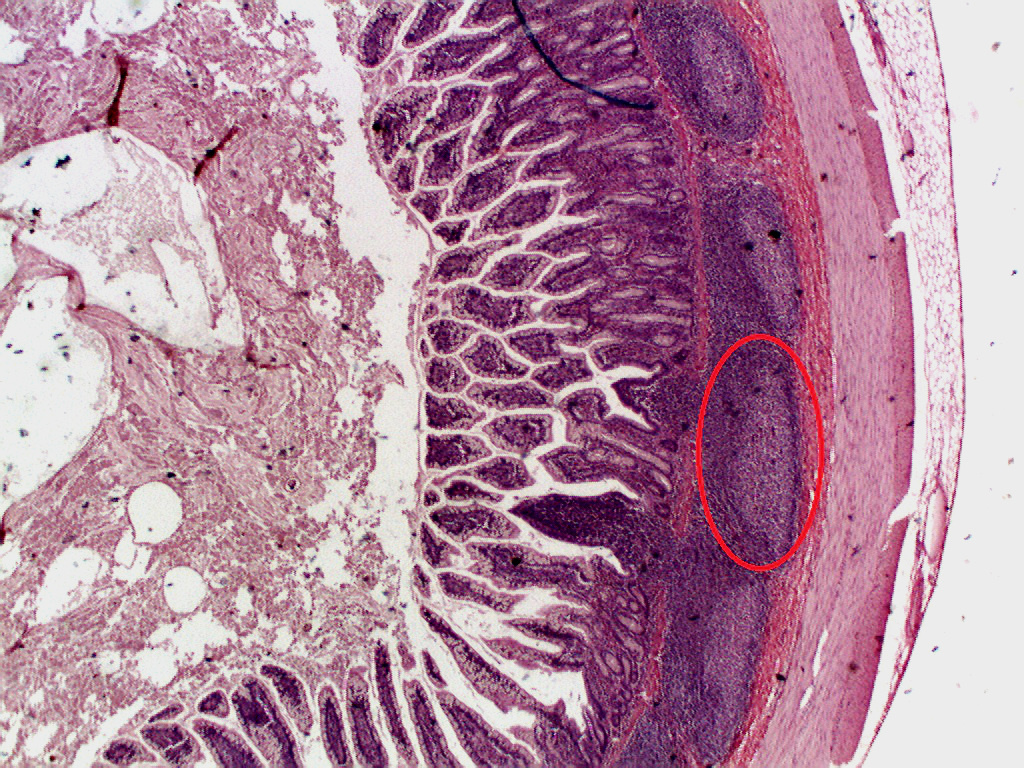
Peyer’s patches (aggregated lymphoid nodules)
Peyer’s patches (or aggregated lymphoid nodules) are organized lymphoid follicles, named after the 17th-century Swiss anatomist Johann Conrad Peyer. They are an important part of gut associated lymphoid tissue usually found in humans in the lowest portion of…
Perivitellin-2 (PV2) is a pore-forming toxin present in the egg perivitelline fluid of apple snails
Perivitellin-2 (PV2) is a pore-forming toxin present in the egg perivitelline fluid of the apple snails Pomacea maculata (PmPV2) and Pomacea canaliculata (PcPV2). This protein, called perivitellin, is massively accumulated in the eggs (~20 % total protein). As a toxin PV2 protects eggs…
Perivitellins are egg proteins found in the perivitelline fluid of many gastropods
Perivitellins are multifunctional complexes providing the developing embryo with nutrition, protection from the environment, and defense against predators. Despite the central role perivitellins play in reproduction and development, there is…
Scalarin carries and stabilizes carotenoid pigments
Scalarin (PsSC) is the most abundant perivitellin of the perivitelline fluid from Pomacea scalaris eggs. This glyco-lipo-caroteno protein is an approx. 380 kDa multimer combining multiple copies of six different 24-35 kDa subunits. As part of the petivitelline…
Pomacea maculata perivitellin-1 (PmPV1) is a glyco-lipo-caroteno protein
Pomacea maculata perivitellin-1 (PmPV1) is the most abundant perivitellin found in the perivitelline fluid from Pomacea maculata snail eggs. This glyco-lipo-caroteno protein is an approx. 294 kDa multimer of a combination of multiple copies of six different ~30…
Ovorubin
Ovorubin (PcOvo or PcPV1) is the most abundant perivitellin (>60 % total protein) of the perivitelline fluid from Pomacea canaliculata snail eggs. This glyco-lipo-caroteno protein complex is a approx. 300 kDa multimer of a combination of multiple copies of six different…
Clusterin (apolipoprotein J)
Clusterin (apolipoprotein J) is a 75-80 kDa disulfide-linked heterodimeric protein associated with the clearance of cellular debris and apoptosis. In humans, clusterin is encoded by the CLU gene on chromosome 8. CLU is a molecular chaperone responsible for aiding protein folding of secreted proteins, and…
The Membrane Attack Complex/Perforin (MACPF) superfamily aka MACPF/CDC superfamily
See also: Complement membrane attack complex The Membrane Attack Complex/Perforin (MACPF) superfamily, sometimes referred to as the MACPF/CDC superfamily, is named after a domain that is common to the membrane attack complex (MAC) proteins of the complement system (C6, C7,…
The membrane attack complex (MAC) or terminal complement complex (TCC) is a complex of proteins typically formed on the surface of pathogen cell membranes as a result of the activation of the host’s complement system, and as such is an effector of the immune system
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia See also: MACPF The membrane attack complex (MAC) or terminal complement complex (TCC) is a complex of proteins typically formed on the surface of pathogen cell membranes as a result of the activation…
Complement control protein are proteins that interact with components of the complement system
The complement system is tightly regulated by a network of proteins known as “regulators of complement activation (RCA)” that help distinguish target cells as “self” or “non-self.” A subset of this family…
Complement receptor type 2 (CR2)
Complement receptor type 2 (CR2), also known as complement C3d receptor, Epstein-Barr virus receptor, and CD21 (cluster of differentiation 21), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CR2 gene. CR2 is involved in the complement system.…
A complement receptor is a membrane-bound receptor belonging to the complement system, which is part of the innate immune system
Complement receptors bind effector protein fragments that are produced in response to antigen-antibody complexes or damage-associated molecules. Complement receptor activation contributes to the regulation of inflammation, leukocyte extravasation, and phagocytosis; it also contributes to the adaptive immune response. Different…