🧬 What Is Beta-Glucuronidase?
Beta-glucuronidase (βG) is a lysosomal enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of glucuronides—meaning it breaks apart compounds that have been conjugated with glucuronic acid during Phase II liver detoxification. It is the undoer of the covenant—the enzyme that breaks the seal. Sources of Beta-Gl
Reactive arthritis aka Reiter’s syndrome
Reportedly triggered by everything from food poisoning to bug bites to STDs to hormones (estrogen, relaxin) Mnemonic: Can't See, Can't Pee, Can't Climb a Tree
The Yolk’s On Us: Unraveling the Secrets of Vitellogenesis
Hold onto your ovaries, folks! We’re about to dive into the wild world of Vitellogenesis – the cellular rave where eggs get their groove on! Picture this: You’re a lonely liver cell, minding your own business, when suddenly – BAM! – you’re hit with a tsunami of es
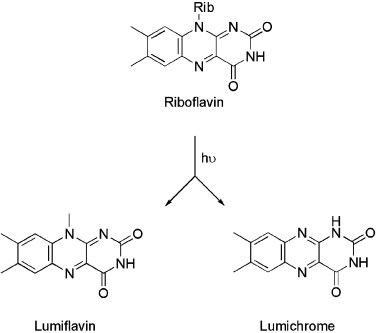
Riboflavin and its breakdown products interact with DNA, making this system attractive in the photodisinfection of blood and blood products
The application of photosensitisers to tropical pathogens in the blood supply Mark Wainwright PhD, Mauricio S. Baptista, in Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy, 2011 Riboflavin As vitamin B2, riboflavin (Fig. 5) is an essential nutrient in humans. The Mirasol system
Mycoestrogens are xenoestrogens produced by fungi. They are sometimes referred to as mycotoxins.
Among important mycoestrogens are zearalenone, zearalenol and zearalanol. Although all of these can be produced by various Fusarium species, zearalenol and zearalanol may also be produced endogenously in ruminants that have ingested zearalenone. Alpha-zearalanol is also produced semisynthetic
Metalloestrogens
Metalloestrogens are a class of inorganic xenoestrogens which can affect the gene expression of human cells responding to estrogen. Effects are related to the physiologic function of estrogen because metalloestrogens have shown affinity for estrogen receptors.