Cathepsin G
Cathepsin G plays an important role in eliminating intracellular pathogens and breaking down tissues at inflammatory sites, as well as in anti-inflammatory response
Acid phosphatase (systematic name phosphate-monoester phosphohydrolase (acid optimum)) is an enzyme that frees attached phosphoryl groups from other molecules during digestion
Acid phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.2, systematic name phosphate-monoester phosphohydrolase (acid optimum)) is an enzyme that frees attached phosphoryl groups from other molecules during digestion. It can be further classified as a phosphomonoesterase. It is stored in lysosomes and functions when these
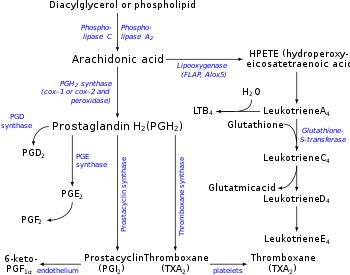
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1)
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1) or Prostaglandin E synthase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTGES gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a glutathione-dependent prostaglandin E synthase. The expression of this gene has been shown to be induced by proinfla
β-Glucuronidases
For α-glucuronidase, see alpha-glucuronidase. β-Glucuronidase β-Glucuronidase asymmetric unit showing active site residues Glu451, Tyr504, and Glu540, along with the potentially supporting Asn450 residue Identifiers Symbol GUSB NCBI gene 2990 HGNC 4696 OMIM 611499 RefSeq NM_000181 UniProt P0
Transferrins
Transferrins are not limited to only binding to iron but also to different metal ions.
Erepsin
Erepsin is a mixture of enzymes contained in a protein fraction found in the intestinal juices that digest peptones into amino acids. It is produced and secreted by the intestinal glands in the ileum and the pancreas, but it is al
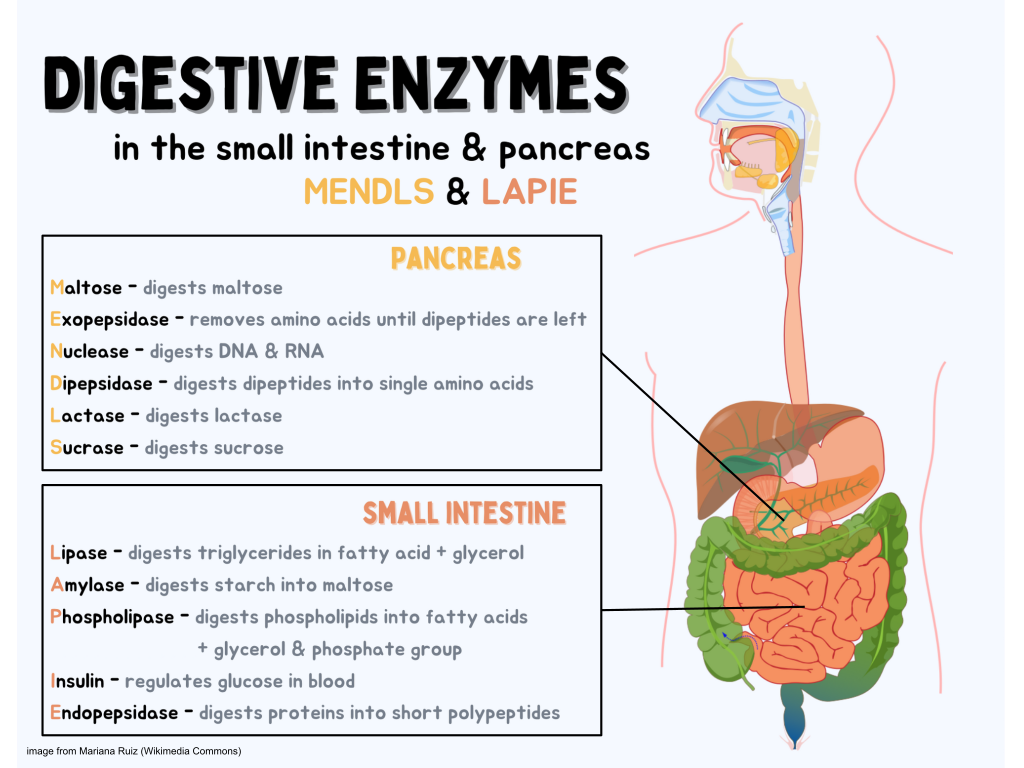
Digestive enzymes
Digestive enzymes are a group of enzymes that break down polymeric macromolecules into their smaller building blocks, in order to facilitate their absorption into the cells of the body. Digestive enzymes are found in the digestive tracts of animals (including humans) and in
Digestive enzymes
In carnivorous plants digestive enzymes and acids break down insects and in some plants small animals. In some plants the leaf collapses on the prey to increase contact, others have a small vessel of digestive liquid. Then digestion fluids are used to digest the prey to get at the needed nitra