Category: Peptides
-
Neurotrophin-3 and Neurotrophin-4
Neurotrophin-4 (NT-4), also known as neurotrophin-5 (NT-5), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NTF4 gene. It is a neurotrophic factor that signals predominantly through the TrkB receptor tyrosine kinase. NT-4 was first discovered and isolated from xenopus and viper in the year 1991 by Finn Hallbook et.al Neurotrophin-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NTF3 gene. The protein encoded by this gene, NT-3, is a neurotrophic factor in the NGF (Nerve…
-
Nerve Growth Factor
Nerve growth factor (NGF) is a neurotrophic factor and neuropeptide primarily involved in the regulation of growth, maintenance, proliferation, and survival of certain target neurons. It is perhaps the prototypical growth factor, in that it was one of the first to be described. Since it was first isolated by Nobel Laureates Rita Levi-Montalcini and Stanley Cohen in 1956, numerous biological processes involving NGF have been identified,…
-
Evidence of the protective effect of smoking against thyroid cancer
Cigarette smoking and the risk of thyroid cancer. Kreiger N, Parkes R. Cigarette smoking and the risk of thyroid cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2000 Oct;36(15):1969-73. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(00)00198-2. PMID: 11000579. Thyroid cancer risk and smoking status: a meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control Cho YA, Kim J. Thyroid cancer risk and smoking status: a meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control.…
-

Three mechanisms predominate for beneficial effects of smoking: the ‘anti-estrogenic effect’ of smoking; alterations in prostaglandin production; and stimulation of nicotinic cholinergic receptors in the central nervous system
Beneficial effects of nicotine and cigarette smoking: the real, the possible and the spurious Baron JA. Beneficial effects of nicotine and cigarette smoking: the real, the possible and the spurious. Br Med Bull. 1996 Jan;52(1):58-73. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a011533. PMID: 8746297.
-
Reactive arthritis aka Reiter’s syndrome
Reportedly triggered by everything from food poisoning to bug bites to STDs to hormones (estrogen, relaxin) Mnemonic: Can't See, Can't Pee, Can't Climb a Tree
-
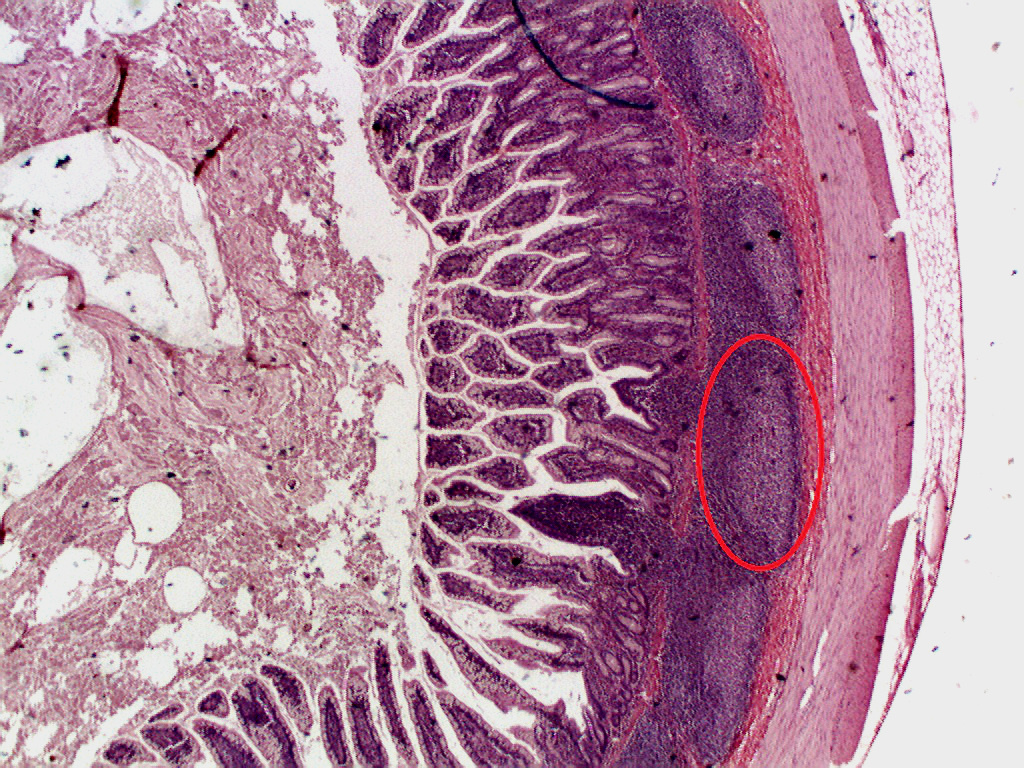
Peyer’s patches (aggregated lymphoid nodules)
Peyer’s patches (or aggregated lymphoid nodules) are organized lymphoid follicles, named after the 17th-century Swiss anatomist Johann Conrad Peyer. They are an important part of gut associated lymphoid tissue usually found in humans in the lowest portion of the small intestine, mainly in the distal jejunum and the ileum, but also could be detected in the duodenum. History Peyer’s patches had been observed and described by several anatomists…
-
Intrauterine Exposure to Paracetamol and Aniline Impairs Female Reproductive Development by Reducing Follicle Reserves and Fertility
Studies report that fetal exposure to paracetamol/acetaminophen by maternal consumption can interfere with male reproductive development. Moreover, recent biomonitoring data report widespread presence of paracetamol in German and Danish populations, suggesting exposure via secondary (nonpharmaceutical) sources, such as metabolic conversion from the ubiquitous industrial compound aniline. In this study, we investigated the extent to which…
-
Aniline, through its conversion into antiandrogenic paracetamol (acetaminophen, tylenol), impairs male reproductive development
Industrial use of aniline is increasing worldwide with production estimated to surpass 5.6 million metric tons in 2016. Exposure to aniline occurs via air, diet, and water augmenting the risk of exposing a large number of individuals. Early observations suggest that aniline is metabolized to paracetamol/acetaminophen, likely explaining the omnipresence of low concentrations of paracetamol…
-
Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) AKA the hepatic sinusoids
They form the lining of the smallest blood vessels in the liver
-
The conjugate (10S,11S) JH diol phosphate is the product of a two-step enzymatic process: conversion of JH to JH diol and then addition of a phosphate group to C10
The conjugate (10S,11S) JH diol phosphate is the product of a two-step enzymatic process: conversion of JH to JH diol and then addition of a phosphate group to C10. The enzyme responsible for the phosphorylation of JH diol is JH diol kinase (JHDK), which was first characterized from the Malpighian tubules of early fifth instars of M. sexta. The Malpighian tubule system is a type of excretory and osmoregulatory system found in…
-
Juvenile hormone (and Methoprene)
Juvenile hormones (JHs) are a group of acyclic sesquiterpenoids that regulate many aspects of insect physiology. The first discovery of a JH was by Vincent Wigglesworth. JHs regulate development, reproduction, diapause, and polyphenisms. The chemical formula for juvenile hormone is C18H30O3. In insects, JH (formerly neotenin) refers to a group of hormones, which ensure growth of the larva, while preventing metamorphosis. Because of their rigid exoskeleton, insects grow…
-
The Yolk’s On Us: Unraveling the Secrets of Vitellogenesis
Hold onto your ovaries, folks! We’re about to dive into the wild world of Vitellogenesis – the cellular rave where eggs get their groove on! Picture this: You’re a lonely liver cell, minding your own business, when suddenly – BAM! – you’re hit with a tsunami of estradiol. It’s like Mother Nature’s Red Bull, and…
-
The PVN Powerhouse: How the Paraventricular Nucleus Rules Hormone Secretion
Hold onto your hypothalamus, folks! We’re about to dive into the wild world of the Paraventricular Nucleus (PVN), where tiny cells pack a mighty hormonal punch! Picture this: deep in the brain’s control center, the hypothalamus, sits the PVN – a cluster of cells that’s like the body’s own hormone factory. But we’re not talking…
-
Vitellogenin is a precursor of egg yolk that transports protein and some lipid from the liver through the blood to the growing oocytes where it becomes part of the yolk. Normally, it is only found in the blood or hemolymph of females…
Vitellogenin (VTG or less popularly known as VG) (from Latin vitellus, yolk, and genero, I produce) is a precursor of egg yolk that transports protein and some lipid from the liver through the blood to the growing oocytes where it becomes part of the yolk. Normally, it is only found in the blood or hemolymph of females, and can therefore be…
-
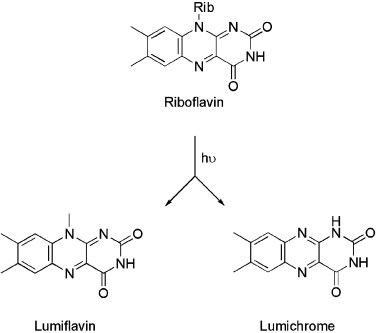
Riboflavin and its breakdown products interact with DNA, making this system attractive in the photodisinfection of blood and blood products
The application of photosensitisers to tropical pathogens in the blood supply Mark Wainwright PhD, Mauricio S. Baptista, in Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy, 2011 Riboflavin As vitamin B2, riboflavin (Fig. 5) is an essential nutrient in humans. The Mirasol system (Navigant Biotechnologies Inc., CO, USA) utilises riboflavin as a photosensitiser in conjunction with long-wave ultraviolet light [37]. Plainly given its essential nature, there are fewer potential toxicity problems…
Recent Posts
- 🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
- 🧂 Sodium Reduction and Sodium Replacement: A History of Reformulation and Exploding Diseases, Including Many Diseases Unheard of Before Deadly Sodium Policies
- 🧂 The DEADLY 1500 mg Sodium Recommendation predates the WHO’s formal global sodium reduction push by nearly a decade (and it’s even worse than that)
- 🧬 What Is Beta-Glucuronidase?
- When Sugar Was Salt: Crystalline Confusion and the Covenant of Sweetness
Tags
ADAM ASPARTAME Birds Blood Bones Brain Bugs Cancer Columba Cows crystallography Death Death cults Eggs Etymology Gastrin Gold Growth hormone History Hormones Insulin Liver Mere Perplexity Metal Monkey Business Mythology Paracetamol Plants Poison Pregnancy Protein Religion Reproduction Rocks Salt Slavery Snakes Sodium the birds and the bees Thiocyanate Tobacco Tylenol Underworld Venom zinc

