The enzyme juvenile hormone esterase catalyzes the hydrolysis of juvenile hormone
The enzyme juvenile hormone esterase (EC 3.1.1.59, systematic name methyl-(2E,6E,10R)-10,11-epoxy-3,7,11-trimethyltrideca-2,6-dienoate acylhydrolase, JH esterase) catalyzes the hydrolysis of juvenile hormone: Nomenclature and function This enzyme belongs
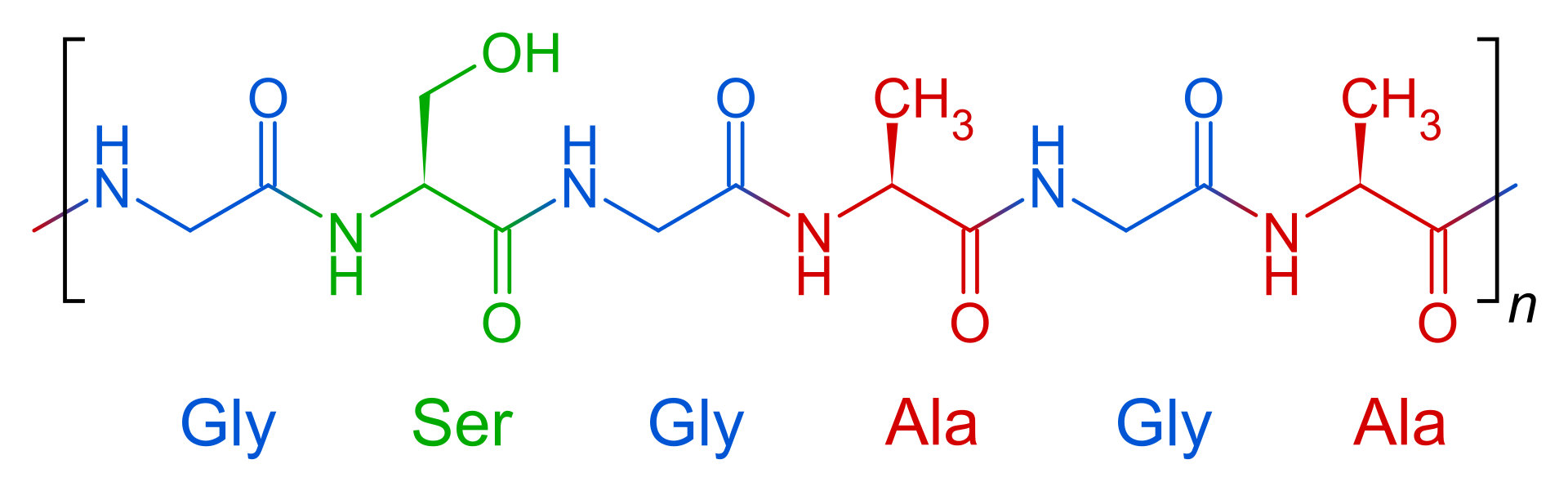
Fibroin is an insoluble protein present in silk produced by numerous insects
Fibroin is an insoluble protein present in silk produced by numerous insects, such as the larvae of Bombyx mori, and other moth genera such as Antheraea, Cricula, Samia and Gonometa. Silk in its raw state consists of two main proteins, seri
Sericin is a protein created by Bombyx mori (silkworms) in the production of silk
Silk is a fibre produced by the silkworm in production of its cocoon. It consists mainly of two proteins, fibroin and sericin. Silk consists of 70–80% fibroin and 20–30% sericin; fibroin being the structural center of the silk, and sericin being the gum coating the fibres and allo
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH+3 form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), a
Goldfinch in art
The bird that repeatedly, almost obsessively, turns up in Renaissance religious painting is the European Goldfinch Carduelis carduelis, almost always in the hands of the Infant Jesus, and symbolising variously the soul, resurrection, sacrifice and death, but with a particular further dimension of m