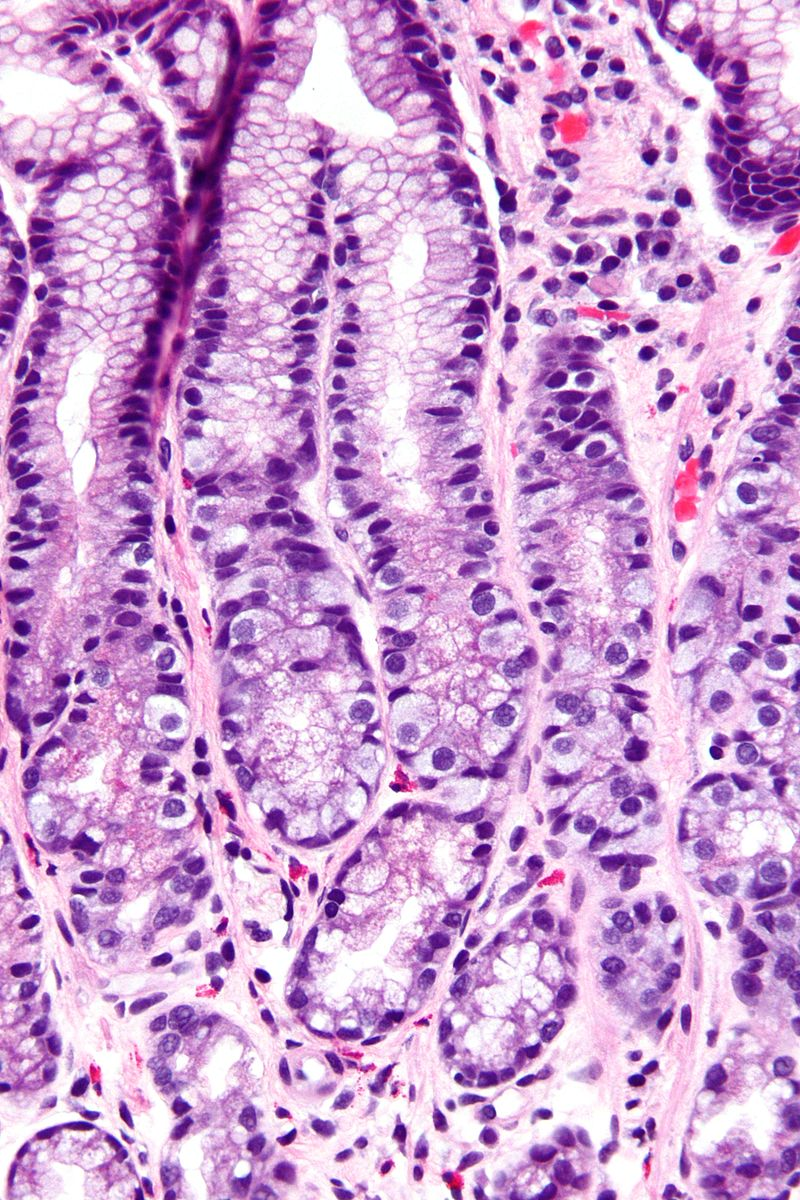
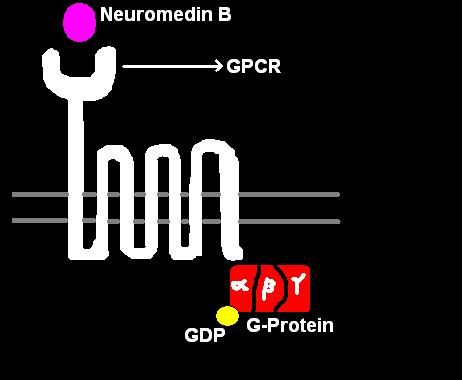
G cells or gastrin cells secrete gastrin. They works in conjunction with gastric chief cells and parietal cells. The peptide hormone bombesin also stimulates gastrin from G cells.
In anatomy, the G cell or gastrin cell, is a type of cell in the stomach and duodenum that secretes gastrin. It works in conjunction with gastric chief cells and parietal cells. G cells are found deep within…