Protein phosphorylation is a reversible post-translational modification of proteins in which an amino acid residue is phosphorylated by a protein kinase by the addition of a covalently bound phosphate group. Phosphorylation alters the structural conformation of a protein, causing it to become activated, deactivated, or otherwise modifying its function. Approximately 13,000 human proteins have sites that are phosphorylated.
- Cohen, Philip (2002-05-01). “The origins of protein phosphorylation”. Nature Cell Biology. 4 (5): E127–130. doi:10.1038/ncb0502-e127. ISSN 1465-7392. PMID 11988757. S2CID 29601670.
- Vlastaridis, Panayotis; Kyriakidou, Pelagia; Chaliotis, Anargyros; Van de Peer, Yves; Oliver, Stephen G.; Amoutzias, Grigoris D. (2017-02-01). “Estimating the total number of phosphoproteins and phosphorylation sites in eukaryotic proteomes”. GigaScience. 6 (2): 1–11. doi:10.1093/gigascience/giw015. PMC 5466708. PMID 28327990.
The reverse reaction of phosphorylation is called dephosphorylation, and is catalyzed by protein phosphatases. Protein kinases and phosphatases work independently and in a balance to regulate the function of proteins.
- Ilan Smoly, Netta Shemesh, Michal Ziv-Ukelson, Anat Ben-Zvi, Esti Yeger-Lotem (January 2017). “An Asymmetrically Balanced Organization of Kinases versus Phosphatases across Eukaryotes Determines Their Distinct Impacts”. PLOS Computational Biology. 13 (1): e1005221. Bibcode:2017PLSCB..13E5221S. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005221. PMC 5279721. PMID 28135269.
The amino acids most commonly phosphorylated are serine, threonine, tyrosine, and histidine. These phosphorylations play important and well-characterized roles in signaling pathways and metabolism. However, other amino acids can also be phosphorylated post-translationally, including arginine, lysine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid and cysteine, and these phosphorylated amino acids have been identified to be present in human cell extracts and fixed human cells using a combination of antibody-based analysis (for pHis) and mass spectrometry (for all other amino acids).
- Potel, Clement M.; Lin, Miao-Hsia; Heck, Albert J. R.; Lemeer, Simone (March 2018). “Widespread bacterial protein histidine phosphorylation revealed by mass spectrometry-based proteomics”. Nature Methods. 15 (3): 187–190. doi:10.1038/nmeth.4580. hdl:1874/362159. ISSN 1548-7105. PMID 29377012. S2CID 3367416.
- Fuhs SR, Meisenhelder J, Aslanian A, Ma L, Zagorska A, Stankova M, Binnie A, Al-Obeidi F, Mauger J, Lemke G, Yates JR 3rd, Hunter T (2015). “Monoclonal 1- and 3-Phosphohistidine Antibodies: New Tools to Study Histidine Phosphorylation”. Cell. 162 (1): 198–210. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.046. PMC 4491144. PMID 26140597.
- Hardman G, Perkins S, Brownridge PJ, Clarke CJ, Byrne DP, Campbell AE, Kalyuzhnyy A, Myall A, Eyers PA, Jones AR, Eyers CE (2019). “Strong anion exchange-mediated phosphoproteomics reveals extensive human non-canonical phosphorylation”. EMBO J. 38 (21): e100847. doi:10.15252/embj.2018100847. PMC 6826212. PMID 31433507.
- Fuhs SR, Hunter T (2017). “pHisphorylation: the emergence of histidine phosphorylation as a reversible regulatory modification”. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 45: 8–16. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2016.12.010. PMC 5482761. PMID 28129587.
- Cieśla J; Frączyk T; Rode W (2011). “Phosphorylation of basic amino acid residues in proteins: important but easily missed” (PDF). Acta Biochimica Polonica. 58 (2): 137–147. doi:10.18388/abp.2011_2258. PMID 21623415.
Protein phosphorylation was first reported in 1906 by Phoebus Levene at the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research with the discovery of phosphorylated vitellin. However, it was nearly 50 years until the enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins by protein kinases was discovered.
- Levene PA; Alsberg CL (1906). “The cleavage products of vitellin” (PDF). J. Biol. Chem. 2 (1): 127–133. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)46054-6. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-06-09. Retrieved 2015-03-13.
- Burnett G; Kennedy EP (December 1954). “The enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins” (PDF). J. Biol. Chem. 211 (2): 969–80. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)71184-8. PMID 13221602. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-06-09. Retrieved 2015-03-13.
History
In 1906, Phoebus Levene at the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research identified phosphate in the protein vitellin (phosvitin) and by 1933 had detected phosphoserine in casein, with Fritz Lipmann.
- Levene PA; Alsberg CL (1906). “The cleavage products of vitellin” (PDF). J. Biol. Chem. 2 (1): 127–133. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)46054-6. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-06-09. Retrieved 2015-03-13.
- Lipmann FA; Levene PA (October 1932). “Serinephosphoric acid obtained on hydrolysis of vitellinic acid” (PDF). J. Biol. Chem. 98 (1): 109–114. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)76142-5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-06-09. Retrieved 2016-11-04.
However, it took another 20 years before Eugene P. Kennedy described the first “enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins”.
- Burnett G; Kennedy EP (December 1954). “The enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins” (PDF). J. Biol. Chem. 211 (2): 969–80. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)71184-8. PMID 13221602. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-06-09. Retrieved 2015-03-13.
The first phosphorylase enzyme was discovered by Carl and Gerty Cori in the late 1930s. Carl and Gerty Cori found two forms of glycogen phosphorylase which they named A and B but did not correctly understand the mechanism of the B form to A form conversion. The interconversion of phosphorylase b to phosphorylase a was later described by Edmond Fischer and Edwin Krebs, as well as, Wosilait and Sutherland, involving a phosphorylation/dephosphorylation mechanism.
- Kresge, Nicole; Simoni, Robert D.; Hill, Robert L. (2011-01-21). “The Process of Reversible Phosphorylation: the Work of Edmond H. Fischer”. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 286 (3): e1–e2. doi:10.1074/jbc.O110.000242. ISSN 0021-9258. PMC 3023531. PMID 21294299.
It was found that an enzyme, named phosphorylase kinase and Mg-ATP were required to phosphorylate glycogen phosphorylase by assisting in the transfer of the γ-phosphoryl group of ATP to a serine residue on phosphorylase b. Protein phosphatase 1 is able to catalyze the dephosphorylation of phosphorylated enzymes by removing the phosphate group. Earl Sutherland explained in 1950, that the activity of phosphorylase was increased and thus glycogenolysis stimulated when liver slices were incubated with adrenalin and glucagon. Phosphorylation was considered a specific control mechanism for one metabolic pathway until the 1970s, when Lester Reed discovered that mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase complex was inactivated by phosphorylation. Also in the 1970s, the term multisite phosphorylation was coined in response to the discovery of proteins that are phosphorylated on two or more residues by two or more kinases. In 1975, it was shown that cAMP-dependent proteins kinases phosphorylate serine residues on specific amino acid sequence motifs. Ray Erikson discovered that v-Src was a kinase and Tony Hunter found that v-Src phosphorylated tyrosine residues on proteins in the 1970s.
- Hunter, Tony (2015-06-30). “Discovering the first tyrosine kinase”. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 112 (26): 7877–7882. Bibcode:2015PNAS..112.7877H. doi:10.1073/pnas.1508223112. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 4491733. PMID 26130799.
In the early 1980, the amino-acid sequence of the first protein kinase was determined which helped geneticists understand the functions of regulatory genes. In the late 1980s and early 1990s, the first protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP1B) was purified and the discovery, as well as, cloning of JAK kinases was accomplished which led to many in the scientific community to name the 1990s as the decade of protein kinase cascades.
- Fischer, Edmond H. (2010). “Phosphorylase and the origin of reversible protein phosphorylation”. Biological Chemistry. 391 (2/3): 131–7. doi:10.1515/bc.2010.011. PMID 20030590. S2CID 29724939.
- Cohen, Philip (2002-05-01). “The origins of protein phosphorylation”. Nature Cell Biology. 4 (5): E127–130. doi:10.1038/ncb0502-e127. ISSN 1465-7392. PMID 11988757. S2CID 29601670.
Edmond Fischer and Edwin Krebs were awarded the Nobel prize in 1992 “for their discoveries concerning reversible protein phosphorylation as a biological regulatory mechanism”.
- “The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1992”. www.nobelprize.org. Retrieved 2016-05-19.
Abundance
Reversible phosphorylation of proteins is abundant in both prokaryotic and even more so in eukaryotic organisms. For instance, in bacteria 5-10% of all proteins are thought to be phosphorylated.
- Cozzone AJ (1988). “Protein phosphorylation in prokaryotes”. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 42: 97–125. doi:10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.000525. PMID 2849375.
- Stock JB; Ninfa AJ; Stock AM (December 1989). “Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria”. Microbiol. Rev. 53 (4): 450–90. doi:10.1128/MMBR.53.4.450-490.1989. PMC 372749. PMID 2556636.
- Chang C; Stewart RC (July 1998). “The Two-Component System. Regulation of Diverse Signaling Pathways in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes”. Plant Physiol. 117 (3): 723–31. doi:10.1104/pp.117.3.723. PMC 1539182. PMID 9662515.
- Barford D; Das AK; Egloff MP (1998). “The structure and mechanism of protein phosphatases: insights into catalysis and regulation”. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 27: 133–64. doi:10.1146/annurev.biophys.27.1.133. PMID 9646865. S2CID 12138601.
- Pietack, Nico; Becher, Dörte; Schmidl, Sebastian R.; Saier, Milton H.; Hecker, Michael; Commichau, Fabian M.; Stülke, Jörg (2010). “In vitro phosphorylation of key metabolic enzymes from Bacillus subtilis: PrkC phosphorylates enzymes from different branches of basic metabolism”. Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology. 18 (3): 129–140. doi:10.1159/000308512. ISSN 1660-2412. PMID 20389117. S2CID 19535600.
- Schmidl, Sebastian R.; Gronau, Katrin; Pietack, Nico; Hecker, Michael; Becher, Dörte; Stülke, Jörg (June 2010). “The phosphoproteome of the minimal bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae: analysis of the complete known Ser/Thr kinome suggests the existence of novel kinases”. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 9 (6): 1228–1242. doi:10.1074/mcp.M900267-MCP200. ISSN 1535-9484. PMC 2877983. PMID 20097688.
By contrast, it is estimated that one third of all human proteins is phosphorylated at any point in time, with 230,000, 156,000, and 40,000 unique phosphorylation sites existing in human, mouse, and yeast, respectively.
- Vlastaridis, Panayotis; Kyriakidou, Pelagia; Chaliotis, Anargyros; Van de Peer, Yves; Oliver, Stephen G.; Amoutzias, Grigoris D. (2017-02-01). “Estimating the total number of phosphoproteins and phosphorylation sites in eukaryotic proteomes”. GigaScience. 6 (2): 1–11. doi:10.1093/gigascience/giw015. PMC 5466708. PMID 28327990.
In yeast, about 120 kinases (out of ~6,000 proteins total) cause 8,814 known regulated phosphorylation events, generating about 3,600 phosphoproteins (about 60% of all yeast proteins).
- Bodenmiller, Bernd; Wanka, Stefanie; Kraft, Claudine; Urban, Jörg; Campbell, David; Pedrioli, Patrick G.; Gerrits, Bertran; Picotti, Paola; Lam, Henry; Vitek, Olga; Brusniak, Mi-Youn (2010-12-21). “Phosphoproteomic analysis reveals interconnected system-wide responses to perturbations of kinases and phosphatases in yeast”. Science Signaling. 3 (153): rs4. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2001182. ISSN 1937-9145. PMC 3072779. PMID 21177495.
- Yachie, Nozomu; Saito, Rintaro; Sugiyama, Naoyuki; Tomita, Masaru; Ishihama, Yasushi (2011-01-27). “Integrative features of the yeast phosphoproteome and protein-protein interaction map”. PLOS Computational Biology. 7 (1): e1001064. Bibcode:2011PLSCB…7E1064Y. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1001064. ISSN 1553-7358. PMC 3029238. PMID 21298081.
Hence, phosphorylation is a universal regulatory mechanism that affects a large portion of proteins. Even if a protein is not phosphorylated itself, its interactions with other proteins may be regulated by phosphorylation of these interacting proteins.
Mechanisms and functions of phosphorylation
Phosphorylation introduces a charged and hydrophilic group in the side chain of amino acids, possibly changing a protein’s structure by altering interactions with nearby amino acids. Some proteins such as p53 contain multiple phosphorylation sites, facilitating complex, multi-level regulation. Because of the ease with which proteins can be phosphorylated and dephosphorylated, this type of modification is a flexible mechanism for cells to respond to external signals and environmental conditions.
- Johnson LN, Barford D (1993). “The effects of phosphorylation on the structure and function of proteins[J]”. Annual Review of Biophysics and Biomolecular Structure. 22 (1): 199–232. doi:10.1146/annurev.bb.22.060193.001215. PMID 8347989.
Kinases phosphorylate proteins and phosphatases dephosphorylate proteins. Many enzymes and receptors are switched “on” or “off” by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Reversible phosphorylation results in a conformational change in the structure in many enzymes and receptors, causing them to become activated or deactivated. Phosphorylation usually occurs on serine, threonine, tyrosine and histidine residues in eukaryotic proteins. Histidine phosphorylation of eukaryotic proteins appears to be much more frequent than tyrosine phosphorylation.
- Ciesla J; Fraczyk T; Rode W (2011). “Phosphorylation of basic amino acid residues in proteins: important but easily missed”. Acta Biochim. Pol. 58 (2): 137–47. doi:10.18388/abp.2011_2258. PMID 21623415.
In prokaryotic proteins phosphorylation occurs on the serine, threonine, tyrosine, histidine, arginine or lysine residues.
- Cozzone AJ (1988). “Protein phosphorylation in prokaryotes”. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 42: 97–125. doi:10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.000525. PMID 2849375.
- Stock JB; Ninfa AJ; Stock AM (December 1989). “Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria”. Microbiol. Rev. 53 (4): 450–90. doi:10.1128/MMBR.53.4.450-490.1989. PMC 372749. PMID 2556636
- Ciesla J; Fraczyk T; Rode W (2011). “Phosphorylation of basic amino acid residues in proteins: important but easily missed”. Acta Biochim. Pol. 58 (2): 137–47. doi:10.18388/abp.2011_2258. PMID 21623415.
- Deutscher, J.; Saier, J. (2005). “Ser/Thr/Tyr Protein Phosphorylation in Bacteria – for Long Time Neglected, Now Well Established”. Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology. 9 (3–4): 125–131. doi:10.1159/000089641. PMID 16415586. S2CID 13093867.
The addition of a phosphate (PO43-) molecule to a non-polar R group of an amino acid residue can turn a hydrophobic portion of a protein into a polar and extremely hydrophilic portion of a molecule. In this way protein dynamics can induce a conformational change in the structure of the protein via long-range allostery with other hydrophobic and hydrophilic residues in the protein.
One such example of the regulatory role that phosphorylation plays is the p53 tumor suppressor protein. The p53 protein is heavily regulated and contains more than 18 different phosphorylation sites. Activation of p53 can lead to cell cycle arrest, which can be reversed under some circumstances, or apoptotic cell death.
- Ashcroft M; Kubbutat MH; Vousden KH (March 1999). “Regulation of p53 Function and Stability by Phosphorylation”. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19 (3): 1751–8. doi:10.1128/mcb.19.3.1751. PMC 83968. PMID 10022862.
- Bates S; Vousden KH (February 1996). “p53 in signaling checkpoint arrest or apoptosis”. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 6 (1): 12–8. doi:10.1016/S0959-437X(96)90004-0. PMID 8791489.
This activity occurs only in situations wherein the cell is damaged or physiology is disturbed in normal healthy individuals.
Upon the deactivating signal, the protein becomes dephosphorylated again and stops working.[citation needed] This is the mechanism in many forms of signal transduction, for example the way in which incoming light is processed in the light-sensitive cells of the retina.
- learnwithalbert (2016-09-16). “What is the Difference Between Phosphorylation and Dephosphorylation?”. Albert Blog. Retrieved 2019-02-01.
Regulatory roles of phosphorylation include:
- Biological thermodynamics of energy-requiring reactions
- Phosphorylation of Na+/K+-ATPase during the transport of sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) ions across the cell membrane in osmoregulation to maintain homeostasis of the body’s water content.
- Mediates enzyme inhibition
- Phosphorylation of the enzyme GSK-3 by AKT (Protein kinase B) as part of the insulin signaling pathway.
- van Weeren PC; de Bruyn KM; de Vries-Smits AM; van Lint J; Burgering BM (May 1998). “Essential role for protein kinase B (PKB) in insulin-induced glycogen synthase kinase 3 inactivation. Characterization of dominant-negative mutant of PKB”. J. Biol. Chem. 273 (21): 13150–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.21.13150. PMID 9582355.
- Phosphorylation of src (pronounced “sarc”) tyrosine kinase by C-terminal Src kinase (Csk) induces a conformational change in the enzyme, resulting in a fold in the structure, which masks its kinase domain, and is thus shut “off”.
- Cole PA; Shen K; Qiao Y; Wang D (October 2003). “Protein tyrosine kinases Src and Csk: a tail’s tale”. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 7 (5): 580–5. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2003.08.009. PMID 14580561.
- Phosphorylation of the enzyme GSK-3 by AKT (Protein kinase B) as part of the insulin signaling pathway.
Membrane transport
Further information: Membrane transport
- Phosphorylation of Na+/K+-ATPase during the transport of sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) ions across the cell membrane in osmoregulation to maintain homeostasis of the body’s water content.
- Zubareva, V. M.; Lapashina, A. S.; Shugaeva, T. E.; Litvin, A. V.; Feniouk, B. A. (December 2020). “Rotary Ion-Translocating ATPases/ATP Synthases: Diversity, Similarities, and Differences”. Biochemistry. Biokhimiia. 85 (12): 1613–1630. doi:10.1134/S0006297920120135. ISSN 1608-3040. PMID 33705299. S2CID 229701146.
- ATP-binding cassette transporter
Protein degradation
- Arginine phosphorylation by McsB kinase marks proteins for degradation by a Clp protease. The arginine phosphorylation system, which is widely distributed across Gram-positive bacteria, appears to be functionally analogous to the eukaryotic ubiquitin–proteasome system.
- Broch Trentini, Débora (2016). “Arginine phosphorylation marks proteins for degradation by a Clp protease”. Nature. 539 (7627): 48–53. Bibcode:2016Natur.539…48T. doi:10.1038/nature20122. PMC 6640040. PMID 27749819.
Enzyme regulation (activation and inhibition)
- The first example of protein regulation by phosphorylation to be discovered was glycogen phosphorylase. Eddie Fisher and Ed Krebs described how phosphorylation of glycogen phosphorylase b converted it to the active glycogen phosphorylase a. It was soon discovered that glycogen synthase, another metabolic enzyme, is inactivated by phosphorylation.
- Phosphorylation of the enzyme GSK-3 by AKT (Protein kinase B) as part of the insulin signaling pathway.
- van Weeren PC; de Bruyn KM; de Vries-Smits AM; van Lint J; Burgering BM (May 1998). “Essential role for protein kinase B (PKB) in insulin-induced glycogen synthase kinase 3 inactivation. Characterization of dominant-negative mutant of PKB”. J. Biol. Chem. 273 (21): 13150–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.21.13150. PMID 9582355.
- Phosphorylation of Src tyrosine kinase by C-terminal Src kinase inactivates Src by inducing a conformational change which masks its kinase domain.
- Cole PA; Shen K; Qiao Y; Wang D (October 2003). “Protein tyrosine kinases Src and Csk: a tail’s tale”. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 7 (5): 580–5. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2003.08.009. PMID 14580561.
- Phosphorylation of the H2AX histones on serine 139, within two million bases (0.03% of the chromatin) surrounding a double-strand break in DNA, is needed for repair of the double-strand break. Phosphorylation of methylpurine DNA glycosylase at serine 172 is required for base excision repair of alkylated base damage.
- Rogakou EP, Pilch DR, Orr AH, Ivanova VS, Bonner WM (March 1998). “DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX phosphorylation on serine 139”. J. Biol. Chem. 273 (10): 5858–68. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.10.5858. PMID 9488723.
- Carter RJ, Parsons JL (May 2016). “Base Excision Repair, a Pathway Regulated by Posttranslational Modifications”. Mol. Cell. Biol. 36 (10): 1426–37. doi:10.1128/MCB.00030-16. PMC 4859697. PMID 26976642.
Protein-protein interactions
- Phosphorylation of the cytosolic components of NADPH oxidase, a large membrane-bound, multi-protein enzyme present in phagocytic cells, plays an important role in the regulation of protein-protein interactions in the enzyme.
- Babior BM (March 1999). “NADPH oxidase: an update”. Blood. 93 (5): 1464–76. doi:10.1182/blood.V93.5.1464. PMID 10029572.
- Important in protein degradation.
- In the late 1990s, it was recognized that phosphorylation of some proteins causes them to be degraded by the ATP-dependent ubiquitin/proteasome pathway. These target proteins become substrates for particular E3 ubiquitin ligases only when they are phosphorylated.
Signaling networks
Elucidating complex signaling pathway phosphorylation events can be difficult. In cellular signaling pathways, protein A phosphorylates protein B, and B phosphorylates C. However, in another signaling pathway, protein D phosphorylates A, or phosphorylates protein C. Global approaches such as phosphoproteomics, the study of phosphorylated proteins, which is a sub-branch of proteomics, combined with mass spectrometry-based proteomics, have been utilised to identify and quantify dynamic changes in phosphorylated proteins over time. These techniques are becoming increasingly important for the systematic analysis of complex phosphorylation networks. They have been successfully used to identify dynamic changes in the phosphorylation status of more than 6,000 sites after stimulation with epidermal growth factor. Another approach for understanding Phosphorylation Network, is by measuring the genetic interactions between multiple phosphorylating proteins and their targets. This reveals interesting recurring patterns of interactions – network motifs. Computational methods have been developed to model phosphorylation networks and predict their responses under different perturbations.
- Olsen JV; Blagoev B; Gnad F; Macek B; Kumar C; Mortensen P; Mann M (November 2006). “Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks”. Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983. S2CID 7827573.
- Li-Rong Y; Issaq HJ; Veenstra TD (2007). “Phosphoproteomics for the discovery of kinases as cancer biomarkers and drug targets”. Proteomics: Clinical Applications. 1 (9): 1042–1057. doi:10.1002/prca.200700102. PMID 21136756. S2CID 33999702.
- Fiedler D, Braberg H, Mehta M, Chechik G, Cagney G, Mukherjee P, Silva AC, Shales M, et al. (2009). “Functional Organization of the S. cerevisiae Phosphorylation Network”. Cell. 136 (5): 952–963. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.12.039. PMC 2856666. PMID 19269370.
- Schoeberl, B; Eichler-Jonsson, C; Gilles, ED; Müller, G (Apr 2002). “Computational modeling of the dynamics of the MAP kinase cascade activated by surface and internalized EGF receptors”. Nature Biotechnology. 20 (4): 370–5. doi:10.1038/nbt0402-370. PMID 11923843. S2CID 9851026.
- Aldridge, BB; Burke, JM; Lauffenburger, DA; Sorger, PK (Nov 2006). “Physicochemical modelling of cell signalling pathways”. Nature Cell Biology. 8 (11): 1195–203. doi:10.1038/ncb1497. PMID 17060902. S2CID 14586526.
- Zhu, F; Guan, Y (Jun 11, 2014). “Predicting Dynamic Signaling Network Response under Unseen Perturbations”. Bioinformatics. 30 (19): 2772–8. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu382. PMC 4173019. PMID 24919880.
Phosphorylation of histones
Eukaryotic DNA is organized with histone proteins in specific complexes called chromatin. The chromatin structure functions and facilitates the packaging, organization and distribution of eukaryotic DNA. However, it has a negative impact on several fundamental biological processes such as transcription, replication and DNA repair by restricting the accessibility of certain enzymes and proteins. Post-translational modification of histones such as histone phosphorylation has been shown to modify the chromatin structure by changing protein:DNA or protein:protein interactions. Histone post-translational modifications modify the chromatin structure. The most commonly associated histone phosphorylation occurs during cellular responses to DNA damage, when phosphorylated histone H2A separates large chromatin domains around the site of DNA breakage. Researchers investigated whether modifications of histones directly impact RNA polymerase II directed transcription. Researchers choose proteins that are known to modify histones to test their effects on transcription, and found that the stress-induced kinase, MSK1, inhibits RNA synthesis. Inhibition of transcription by MSK1 was most sensitive when the template was in chromatin, since DNA templates not in chromatin were resistant to the effects of MSK1. It was shown that MSK1 phosphorylated histone H2A on serine 1, and mutation of serine 1 to alanine blocked the inhibition of transcription by MSK1. Thus results suggested that the acetylation of histones can stimulate transcription by suppressing an inhibitory phosphorylation by a kinase as MSK1.
- awicka, Anna; Seiser, Christian (2014-08-01). “Sensing core histone phosphorylation — A matter of perfect timing”. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – Gene Regulatory Mechanisms. 1839 (8): 711–718. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.04.013. PMC 4103482. PMID 24747175.
- Rossetto, Dorine; Avvakumov, Nikita; Côté, Jacques (2012-10-01). “Histone phosphorylation”. Epigenetics. 7 (10): 1098–1108. doi:10.4161/epi.21975. ISSN 1559-2294. PMC 3469451. PMID 22948226.
- Zhang, Ye; Griffin, Karen; Mondal, Neelima; Parvin, Jeffrey D. (2004-05-21). “Phosphorylation of Histone H2A Inhibits Transcription on Chromatin Templates”. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (21): 21866–21872. doi:10.1074/jbc.M400099200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 15010469.
Kinases
Further information: Kinase
Within a protein, phosphorylation can occur on several amino acids. Phosphorylation on serine is thought to be the most common, followed by threonine. Tyrosine phosphorylation is relatively rare but lies at the head of many protein phosphorylation signalling pathways (e.g. in tyrosine kinase-linked receptors) in most of the eukaryotes. Phosphorylation on amino acids, such as serine, threonine, and tyrosine results in the formation of a phosphoprotein, when the phosphate group of the phosphoprotein reacts with the -OH group of a Ser, Thr, or Tyr sidechain in an esterification reaction.
- Grisham, Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. (2013). Biochemistry (5th ed.). Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole, Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-1133106296.
However, since tyrosine phosphorylated proteins are relatively easy to purify using antibodies, tyrosine phosphorylation sites are relatively well understood. Histidine and aspartate phosphorylation occurs in prokaryotes as part of two-component signaling and in some cases in eukaryotes in some signal transduction pathways. The analysis of phosphorylated histidine using standard biochemical and mass spectrometric approaches is much more challenging than that of Ser, Thr or Tyr and (and what?). In prokaryotes, archaea, and some lower eukaryotes, histidine’s nitrogen act as a nucleophile and binds to a phosphate group.
- Gonzalez-Sanchez MB, Lanucara F, Helm M, Eyers CE (2013). “Attempting to rewrite History: challenges with the analysis of histidine-phosphorylated peptides”. Biochem Soc Trans. 41 (4): 1089–1095. doi:10.1042/bst20130072. PMID 23863184.
- Thomason P; Kay R (September 2000). “Eukaryotic signal transduction via histidine-aspartate phosphorelay” (PDF). J. Cell Sci. 113 (18): 3141–50. doi:10.1242/jcs.113.18.3141. PMID 10954413.
- Puttick, Jennifer; Baker, Edward N.; Delbaere, Louis T.J. (2008). “Histidine phosphorylation in biological systems”. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – Proteins and Proteomics. 1784 (1): 100–105. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2007.07.008. ISSN 1570-9639. PMID 17728195.
- Fuhs SR, Meisenhelder J, Aslanian A, Ma L, Zagorska A, Stankova M, Binnie A, Al-Obeidi F, Mauger J, Lemke G, Yates JR 3rd, Hunter T (2015). “Monoclonal 1- and 3-Phosphohistidine Antibodies: New Tools to Study Histidine Phosphorylation”. Cell. 162 (1): 198–210. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.046. PMC 4491144. PMID 26140597.
- Fuhs SR, Hunter T (2017). “pHisphorylation: the emergence of histidine phosphorylation as a reversible regulatory modification”. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 45: 8–16. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2016.12.010. PMC 5482761. PMID 28129587.
Once histidine is phosphorylated the regulatory domain of the response regulator catalyzes the transfer of the phosphate to aspartate.
Response regulator notes
A response regulator is a protein that mediates a cell‘s response to changes in its environment as part of a two-component regulatory system. Response regulators are coupled to specific histidine kinases which serve as sensors of environmental changes. Response regulators and histidine kinases are two of the most common gene families in bacteria, where two-component signaling systems are very common; they also appear much more rarely in the genomes of some archaea, yeasts, filamentous fungi, and plants. Two-component systems are not found in metazoans.
- Stock AM, Robinson VL, Goudreau PN (2000). “Two-component signal transduction”. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 69: 183–215. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.183. PMID 10966457.
- West AH, Stock AM (June 2001). “Histidine kinases and response regulator proteins in two-component signaling systems”. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 26 (6): 369–76. doi:10.1016/s0968-0004(01)01852-7. PMID 11406410.
- Galperin MY (June 2005). “A census of membrane-bound and intracellular signal transduction proteins in bacteria: bacterial IQ, extroverts and introverts”. BMC Microbiology. 5: 35. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-5-35. PMC 1183210. PMID 15955239.
- Capra EJ, Laub MT (2012). “Evolution of two-component signal transduction systems”. Annual Review of Microbiology. 66: 325–47. doi:10.1146/annurev-micro-092611-150039. PMC 4097194. PMID 22746333.
Function
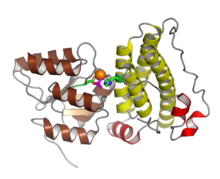
Response regulator proteins typically consist of a receiver domain and one or more effector domains, although in some cases they possess only a receiver domain and exert their effects through protein-protein interactions. In two-component signaling, a histidine kinase responds to environmental changes by autophosphorylation on a histidine residue, following which the response regulator receiver domain catalyzes transfer of the phosphate group to its own recipient aspartate residue. This induces a conformational change that alters the function of the effector domains, usually resulting in increased transcription of target genes. The mechanisms by which this occurs are diverse and include allosteric activation of the effector domain or oligomerization of phosphorylated response regulators.
- West AH, Stock AM (June 2001). “Histidine kinases and response regulator proteins in two-component signaling systems”. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 26 (6): 369–76. doi:10.1016/s0968-0004(01)01852-7. PMID 11406410.
In a common variation on this theme, called a phosphorelay, a hybrid histidine kinase possesses its own receiver domain, and a histidine phosphotransfer protein performs the final transfer to a response regulator.
- Capra EJ, Laub MT (2012). “Evolution of two-component signal transduction systems”. Annual Review of Microbiology. 66: 325–47. doi:10.1146/annurev-micro-092611-150039. PMC 4097194. PMID 22746333.
In many cases, histidine kinases are bifunctional and also serve as phosphatases, catalyzing the removal of phosphate from response regulator aspartate residues, such that the signal transduced by the response regulator reflects the balance between kinase and phosphatase activity.
- Capra EJ, Laub MT (2012). “Evolution of two-component signal transduction systems”. Annual Review of Microbiology. 66: 325–47. doi:10.1146/annurev-micro-092611-150039. PMC 4097194. PMID 22746333.
Many response regulators are also capable of autodephosphorylation, which occurs on a wide range of time scales.
- West AH, Stock AM (June 2001). “Histidine kinases and response regulator proteins in two-component signaling systems”. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 26 (6): 369–76. doi:10.1016/s0968-0004(01)01852-7. PMID 11406410.
In addition, phosphoaspartate is relatively chemically unstable and may be hydrolyzed non-enzymatically.
- Stock AM, Robinson VL, Goudreau PN (2000). “Two-component signal transduction”. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 69: 183–215. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.183. PMID 10966457.
Histidine kinases are highly specific for their cognate response regulators; there is very little cross-talk between different two-component signaling systems in the same cell.
- Rowland MA, Deeds EJ (April 2014). “Crosstalk and the evolution of specificity in two-component signaling”. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 111 (15): 5550–5. Bibcode:2014PNAS..111.5550R. doi:10.1073/pnas.1317178111. PMC 3992699. PMID 24706803.
Classification
Response regulators can be divided into at least three broad classes, based on the features of effector domains: regulators with a DNA-binding effector domain, regulators with an enzymatic effector domain, and single-domain response regulators. More comprehensive classifications based on more detailed analysis of domain architecture are possible. Beyond these broad categorizations, there are response regulators with other types of effector domains, including RNA-binding effector domains.
- Galperin MY (June 2005). “A census of membrane-bound and intracellular signal transduction proteins in bacteria: bacterial IQ, extroverts and introverts”. BMC Microbiology. 5: 35. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-5-35. PMC 1183210. PMID 15955239.
Regulators with a DNA-binding effector domain are the most common response regulators, and have direct impacts on transcription. They tend to interact with their cognate regulators at an N-terminus receiver domain, and contain the DNA-binding effector towards the C-terminus. Once phosphorylated at the receiver domain, the response regulator dimerizes, gains enhanced DNA binding capacity and acts as a transcription factor. The architecture of DNA binding domains are characterized as being variations on helix-turn-helix motifs. One variation, found on the response regulator OmpR of the EnvZ/OmpR two-component system and other OmpR-like response regulators, is a “winged helix” architecture. OmpR-like response regulators are the largest group of response regulators and the winged helix motif is widespread. Other subtypes of DNA-binding response regulators include FixJ-like and NtrC-like regulators. DNA-binding response regulators are involved in various uptake processes, including nitrate/nitrite (NarL, found in most prokaryotes).
- Galperin MY (June 2006). “Structural classification of bacterial response regulators: diversity of output domains and domain combinations”. Journal of Bacteriology. 188 (12): 4169–82. doi:10.1128/jb.01887-05. PMC 1482966. PMID 16740923.
- Barbieri CM, Wu T, Stock AM (May 2013). “Comprehensive analysis of OmpR phosphorylation, dimerization, and DNA binding supports a canonical model for activation”. Journal of Molecular Biology. 425 (10): 1612–26. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2013.02.003. PMC 3646996. PMID 23399542.
- Kenney, Linda J (2002-04-01). “Structure/function relationships in OmpR and other winged-helix transcription factors”. Current Opinion in Microbiology. 5 (2): 135–141. doi:10.1016/S1369-5274(02)00310-7. PMID 11934608.
- Rajeev L, Luning EG, Dehal PS, Price MN, Arkin AP, Mukhopadhyay A (October 2011). “Systematic mapping of two component response regulators to gene targets in a model sulfate reducing bacterium”. Genome Biology. 12 (10): R99. doi:10.1186/gb-2011-12-10-r99. PMC 3333781. PMID 21992415.
- Baikalov I, Schröder I, Kaczor-Grzeskowiak M, Grzeskowiak K, Gunsalus RP, Dickerson RE (August 1996). “Structure of the Escherichia coli response regulator NarL”. Biochemistry. 35 (34): 11053–61. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.580.6078. doi:10.1021/bi960919o. PMID 8780507.
The second class of multidomain response regulators are those with enzymatic effector domains. These response regulators can participate in signal transduction, and generate secondary messenger molecules. Examples include the chemotaxis regulator CheB, with a methylesterase domain that is inhibited when the response regulator is in the inactive unphosphorylated conformation. Other enzymatic response regulators include c-di-GMP phosphodiesterases (e.g. VieA in V. cholerae), protein phosphatases and histidine kinases.
- Galperin MY (April 2010). “Diversity of structure and function of response regulator output domains”. Current Opinion in Microbiology. 13 (2): 150–9. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2010.01.005. PMC 3086695. PMID 20226724.
A relatively small number of response regulators, single-domain response regulators, only contain a receiver domain, relying on protein-protein interactions to exert their downstream biological effects. The receiver domain undergoes a conformational change as it interacts with an autophosphorylated histidine kinase, and consequently, the response regulator can initiate further reactions along a signaling cascade. Prominent examples include the chemotaxis regulator CheY, which interacts with flagellar motor proteins directly in its phosphorylated state.
- Sarkar MK, Paul K, Blair D (May 2010). “Chemotaxis signaling protein CheY binds to the rotor protein FliN to control the direction of flagellar rotation in Escherichia coli”. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 107 (20): 9370–5. Bibcode:2010PNAS..107.9370S. doi:10.1073/pnas.1000935107. PMC 2889077. PMID 20439729.
Sequencing has so far shown that the distinct classes of response regulators are unevenly distributed throughout various taxa, including across domains. While response regulators with DNA-binding domains are the most common in bacteria, single-domain response regulators are more common in archaea, with other major classes of response regulators seemingly absent from archaeal genomes.
- “Census of prokaryotic response regulators”. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2017-10-08.
Evolution
The number of two-component systems present in a bacterial genome is highly correlated with genome size as well as ecological niche; bacteria that occupy niches with frequent environmental fluctuations possess more histidine kinases and response regulators. New two-component systems may arise by gene duplication or by lateral gene transfer, and the relative rates of each process vary dramatically across bacterial species. In most cases, response regulator genes are located in the same operon as their cognate histidine kinase; lateral gene transfers are more likely to preserve operon structure than gene duplications. The small number of two-component systems present in eukaryotes most likely arose by lateral gene transfer from endosymbiotic organelles; in particular, those present in plants likely derive from chloroplasts.
- Capra EJ, Laub MT (2012). “Evolution of two-component signal transduction systems”. Annual Review of Microbiology. 66: 325–47. doi:10.1146/annurev-micro-092611-150039. PMC 4097194. PMID 22746333.
- Galperin MY (June 2006). “Structural classification of bacterial response regulators: diversity of output domains and domain combinations”. Journal of Bacteriology. 188 (12): 4169–82. doi:10.1128/jb.01887-05. PMC 1482966. PMID 16740923.
- Alm E, Huang K, Arkin A (November 2006). “The evolution of two-component systems in bacteria reveals different strategies for niche adaptation”. PLOS Computational Biology. 2 (11): e143. Bibcode:2006PLSCB…2..143A. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.0020143. PMC 1630713. PMID 17083272.
Response Regulators Categories:
Receptor tyrosine kinases
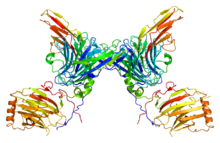
While tyrosine phosphorylation is found in relatively low abundance, it is well studied due to the ease of purification of phosphotyrosine using antibodies. Receptor tyrosine kinases are an important family of cell surface receptors involved in the transduction of extracellular signals such as hormones, growth factors, and cytokines. Binding of a ligand to a monomeric receptor tyrosine kinase stabilizes interactions between two monomers to form a dimer, after which the two bound receptors phosphorylate tyrosine residues in trans. Phosphorylation and activation of the receptor activates a signaling pathway through enzymatic activity and interactions with adaptor proteins. Signaling through the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), a receptor tyrosine kinase, is critical for the development of multiple organ systems including the skin, lung, heart, and brain. Excessive signaling through the EGFR pathway is found in many human cancers.
- Lemmon, Mark A.; Schlessinger, Joseph (June 2010). “Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases”. Cell. 141 (7): 1117–34. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.06.011. PMC 2914105. PMID 20602996.
- Cho HS, Leahy DJ; Leahy (2002). “Structure of the extracellular region of HER3 reveals an interdomain tether”. Science. 297 (5585): 1330–1333. Bibcode:2002Sci…297.1330C. doi:10.1126/science.1074611. PMID 12154198. S2CID 23069349.
Cyclin-dependent kinases
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are serine-threonine kinases which regulate progression through the eukaryotic cell cycle. CDKs are catalytically active only when bound to a regulatory cyclin. Animal cells contain at least nine distinct CDKs which bind to various cyclins with considerable specificity. CDK inhibitors (CKIs) block kinase activity in the cyclin-CDK complex to halt the cell cycle in G1 or in response to environmental signals or DNA damage. The activity of different CDKs activate cell signaling pathways and transcription factors that regulate key events in mitosis such as the G1/S phase transition. Earlier cyclin-CDK complexes provide the signal to activate subsequent cyclin-CDK complexes.
- Morgan, David O. (2007). The Cell Cycle: Principles of Control. London: New Science Press, 1st ed.
Sites
There are thousands of distinct phosphorylation sites in a given cell since:
- There are thousands of proteins in any particular cell.
- An estimated 1/10 to 1/2 of proteins are phosphorylated in some cellular state.
- 30–65% of proteins in humans and ~50% of proteins in yeast may be phosphorylated.
- Cohen, Philip (2002-05-01). “The origins of protein phosphorylation”. Nature Cell Biology. 4 (5): E127–130. doi:10.1038/ncb0502-e127. ISSN 1465-7392. PMID 11988757. S2CID 29601670.
- Vlastaridis, Panayotis; Kyriakidou, Pelagia; Chaliotis, Anargyros; Van de Peer, Yves; Oliver, Stephen G.; Amoutzias, Grigoris D. (2017-02-01). “Estimating the total number of phosphoproteins and phosphorylation sites in eukaryotic proteomes”. GigaScience. 6 (2): 1–11. doi:10.1093/gigascience/giw015. PMC 5466708. PMID 28327990.
- An estimated 230,000, 156,000, and 40,000 phosphorylation sites exist in human, mouse, and yeast, respectively.
- Vlastaridis, Panayotis; Kyriakidou, Pelagia; Chaliotis, Anargyros; Van de Peer, Yves; Oliver, Stephen G.; Amoutzias, Grigoris D. (2017-02-01). “Estimating the total number of phosphoproteins and phosphorylation sites in eukaryotic proteomes”. GigaScience. 6 (2): 1–11. doi:10.1093/gigascience/giw015. PMC 5466708. PMID 28327990.
- Phosphorylation often occurs on multiple distinct sites on a given protein.
Since phosphorylation of any site on a given protein can change the function or localization of that protein, understanding the “state” of a cell requires knowing the phosphorylation state of its proteins. For example, generally, if amino acid Serine-473 in the protein AKT is phosphorylated, AKT is functionally active as a kinase, and if it is not phosphorylated, AKT is an inactive kinase.
Phosphorylation sites are crucial for proteins and their transportation and functions. They are the covalent modification of proteins through reversible phosphorylation. This enables proteins to stay inbound within a cell since the negative phosphorylated site disallows their permeability through the cellular membrane. Protein dephosphorylation allows the cell to replenish phosphates through release of pyrophosphates which saves ATP use in the cell. An example of phosphorylating enzyme is found in E. coli bacteria. It possesses alkaline phosphatase in its periplasmic region of its membrane. The outermost membrane is permeable to phosphorylated molecules however the inner cytoplasmic membrane is impermeable due to large negative charges. In this way, the E. coli bacteria stores proteins and pyrophosphates in its periplasmic membrane until either are needed within the cell.
- Garrett, Reginald H.; Grisham, Charles m. (2013). Biochemistry. Mary Finch, Cengage Learning. pp. 489–491.
- Ninfa, Alexander; David P. Ballou, David (1998). Fundamental Laboratory Approaches for Biochemistry and Biotechnology (2nd ed.). Fitzgerald Science Press. pp. 230–231.
Recent advancement in phosphoproteomic identification has resulted in the discoveries of countless phosphorylation sites in proteins. This required an integrative medium for accessible data in which known phosphorylation sites of proteins are organized. A curated database of dbPAF was created, containing known phosphorylation sites in H. sapiens, M. musculus, R. norvegicus, D. melanogaster, C. elegans, S. pombe and S. cerevisiae. The database currently holds 294,370 non-redundant phosphorylation sites of 40,432 proteins. Other tools of phosphorylation prediction in proteins include NetPhos for eukaryotes, NetPhosBac for bacteria, and ViralPhos for viruses.
- Ullah, Shahid; Lin, Shaofeng (2016). “dbPAF: an integrative database of protein phosphorylation in animals and fungi”. Scientific Reports. 6: 23534. Bibcode:2016NatSR…623534U. doi:10.1038/srep23534. PMC 4806352. PMID 27010073. Retrieved 17 May 2016.
- Blom, Nikolaj; Gammeltoft, Steen; Brunak, Søren (1999-12-17). “Sequence and structure-based prediction of eukaryotic protein phosphorylation sites1”. Journal of Molecular Biology. 294 (5): 1351–1362. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1999.3310. PMID 10600390.
- Huang, Kai-Yao; Lu, Cheng-Tsung; Bretaña, Neil Arvin; Lee, Tzong-Yi; Chang, Tzu-Hao (2013-01-01). “ViralPhos: incorporating a recursively statistical method to predict phosphorylation sites on virus proteins”. BMC Bioinformatics. 14 (16): S10. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-14-S16-S10. ISSN 1471-2105. PMC 3853219. PMID 24564381.
Serine and threonine
There are a large variety of serine residues, and the phosphorylation of each residue can lead to different metabolic consequences.
- Protein kinase N1 is responsible for the phosphorylation of the TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF1) on serine 139 under specific conditions. Murine TRAF1 is also phosphorylated by the same kinase, which leads to the silencing of IKK/NF-κB activity. The elimination of phosphorylation on serine 139 can be achieved by the replacement of TRAF1 with an Alanine residue, which consequently leads to the improved recruitment of TBK1.
- Oussa, N.A. (March 1, 2013). “TRAF1 phosphorylation on Serine 139 modulates NF-κB activity downstream of 4-1BB in T cells”. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 432 (1): 129–134. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.01.073. PMID 23376065.
- At the serine 789 residue, FGFR1 is phosphorylated by RSK2 when the kinase is in its active form. The signaling capabilities of FGFR1 at the serine 777 site can be weakened by phosphorylation. Serine 1047 and serine 1048 have been linked to the decreased binding affinity of ubiquitin ligase c-Cbl to EFGR when they are phosphorylated.
- Nadratowska-Wesolowska, B (October 21, 2016). “RSK2 regulates endocytosis of FGF receptor 1 by phosphorylation on serine 789”. Oncogene. 33 (40): 4823–4836. doi:10.1038/onc.2013.425. PMID 24141780.
- When serine 349 is phosphorylated, the binding affinity between protein complex p62 and the protein Keap1 is strengthened, which is linked to stress response.
- Tanji, Kunikazu (May 3, 2014). “Phosphorylation of serine 349 of p62 in Alzheimer’s disease brain”. Acta Neuropathologica Communications. 2 (50): 50. doi:10.1186/2051-5960-2-50. PMC 4035093. PMID 24886973.
- When serine 337 is phosphorylated by protein kinase A in vitro, the DNA binding efficiency of the p50 subunit of NF-κB is greatly increased.
- Hou, Shihe (November 14, 2003). “Phosphorylation of serine 337 of NF-kappaB p50 is critical for DNA binding”. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (46): 45994–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.m307971200. PMID 12947093.
Phosphorylation of serine and threonine residues is known to crosstalk with O-GlcNAc modification of serine and threonine residues.
Tyrosine
Main article: Tyrosine phosphorylation
Tyrosine phosphorylation is a fast, reversible reaction, and one of the major regulatory mechanisms in signal transduction. Cell growth, differentiation, migration, and metabolic homeostasis are cellular processes maintained by tyrosine phosphorylation. The function of protein tyrosine kinases and protein-tyrosine phosphatase counterbalances the level of phosphotyrosine on any protein. The malfunctioning of specific chains of protein tyrosine kinases and protein tyrosine phosphatase has been linked to multiple human diseases such as obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- editor, Kendra K. Bence (2013). Protein tyrosine phosphatase control of metabolism. New York, NY: Springer New York. ISBN 978-1-4614-7855-3.
{{cite book}}:|last1=has generic name (help)
Phosphorylation on tyrosine occurs in eukaryotes, select bacterial species, and is present among prokaryotes. Phosphorylation on tyrosine maintains the cellular regulation in bacteria similar to its function in eukaryotes.
- Cozzone, Alain J.; Grangeasse, Christophe; Doublet, Patricia; Duclos, Bertrand (1 March 2004). “Protein phosphorylation on tyrosine in bacteria”. Archives of Microbiology. 181 (3): 171–181. doi:10.1007/s00203-003-0640-6. PMID 14745484. S2CID 37161183.
Arginine
Arginine phosphorylation in many Gram-positive bacteria marks proteins for degradation by a Clp protease.
- Broch Trentini, Débora (2016). “Arginine phosphorylation marks proteins for degradation by a Clp protease”. Nature. 539 (7627): 48–53. Bibcode:2016Natur.539…48T. doi:10.1038/nature20122. PMC 6640040. PMID 27749819.
Non-canonical phosphorylation on His, Asp, Cys, Glu, Arg and Lys in human cells
Widespread human protein phosphorylation occurs on multiple non-canonical amino acids, including motifs containing phosphorylated histidine (1 and 3 positions), aspartate, cysteine, glutamate, arginine, and lysine in HeLa cell extracts. Due to the chemical and thermal lability of these phosphorylated residues, special procedures and separation techniques are required for preservation alongside the heat stable ‘classical’ Ser, Thr and Tyr phosphorylation.
- Eyers CE, Hardman G (August 21, 2019). “Strong anion exchange-mediated phosphoproteomics reveals extensive human non-canonical phosphorylation”. The EMBO Journal. 38 (21): e100847. doi:10.15252/embj.2018100847. PMC 6826212. PMID 31433507.
Detection and characterization
Antibodies can be used as powerful tool to detect whether a protein is phosphorylated at a particular site. Antibodies bind to and detect phosphorylation-induced conformational changes in the protein. Such antibodies are called phospho-specific antibodies; hundreds of such antibodies are now available. They are becoming critical reagents both for basic research and for clinical diagnosis.
Post-translational modification (PTM) isoforms are easily detected on 2D gels. Indeed, phosphorylation replaces neutral hydroxyl groups on serines, threonines, or tyrosines with negatively charged phosphates with pKs near 1.2 and 6.5. Thus, below pH 5.5, phosphates add a single negative charge; near pH 6.5, they add 1.5 negative charges; above pH 7.5, they add 2 negative charges. The relative amount of each isoform can also easily and rapidly be determined from staining intensity on 2D gels.
In some very specific cases, the detection of the phosphorylation as a shift in the protein’s electrophoretic mobility is possible on simple 1-dimensional SDS-PAGE gels, as it is described for instance for a transcriptional coactivator by Kovacs et al. Strong phosphorylation-related conformational changes (that persist in detergent-containing solutions) are thought to underlie this phenomenon. Most of the phosphorylation sites for which such a mobility shift has been described fall in the category of SP and TP sites (i.e. a proline residue follows the phosphorylated serine or threonine residue).
- Kovacs KA, Steinmann M; Magistretti PJ; Halfon O; Cardinaux JR (Sep 2003). “CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein family members recruit the coactivator CREB-binding protein and trigger its phosphorylation”. J. Biol. Chem. 278 (38): 36959–65. doi:10.1074/jbc.M303147200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12857754.
Large-scale mass spectrometry analyses have been used to determine sites of protein phosphorylation. Dozens of studies have been published, each identifying thousands of sites, many of which were previously undescribed. Mass spectrometry is ideally suited for such analyses using HCD or ETD fragmentation, as the addition of phosphorylation results in an increase in the mass of the protein and the phosphorylated residue. Advanced, highly accurate mass spectrometers are needed for these studies, limiting the technology to labs with high-end mass spectrometers. However, the analysis of phosphorylated peptides by mass spectrometry is still not as straightforward as for “regular”, unmodified peptides. EThcD has been developed combining electron-transfer and higher-energy collision dissociation. Compared to the usual fragmentation methods, EThcD scheme provides more informative MS/MS spectra for unambiguous phosphosite localization.
- Munton RP, Tweedie-Cullen R, Livingstone-Zatchej M, Weinandy F, Waidelich M, Longo D, Gehrig P, Potthast F, et al. (February 2007). “Qualitative and quantitative analyses of protein phosphorylation in naive and stimulated mouse synaptosomal preparations” (PDF). Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 6 (2): 283–93. doi:10.1074/mcp.M600046-MCP200. PMID 17114649. S2CID 18221665.
- Trinidad JC; Thalhammer A; Specht CG; Lynn AJ; Baker PR; Schoepfer R; Burlingame AL (April 2008). “Quantitative analysis of synaptic phosphorylation and protein expression”. Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 7 (4): 684–96. doi:10.1074/mcp.M700170-MCP200. PMID 18056256.
- Frese, Christian; Houjiang Zhou; Thomas Taus; A. F. Maarten Altelaar; Karl Mechtler; Albert J. R. Heck; Shabaz Mohammed (March 1, 2013). “Unambiguous Phosphosite Localization using Electron-Transfer/Higher-Energy Collision Dissociation (EThcD)”. J Proteome Res. 12 (3): 1520–1525. doi:10.1021/pr301130k. PMC 3588588. PMID 23347405.
A detailed characterization of the sites of phosphorylation is very difficult, and the quantitation of protein phosphorylation by mass spectrometry requires isotopic internal standard approaches. A relative quantitation can be obtained with a variety of differential isotope labeling technologies. There are also several quantitative protein phosphorylation methods, including fluorescence immunoassays, microscale thermophoresis, FRET, TRF, fluorescence polarization, fluorescence-quenching, mobility shift, bead-based detection, and cell-based formats.
- Gerber SA; Rush J; Stemman O; Kirschner MW; Gygi SP (June 2003). “Absolute quantification of proteins and phosphoproteins from cell lysates by tandem MS”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 (12): 6940–5. Bibcode:2003PNAS..100.6940G. doi:10.1073/pnas.0832254100. PMC 165809. PMID 12771378.
- Gygi SP; Rist B; Griffin TJ; Eng J; Aebersold R (2002). “Proteome analysis of low-abundance proteins using multidimensional chromatography and isotope-coded affinity tags”. J. Proteome Res. 1 (1): 47–54. doi:10.1021/pr015509n. PMID 12643526.
- Olive DM (October 2004). “Quantitative methods for the analysis of protein phosphorylation in drug development”. Expert Rev Proteomics. 1 (3): 327–41. doi:10.1586/14789450.1.3.327. PMID 15966829. S2CID 30003827.
- Chen H, Kovar J, Sissons S, Cox K, Matter W, Chadwell F, Luan P, Vlahos CJ, et al. (March 2005). “A cell-based immunocytockemical assay for monitoring kinase signaling pathways and drug efficacy” (PDF). Anal. Biochem. 338 (1): 136–42. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.335.3523. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2004.11.015. PMID 15707944. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-02-22. Retrieved 2019-05-26.
Evolution
Protein phosphorylation is common among all clades of life, including all animals, plants, fungi, bacteria, and archaea. The origins of protein phosphorylation mechanisms are ancestral and have diverged greatly between different species. In eukaryotes, it is estimated that between 30 – 65% of all proteins may be phosphorylated, with tens or even hundreds of thousands of distinct phosphorylation sites. Some phosphorylation sites appear to have evolved as conditional “off” switches, blocking the active site of an enzyme, such as in the prokaryotic metabolic enzyme isocitrate dehydrogenase. However, in the case of proteins that must be phosphorylated to be active, it is less clear how they could have emerged from non-phosphorylated ancestors. It has been shown that a subset of serine phosphosites are often replaced by acidic residues such as aspartate and glutamate between different species. These anionic residues can interact with cationic residues such as lysine and arginine to form salt bridges, stable non-covalent interactions that alter a protein’s structure. These phosphosites often participate in salt bridges, suggesting that some phosphorylation sites evolved as conditional “on” switches for salt bridges, allowing these proteins to adopt an active conformation only in response to a specific signal.
- Vlastaridis, Panayotis; Kyriakidou, Pelagia; Chaliotis, Anargyros; Van de Peer, Yves; Oliver, Stephen G.; Amoutzias, Grigoris D. (2017-02-01). “Estimating the total number of phosphoproteins and phosphorylation sites in eukaryotic proteomes”. GigaScience. 6 (2): 1–11. doi:10.1093/gigascience/giw015. PMC 5466708. PMID 28327990.
- Cohen P (2000). “The regulation of protein function by multisite phosphorylation – a 25 year update”. Trends Biochem. Sci. 25 (12): 596–601. doi:10.1016/S0968-0004(00)01712-6. PMID 11116185.
- Pearlman SM, Serber Z, Ferrell JE (2011). “A Mechanism for the Evolution of Phosphorylation Sites”. Cell. 147 (4): 934–946. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.052. PMC 3220604. PMID 22078888.
There are around 600 known eukaryotic protein kinases, making them one of the largest eukaryotic gene families. Most phosphorylation is carried out by a single superfamily of protein kinases that share a conserved kinase domain. Protein phosphorylation is highly conserved in pathways central to cell survival, such as cell cycle progression relying on cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), but individual phosphorylation sites are often flexible. Targets of CDK phosphorylation often have phosphosites in disordered segments, which are found in non-identical locations even in close species. Conversely, targets of CDK phosphorylation in structurally defined regions are more highly conserved. While CDK activity is critical for cell growth and survival in all eukaryotes, only very few phosphosites show strong conservation of their precise positions. Positioning is likely to be highly important for phosphates that allosterically regulate protein structure, but much more flexible for phosphates that interact with phosphopeptide-binding domains to recruit regulatory proteins.
- Holt LJ, Tuch BB, Villén J, Johnson AD, Gygi SP, Morgan DO (2009). “Global Analysis of Cdk1 Substrate Phosphorylation Sites Provides Insights into Evolution”. Science. 325 (5948): 1682–1686. Bibcode:2009Sci…325.1682H. doi:10.1126/science.1172867. PMC 2813701. PMID 19779198.
Comparisons between eukaryotes and prokaryotes
Protein phosphorylation is a reversible post-translational modification of proteins. In eukaryotes, protein phosphorylation functions in cell signaling, gene expression, and differentiation. It is also involved in DNA replication during the cell cycle, and the mechanisms that cope with stress-induced replication blocks. Compared to eukaryotes, prokaryotes use Hanks-type kinases and phosphatases for signal transduction. Whether or not the phosphorylation of proteins in bacteria can also regulate processes like DNA repair or replication still remains unclear.
- Garcia-Garcia, Transito (2016). “Role Of Protein Phosphorylation In The Regulation Of Cell Cycle And DNA-Related Processes In Bacteria”. Frontiers in Microbiology. 7: 184. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2016.00184. PMC 4754617. PMID 26909079.
Compared to the protein phosphorylation of prokaryotes, studies of protein phosphorylation in eukaryotes from yeast to human cells have been rather extensive. It is known that eukaryotes rely on the phosphorylation of the hydroxyl group on the side chains of serine, threonine, and tyrosine for cell signaling. These are the main regulatory post-translational modifications in eukaryotic cells but the protein phosphorylation of prokaryotes are less intensely studied. While serine, threonine, and tyrosine are phosphorylated in eukaryotes, histidine and aspartate is phosphorylated in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In bacteria, histidine phosphorylation occurs in the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase systems (PTSs), which are involved in the process of internalization as well as the phosphorylation of sugars.
- Macek, B.; Mijakovic, I.; Olsen, J.; Gnad, F; Kumar, C.; Jensen, P. (2007). “The serine/threonine/tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis”. Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 6 (4): 697–707. doi:10.1074/mcp.m600464-mcp200. PMID 17218307.
Protein phosphorylation by protein kinase was first shown in E. coli and Salmonella typhimurium and has since been demonstrated in many other bacterial cells.
- Cozzone, AJ (1988). “Protein phosphorylation in prokaryotes”. Annu Rev Microbiol. 42: 97–125. doi:10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.000525. PMID 2849375.
It was found that bacteria use histidine and aspartate phosphorylation as a model for bacterial signaling transduction. Serine, threonine and tyrosine phosphorylation are also present in bacteria. Bacteria carry kinases and phosphatases similar to that of their eukaryotic equivalent and have also developed unique kinases and phosphatases not found in eukaryotes.
- Macek, B.; Mijakovic, I.; Olsen, J.; Gnad, F; Kumar, C.; Jensen, P. (2007). “The serine/threonine/tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis”. Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 6 (4): 697–707. doi:10.1074/mcp.m600464-mcp200. PMID 17218307.
Pathology
Abnormal protein phosphorylation has been implicated in a number of diseases, including cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and other degenerative disorders.
Tau protein belongs to a group of microtubule associated proteins (MAPs) which help stabilize microtubules in cells, including neurons.
- Wolfe, Michael S. (2012-12-19). “The Role of Tau in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Its Potential as a Therapeutic Target”. Scientifica. 2012: 796024. doi:10.6064/2012/796024. PMC 3820460. PMID 24278740.
Association and stabilizing activity of tau protein depends on its phosphorylated state. In Alzheimer’s disease, due to misfoldings and abnormal conformational changes in tau protein structure, it is rendered ineffective at binding to microtubules and unable to keep the neural cytoskeletal structure organized during neural processes. Abnormal tau inhibits and disrupts microtubule organization and disengages normal tau from microtubules into cytosolic phase. The misfoldings lead to the abnormal aggregation into fibrillary tangles inside the neurons. The tau protein needs to be phosphorylated to function, but hyperphosphorylation of tau protein is one of the major influences on its incapacity to associate.
- Kolarova, Michala; García-Sierra, Francisco; Bartos, Ales; Ricny, Jan; Ripova, Daniela (2012-05-29). “Structure and Pathology of Tau Protein in Alzheimer Disease”. International Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. 2012: 731526. doi:10.1155/2012/731526. ISSN 2090-8024. PMC 3368361. PMID 22690349.
Phosphatases PP1, PP2A, PP2B, and PP2C dephosphorylate tau protein in vitro, and their activities are reduced in areas of the brain in Alzheimer patients.
- Kolarova, Michala; García-Sierra, Francisco; Bartos, Ales; Ricny, Jan; Ripova, Daniela (2012-05-29). “Structure and Pathology of Tau Protein in Alzheimer Disease”. International Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. 2012: 731526. doi:10.1155/2012/731526. ISSN 2090-8024. PMC 3368361. PMID 22690349.
- Crespo-Biel, Natalia; Theunis, Clara; Leuven, Fred Van (2012-06-08). “Protein Tau: Prime Cause of Synaptic and Neuronal Degeneration in Alzheimer’s Disease”. International Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. 2012: 251426. doi:10.1155/2012/251426. ISSN 2090-8024. PMC 3376502. PMID 22720188.
Tau phosphoprotein is three to fourfold hyperphosphorylated in an Alzheimer patient compared to an aged non-afflicted individual. Alzheimer disease tau seems to remove MAP1 and MAP2 (two other major associated proteins) from microtubules and this deleterious effect is reversed when dephosphorylation is performed, evidencing hyperphosphorylation as the sole cause of the crippling activity.
- Kolarova, Michala; García-Sierra, Francisco; Bartos, Ales; Ricny, Jan; Ripova, Daniela (2012-05-29). “Structure and Pathology of Tau Protein in Alzheimer Disease”. International Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. 2012: 731526. doi:10.1155/2012/731526. ISSN 2090-8024. PMC 3368361. PMID 22690349.
Parkinson’s disease
α-Synuclein is a protein that is associated with Parkinson’s disease. In humans, this protein is encoded by the SNCA gene. α-Synuclein is involved in recycling synaptic vesicles that carry neurotransmitters and naturally occurs in an unfolded form. Elevated levels of α-Synuclein are found in patients with Parkinson’s disease. There is a correlation between the concentration of unphosphorylated α-Synuclein present in the patient and the severity of Parkinson’s disease.
- Spillantini, MG; Crowther, RA; Jakes, R; Hasegawa, M; Goedert, M (26 May 1998). “alpha-Synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with lewy bodies”. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 95 (11): 6469–73. Bibcode:1998PNAS…95.6469S. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.11.6469. PMC 27806. PMID 9600990.
- “Genetics Home Reference: SNCA”. U.S. National Library of Medicine. 12 Nov 2013. Retrieved 14 Nov 2013.
- Burré, J; Sharma, M; Südhof, TC (1 March 2018). “Cell Biology and Pathophysiology of α-Synuclein”. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine. 8 (3): a024091. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a024091. PMC 5519445. PMID 28108534.
Specifically, phosphorylation of Ser129 in α-Synuclein has an impact on severity. Healthy patients have higher levels of unphosphorylated α-Synuclein than patients with Parkinson’s disease. The measurement of change in the ratio of concentrations of phosphorylated α-Synuclein to unphosphorylated α-Synuclein within a patient could be a marker of the disease progression. Antibodies that target α-Synuclein at phosphorylated Ser129 are used to study the molecular aspects of synucleinopathies.
- Rutherford, NJ; Brooks, M; Giasson, BI (8 August 2016). “Novel antibodies to phosphorylated α-synuclein serine 129 and NFL serine 473 demonstrate the close molecular homology of these epitopes”. Acta Neuropathologica Communications. 4 (1): 80. doi:10.1186/s40478-016-0357-9. PMC 4977832. PMID 27503460.
- Paleologou, KE; Schmid, AW; Rospigliosi, CC; Kim, HY; Lamberto, GR; Fredenburg, RA; Lansbury PT, Jr; Fernandez, CO; Eliezer, D; Zweckstetter, M; Lashuel, HA (13 June 2008). “Phosphorylation at Ser-129 but not the phosphomimics S129E/D inhibits the fibrillation of alpha-synuclein”. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 283 (24): 16895–905. doi:10.1074/jbc.M800747200. PMC 2423264. PMID 18343814.
Phosphorylation of Ser129 is associated with the aggregation of the protein and further damage to the nervous system. The aggregation of phosphorylated α-Synuclein can be enhanced if a presynaptic scaffold protein, Sept4, is present in insufficient quantities. Direct interaction of α-Synuclein with Sept4 inhibits the phosphorylation of Ser129.
- “Parkinson’s Disease | Elucidating the Role of Phosphorylation in modulating alpha-synuclein aggregation and toxicity in Parkinson’s disease and related disorders”. Parkinson’s Disease | The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research. Retrieved 2016-05-14.
- Wang, Yu; Shi, Min; Chung, Kathryn A.; Zabetian, Cyrus P.; Leverenz, James B.; Berg, Daniela; Srulijes, Karin; Trojanowski, John Q.; Lee, Virginia M.-Y. (2012-02-15). “Phosphorylated α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s Disease”. Science Translational Medicine. 4 (121): 121ra20. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3002566. ISSN 1946-6234. PMC 3302662. PMID 22344688.
- Stewart, Tessandra; Sossi, Vesna; Aasly, Jan O; Wszolek, Zbigniew K; Uitti, Ryan J; Hasegawa, Kazuko; Yokoyama, Teruo; Zabetian, Cyrus P; Leverenz, James B (2015-01-31). “Phosphorylated α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease: correlation depends on disease severity”. Acta Neuropathologica Communications. 3 (1): 7. doi:10.1186/s40478-015-0185-3. ISSN 2051-5960. PMC 4362824. PMID 25637461.
However, phosphorylation of Ser129 can be observed without synuclein aggregation in conditions of overexpression.
- Laferrière, Florent; He, Xin; Zinghirino, Federica; Doudnikoff, Evelyne; Faggiani, Emilie; Meissner, Wassilios G.; Bezard, Erwan; De Giorgi, Francesca; Ichas, François (2020-10-29). “Overexpression of α-Synuclein by Oligodendrocytes in Transgenic Mice Does Not Recapitulate the Fibrillar Aggregation Seen in Multiple System Atrophy”. Cells. 9 (11): 2371. doi:10.3390/cells9112371. ISSN 2073-4409. PMC 7693764. PMID 33138150.
Sept4
Septin-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SEPT4 gene. This gene is a member of the septin gene family of nucleotide binding proteins, originally described in yeast as cell division cycle regulatory proteins. Septins are highly conserved in yeast, Drosophila, and mouse and appear to regulate cytoskeletal organization. The protein encoded by this gene is thought to be part of a complex involved in cytokinesis. Alternatively spliced variants which encode different protein isoforms have been described; however, not all variants have been fully characterized.
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000108387 – Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000020486 – Ensembl, May 2017
- “Human PubMed Reference:”. National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- “Mouse PubMed Reference:”. National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Paavola P, Horelli-Kuitunen N, Palotie A, Peltonen L (January 1999). “Characterization of a novel gene, PNUTL2, on human chromosome 17q22-q23 and its exclusion as the Meckel syndrome gene”. Genomics. 55 (1): 122–5. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5612. PMID 9889007.
- “Entrez Gene: SEPT4 septin 4”.
Sept4 Further reading
- Xie H, Surka M, Howard J, Trimble WS (1999). “Characterization of the mammalian septin H5: distinct patterns of cytoskeletal and membrane association from other septin proteins”. Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton. 43 (1): 52–62. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0169(1999)43:1<52::AID-CM6>3.0.CO;2-5. PMID 10340703.
- Larisch S, Yi Y, Lotan R, Kerner H, Eimerl S, Tony Parks W, Gottfried Y, Birkey Reffey S, de Caestecker MP, Danielpour D, Book-Melamed N, Timberg R, Duckett CS, Lechleider RJ, Steller H, Orly J, Kim SJ, Roberts AB (December 2000). “A novel mitochondrial septin-like protein, ARTS, mediates apoptosis dependent on its P-loop motif”. Nature Cell Biology. 2 (12): 915–21. doi:10.1038/35046566. PMID 11146656. S2CID 12321788.
- Zieger B, Tran H, Hainmann I, Wunderle D, Zgaga-Griesz A, Blaser S, Ware J (December 2000). “Characterization and expression analysis of two human septin genes, PNUTL1 and PNUTL2”. Gene. 261 (2): 197–203. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(00)00527-8. PMID 11167005.
- Tanaka M, Tanaka T, Kijima H, Itoh J, Matsuda T, Hori S, Yamamoto M (August 2001). “Characterization of tissue- and cell-type-specific expression of a novel human septin family gene, Bradeion”. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 286 (3): 547–53. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.5413. PMID 11511094.
- Tanaka M, Kijima H, Itoh J, Matsuda T, Tanaka T (June 2002). “Impaired expression of a human septin family gene Bradeion inhibits the growth and tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer in vitro and in vivo”. Cancer Gene Therapy. 9 (6): 483–8. doi:10.1038/sj.cgt.7700460. PMID 12032658.
- Vega IE, Hsu SC (January 2003). “The septin protein Nedd5 associates with both the exocyst complex and microtubules and disruption of its GTPase activity promotes aberrant neurite sprouting in PC12 cells”. NeuroReport. 14 (1): 31–7. doi:10.1097/00001756-200301200-00006. PMID 12544826. S2CID 22757290.
- Ihara M, Tomimoto H, Kitayama H, Morioka Y, Akiguchi I, Shibasaki H, Noda M, Kinoshita M (June 2003). “Association of the cytoskeletal GTP-binding protein Sept4/H5 with cytoplasmic inclusions found in Parkinson’s disease and other synucleinopathies”. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (26): 24095–102. doi:10.1074/jbc.M301352200. PMID 12695511.
- Choi P, Snyder H, Petrucelli L, Theisler C, Chong M, Zhang Y, Lim K, Chung KK, Kehoe K, D’Adamio L, Lee JM, Cochran E, Bowser R, Dawson TM, Wolozin B (October 2003). “SEPT5_v2 is a parkin-binding protein”. Brain Research. Molecular Brain Research. 117 (2): 179–89. doi:10.1016/S0169-328X(03)00318-8. PMID 14559152.
- Gottfried Y, Rotem A, Lotan R, Steller H, Larisch S (April 2004). “The mitochondrial ARTS protein promotes apoptosis through targeting XIAP”. The EMBO Journal. 23 (7): 1627–35. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600155. PMC 391065. PMID 15029247.
- Bläser S, Horn J, Würmell P, Bauer H, Strümpell S, Nurden P, Pagenstecher A, Busse A, Wunderle D, Hainmann I, Zieger B (May 2004). “The novel human platelet septin SEPT8 is an interaction partner of SEPT4”. Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 91 (5): 959–66. doi:10.1160/TH03-09-0578. PMID 15116257.
- Elhasid R, Sahar D, Merling A, Zivony Y, Rotem A, Ben-Arush M, Izraeli S, Bercovich D, Larisch S (July 2004). “Mitochondrial pro-apoptotic ARTS protein is lost in the majority of acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients”. Oncogene. 23 (32): 5468–75. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207725. PMID 15122323.
- Martínez C, Sanjuan MA, Dent JA, Karlsson L, Ware J (September 2004). “Human septin-septin interactions as a prerequisite for targeting septin complexes in the cytosol”. The Biochemical Journal. 382 (Pt 3): 783–91. doi:10.1042/BJ20040372. PMC 1133953. PMID 15214843.
- Lotan R, Rotem A, Gonen H, Finberg JP, Kemeny S, Steller H, Ciechanover A, Larisch S (July 2005). “Regulation of the proapoptotic ARTS protein by ubiquitin-mediated degradation”. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 280 (27): 25802–10. doi:10.1074/jbc.M501955200. PMID 15837787.
- Lee JW, Soung YH, Young Kim S, Woo Nam S, Sang Park W, Young Lee J, Jin Yoo N, Lee SH (2006). “Mutational analysis of proapoptotic ARTS P-loop domain in common human cancers”. Pathology, Research and Practice. 202 (2): 67–70. doi:10.1016/j.prp.2005.11.001. PMID 16376484.
- Lee JW, Soung YH, Kim SY, Nam SW, Park WS, Lee JY, Yoo NJ, Lee SH (2006). “Mutational analysis of P-loop domains of proapoptotic Nod1 and ARTS genes in colon carcinomas”. Acta Oncologica. 45 (1): 101–2. doi:10.1080/02841860500374497. PMID 16464805. S2CID 218896700.
- Garcia W, de Araújo AP, Neto Mde O, Ballestero MR, Polikarpov I, Tanaka M, Tanaka T, Garratt RC (November 2006). “Dissection of a human septin: definition and characterization of distinct domains within human SEPT4”. Biochemistry. 45 (46): 13918–31. doi:10.1021/bi061549z. PMID 17105210.
Sept4 Categories:
Main Subject Categories:
Leave a Reply