Adrenal axis
-
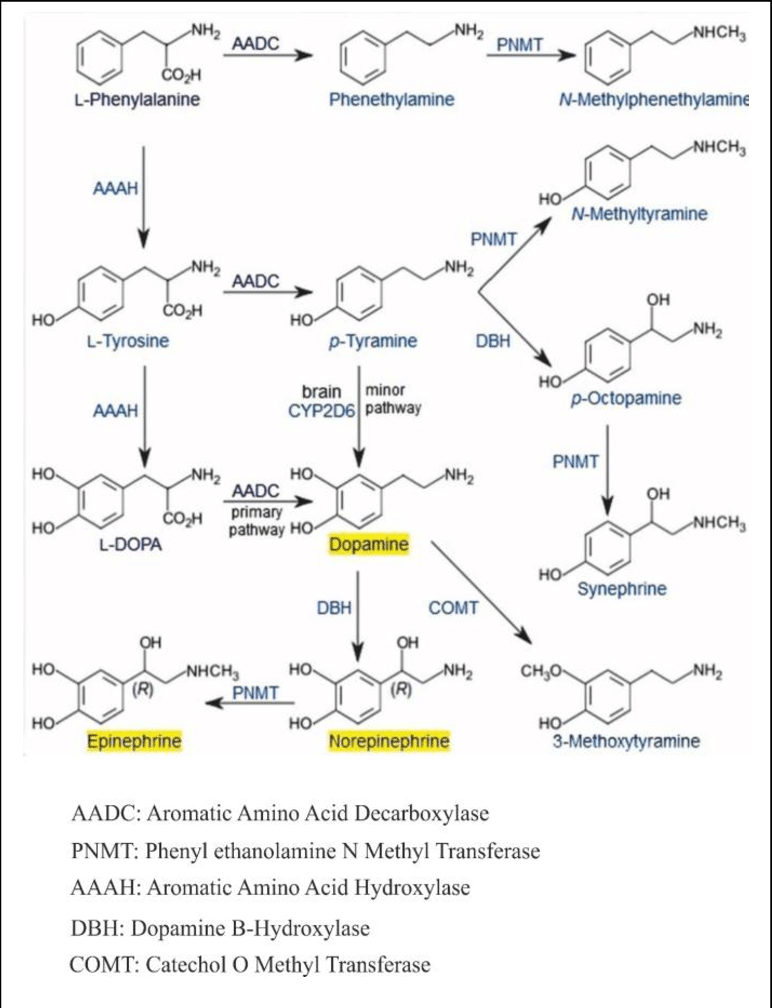
The adrenal medulla is the principal site of the conversion of the amino acid tyrosine into the catecholamines; epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine
The adrenal medulla (Latin: medulla glandulae suprarenalis) is part of the adrenal gland. It is located at the center of the gland, being surrounded by the adrenal cortex. It is the innermost part of the adrenal gland,… Read more.
-
Pulmonary neuroendocrine cells
Neuroendocrine cells are cells that receive neuronal input (through neurotransmitters released by nerve cells or neurosecretory cells) and, as a consequence of this input, release messenger molecules (hormones) into the blood. In this… Read more.
-
Chromaffin cells aka pheochromocytes
Chromaffin cells, also called pheochromocytes (or phaeochromocytes), are neuroendocrine cells found mostly in the medulla of the adrenal glands in mammals. These cells serve a variety of functions such as serving as a response to stress, monitoring carbon dioxide and… Read more.
-
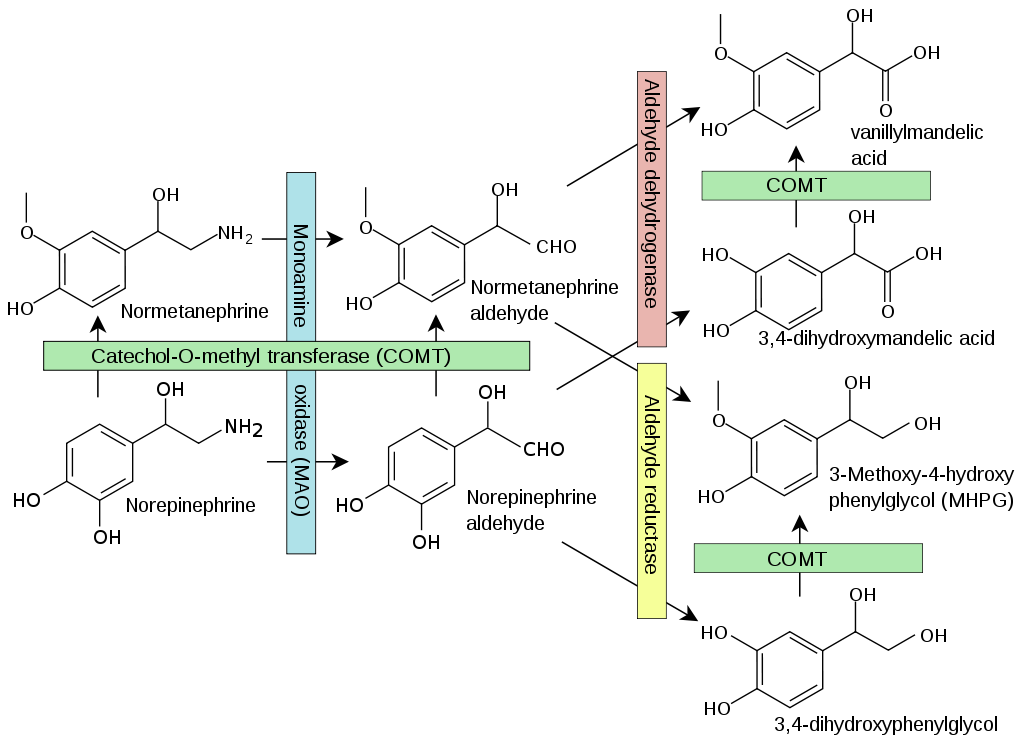
Catecholamine (CA)
A catecholamine (abbreviated CA) is a monoamine neurotransmitter, an organic compound that has a catechol (benzene with two hydroxyl side groups next to each other) and a side-chain amine. Fitzgerald, P. A. (2011). “Chapter 11. Adrenal Medulla and Paraganglia”. In Gardner, D. G.; Shoback,… Read more.
-
Neuromedin U
Neuromedin U (or NmU) is a neuropeptide found in the brain of humans and other mammals, which has a number of diverse functions including contraction of smooth muscle, regulation of blood pressure, pain perception,… Read more.
-
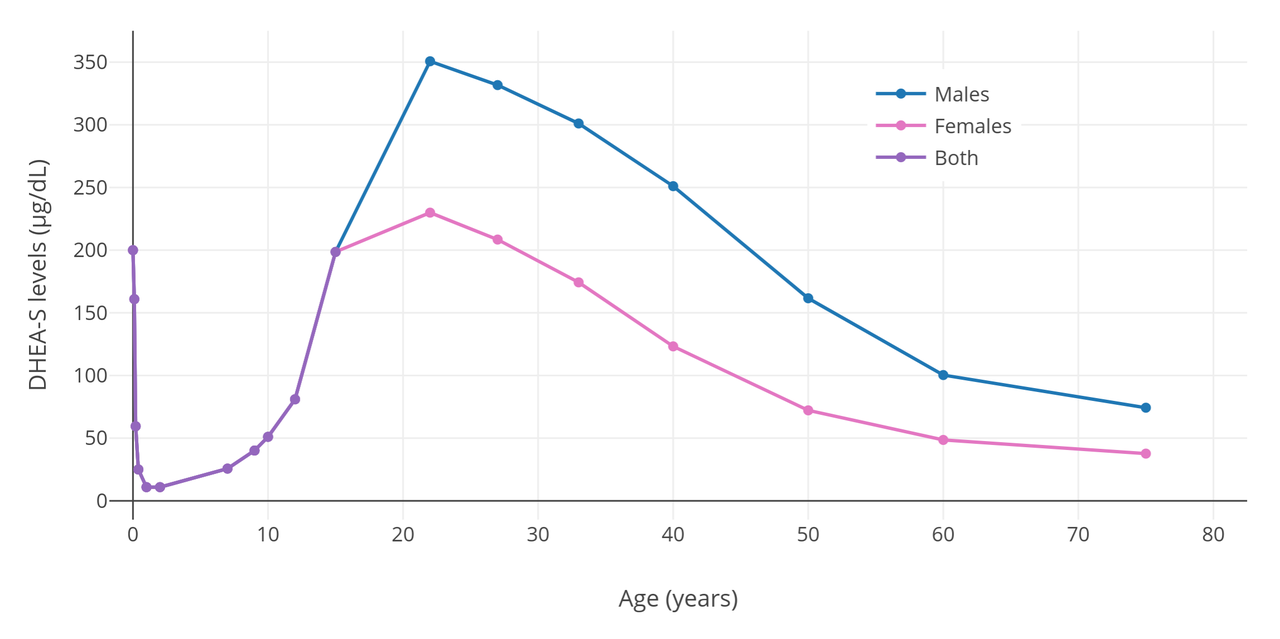
Adrenarche and Adrenopause
Adrenarche is an early stage in sexual maturation that happens in some higher primates and in humans, typically peaks at around 20 years of age, and is involved in the development of pubic hair, body odor, skin oiliness, axillary hair, sexual attraction/sexual desire/increased libido and… Read more.
-
Carbazochrome is an antihemorrhagic or hemostatic agent
Carbazochrome is an antihemorrhagic, or hemostatic, agent that will cease blood flow by causing the aggregation and adhesion of platelets in the blood to form a platelet plug, ceasing blood flow from an… Read more.
-
Adrenochrome
Adrenochrome is a chemical compound produced by the oxidation of adrenaline (epinephrine). It was the subject of limited research from the 1950s through to the 1970s as a potential cause of schizophrenia. While it has no current medical… Read more.
-
Medical uses of adrenaline
Main article: Epinephrine (medication) As a medication, it is used to treat several conditions, including allergic reaction anaphylaxis, cardiac arrest, and superficial bleeding. Inhaled adrenaline may be used to improve the symptoms of croup. It may… Read more.