Ecdysis: Nature’s Grand Wardrobe Change
Darling, buckle up your exoskeletons because we’re about to sashay into the most FABULOUS biological runway show ever – it’s ECDYSIS, honey! 💃🐛✨ Picture this: You’re a gorgeous little arthropod, feeling a bit tight in your current outfit. But fear not! Mother Nature’
Cephalothorax aka prosoma
The cephalothorax, also called prosoma in some groups, is a tagma of various arthropods, comprising the head and the thorax fused together, as distinct from the abdomen behind.[1] (The terms prosoma and opisthosoma are equiva
Asynchronous Muscles
Asynchronous muscles are muscles in which there is no one-to-one relationship between electrical stimulation and mechanical contraction. These muscles are found in 75% of flying insects and have convergently evolved 7-10 times.[1] Unlike their synchronous counterparts t
Thorax (arthropod anatomy)
The thorax is the midsection (tagma) of the hexapod body (insects and entognathans). It holds the head, legs, wings and abdomen. It is also called mesosoma or cephalothorax in other arthropods. It is formed by the prothorax,&
Egg Case (mermaid’s Purse)
An egg case or egg capsule, often colloquially called a mermaid’s purse, is the casing that surrounds the eggs of oviparous chondrichthyans. Living chondricthyans that produce egg cases include some sharks, skates and chimaeras. Egg cases typically contain one embryo, except for b
Magical Mantis Mojo
Hold onto your ootheca, folks, because we’re about to dive deep into the wild world of Sang Piao Xiao! 🐛🥚🔬 Imagine you’re an ancient Chinese healer, strolling through a mulberry grove, when suddenly you spot a peculiar foam-like structure clinging to a branch. “Eureka!R
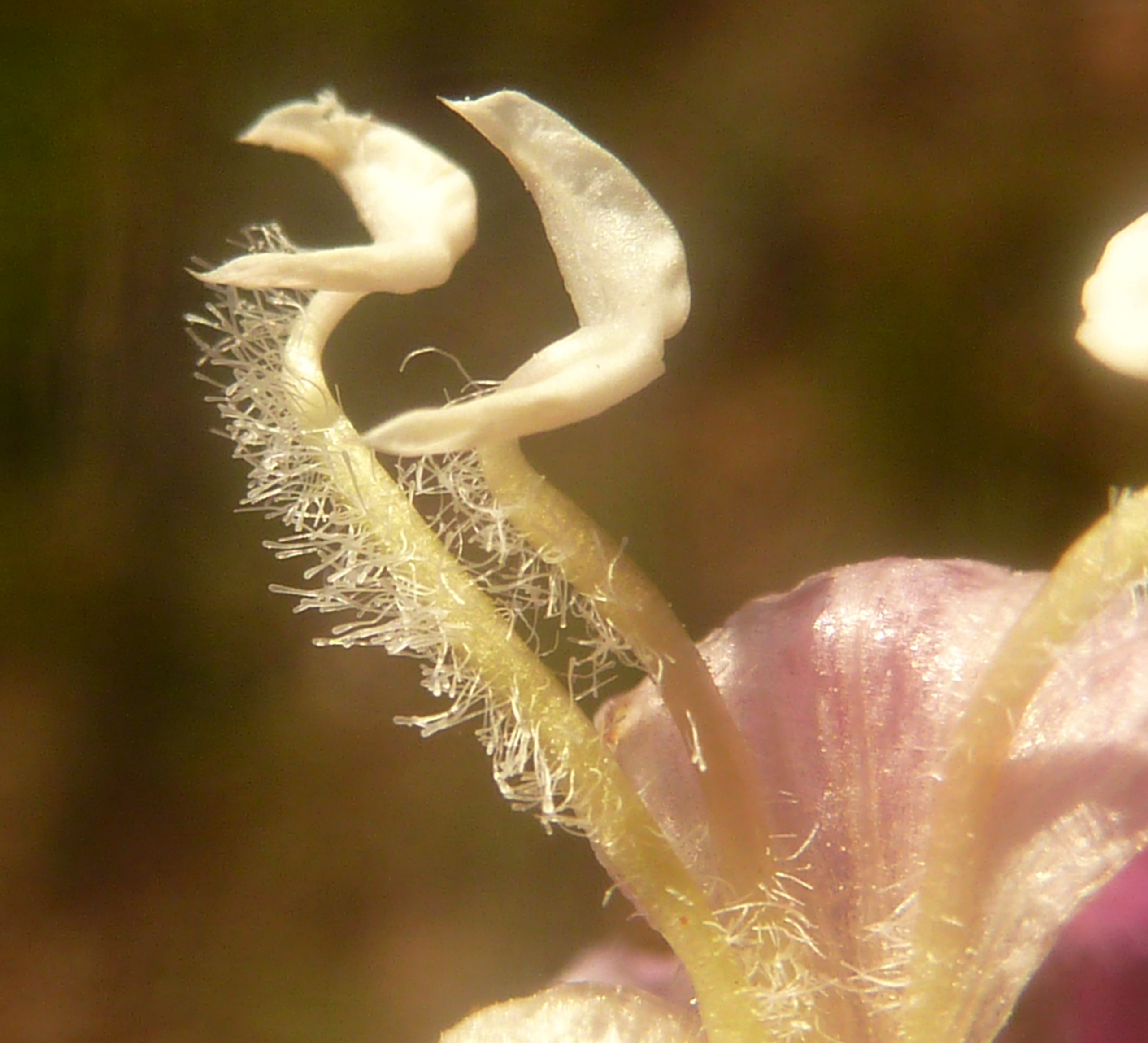
Ootheca
Buckle up, bug lovers, because we’re about to embark on a wild ride through the wacky world of oothecae! 🐛🥚🎢 Picture this: You’re a lady mantis, feeling frisky after a hot date (and maybe a little post-coital cannibalism, because why not?). But instead of popping out eggs willy-
Ascus (Mythology)
Ascus (Ancient Greek: Ἄσκος) was a giant from ancient Greek mythology, who in conjunction with Lycurgus of Thrace chained the god Dionysus and threw him into a river. The god Hermes (or, according to other tellings, Zeus) rescued Dionysus, conq
Ascus (bethesda System)
The Bethesda system (TBS), officially called The Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical Cytology, is a system for reporting cervical or vaginal cytologic diagnoses,[1] used for reporting Pap smear results. It was introduced in 1988[2] and revised in 1991,[3] 2001,[1][4][5] and 2014.[6]
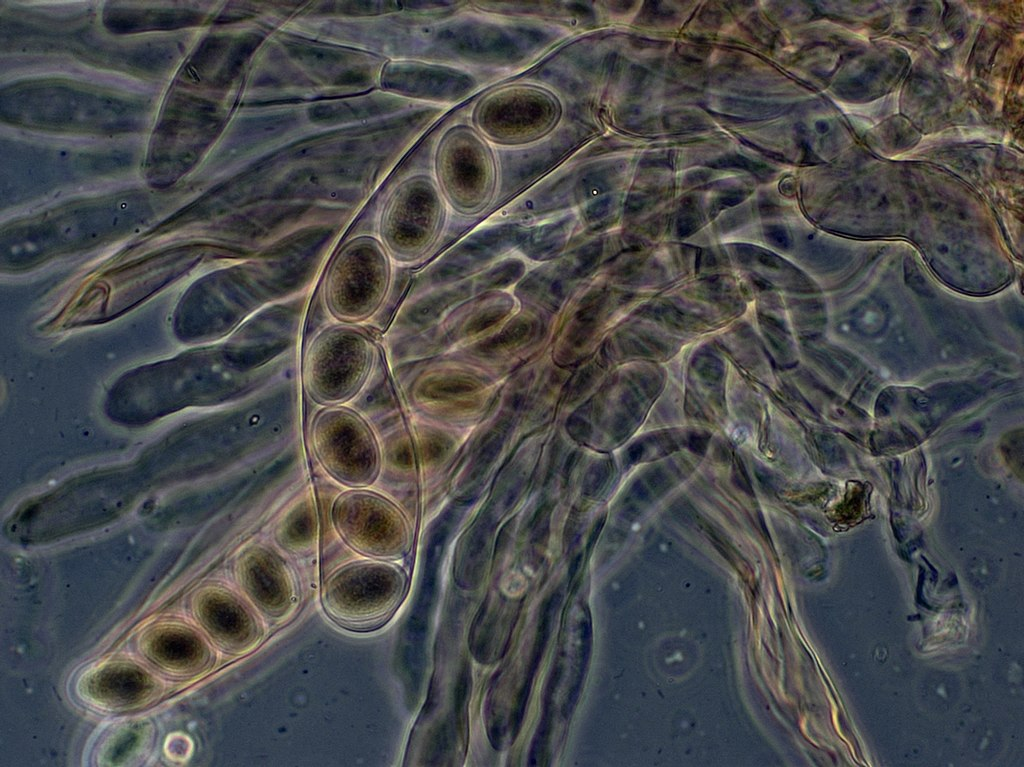
ASCUS (Formerly Theca)
This article is about the spore-bearing cell in fungi. For Atypical Squamous Cells of Undetermined Significance (ASCUS), see Bethesda system. For the Greek mythological giant, see Ascus (mythology). (pl. asci) a cell present in the fruiting body of ASCOMYCETE fungi in which the fusi
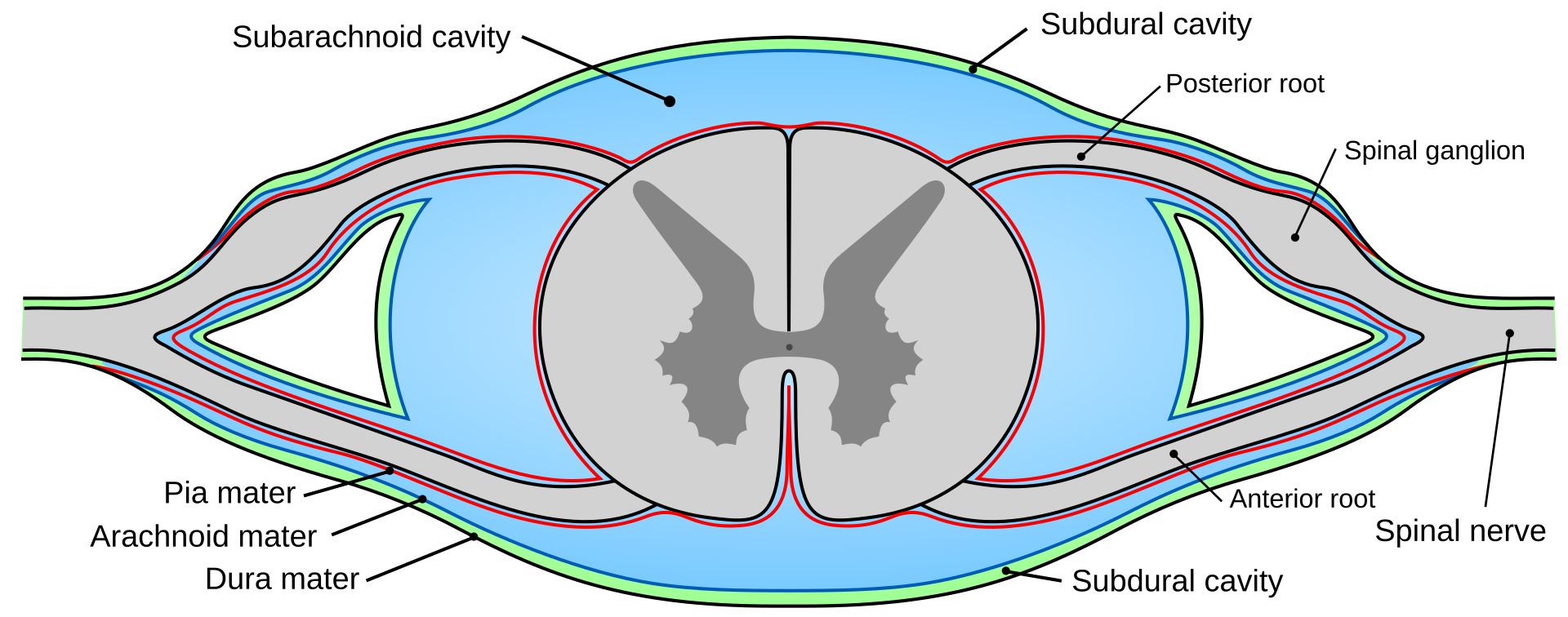
Thecal Sac or Dural Sac
The thecal sac or dural sac is the membranous sheath (theca) or tube of dura mater that surrounds the spinal cord and the cauda equina. The thecal sac contains the cerebrospinal fluid which provides nutrients and buoyancy to the spinal cord.[1] From the skull the tube adheres to bon
Relaxin
We’re about to dive into the wild world of Relaxin, the protein hormone that’s been turning heads since 1926 when Frederick Hisaw first stumbled upon it. This isn’t your average hormone – it’s a multitasking marvel that’s about to blow your mind! Researchers say t
Theca folliculi
The theca folliculi comprise a layer of the ovarian follicles. They appear as the follicles become secondary follicles. The theca are divided into two layers, the theca interna and the theca externa.[1] Theca cells are a group of endocrine cells in the ovary made u
Theca
In biology, a theca (pl.: thecae) is a sheath or a covering. Botany The typical anther is bilocular, i.e. it consists of two thecae. Each theca contains two microsporangia, also known as pollen sacs. The microsporangia produce the microspores, which for seed plants 
Xylotheque
A xylotheque or xylothek (from the Greek xylon for “wood” and theque meaning “repository”) is special form of herbarium that consists of a collection of authenticated wood specimens.[1] It is also known as a xylarium (from the Greek xylon for “wood”