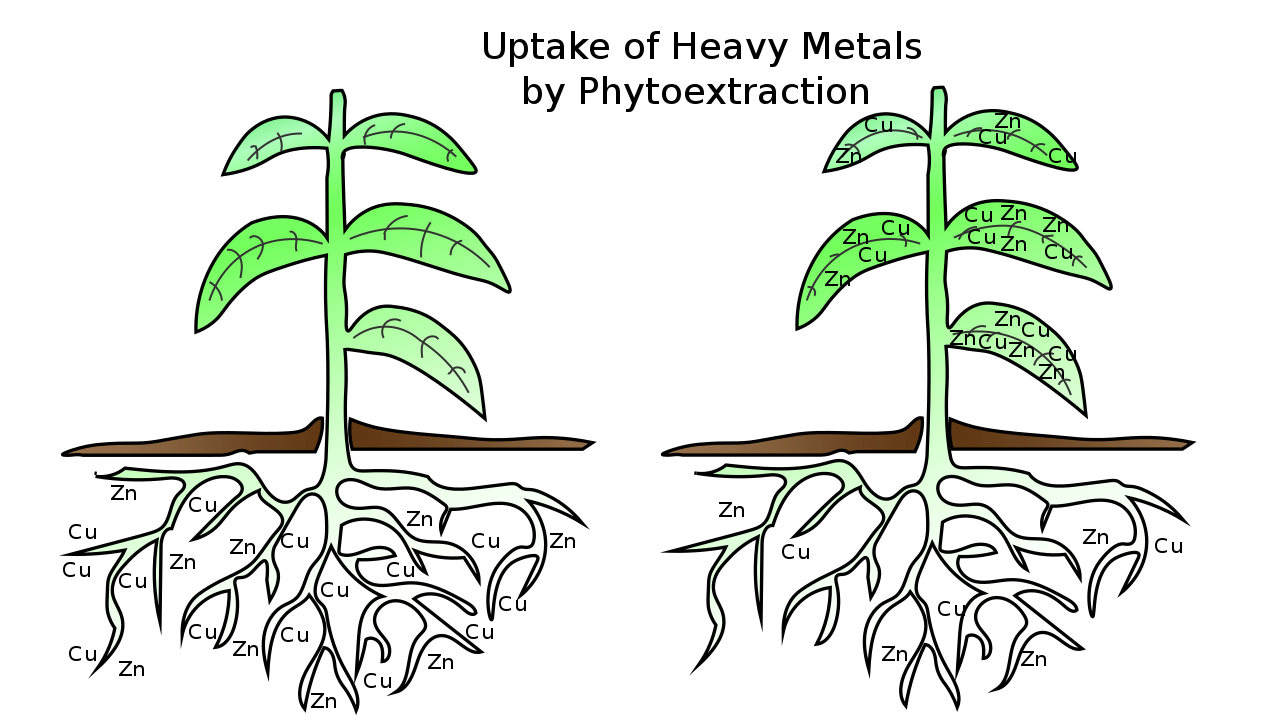
Phytoextraction is the removal of dangerous elements or compounds from soil or water by plants
Phytoextraction is a subprocess of phytoremediation in which plants remove dangerous elements or compounds from soil or water, most usually heavy metals, metals that have a high density and may be toxic to organisms even at relatively low concentrations. The heavy metals that plants extract are
Langgan 琅玕 is the ancient Chinese name of a gemstone which remains an enigma in the history of mineralogy; it has been identified, variously, as blue-green malachite, blue coral, white coral, whitish chalcedony, red spinel, and red jade
It is also the name of a mythological langgan tree of immortality found in the western paradise of Kunlun Mountain, and the name of the classic waidan alchemical elixir of immortality langgan huadan 琅玕華丹 “Elixir Efflorescence of Langgan̶
In Chinese alchemy, elixir poisoning refers to the toxic effects from elixirs of immortality that contained metals and minerals such as mercury and arsenic
In Chinese alchemy, elixir poisoning refers to the toxic effects from elixirs of immortality that contained metals and minerals such as mercury and arsenic. The official Twenty-Four Histories record numerous Chinese emperors, nobles, and&nb
Cold-Food Powder or Five Minerals Powder, poisonous psychoactive drug popular during the Six Dynasties (220–589) and Tang dynasty (618–907)
Cold-Food Powder (Chinese: 寒食散; pinyin: hánshísǎn; Wade–Giles: han-shih-san) or Five Minerals Powder (Chinese: 五石散; pinyin: wǔshísǎn; Wade–Giles: wu-shih-san) was a poisonous psychoactive drug popular du
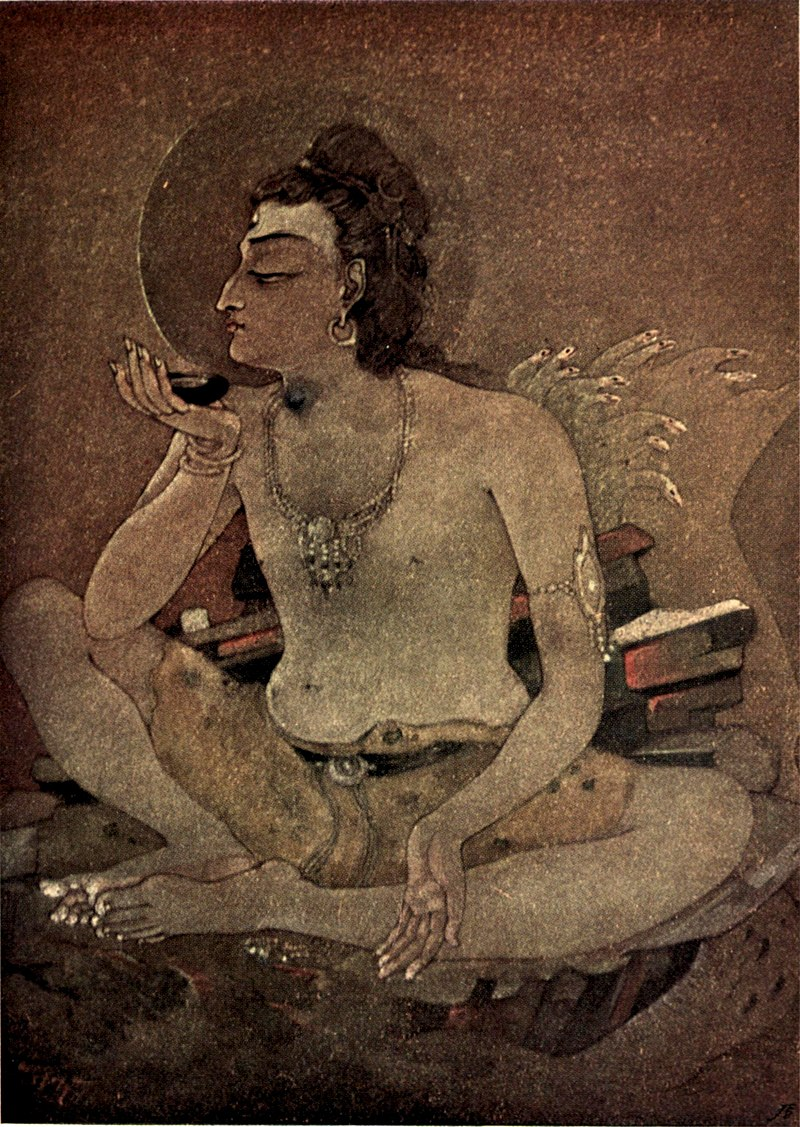
Kaustubha, divine ruby or gem in Hindu mythology
Kaustubha (Sanskrit: कौस्तुभ, romanized: Kaustubha, lit. ‘crest jewel’) is a divine ruby or ratnam (gem) in Hindu mythology.[1] This gem is in the possession of Vishnu, granting him the epithet of Kaustubhadhari. It is believed in Hindu scriptures to be the m
Halāhala or kālakūṭa poison
Halāhala (Sanskrit हलाहल) or kālakūṭa (Sanskrit कालकूटं, literally: ‘black mass’ or ‘time puzzle’[1]) is the name of a poison in Hindu mythology. It was created from the Ocean of Milk when the devas and the asuras churned it (see Samu
Lumiflavin and Lumichrome notes (and something called Autochrome)
Lumiflavin is a toxic product of photolysis of vitamin B2. Lumiflavin is a compound showing yellow-green fluorescence, formed by a photolysis of riboflavin in alkaline solution. Lumiflavin 1948-Present Lumichrome 1944-Present The Autochrome Lumière
Kodoku: The Venomous Vortex of Ancient Curses
Here’s one that might make your skin crawl and your blood run cold! Welcome to the world of Kodoku, the sinister sorcery that turns creepy crawlies into catastrophic curses! Imagine, if you dare, a jar teeming with nature’s most venomous vermin – scorpions, centipedes, and snakes,
Gu: The Venomous Vortex of Ancient Chinese Sorcery
Here is another that may make your skin crawl and your blood run cold! Welcome to the world of Gu, the sinister sorcery that turns creepy crawlies into catastrophic curses! Picture, if you dare, a jar teeming with nature’s most venomous vermin – centipedes, snakes, and scorpions, oh my!