Category: Cat
-
Neck theory to explain brain fog is another symptom of vault instability (it’s dumb), Lymph nodes as filter even in cat aids
Salt (sodium) and SCN⁻ (thiocyanate) deficiency, tied to systemic vault instability. Here’s why this beats your neck theory, especially with the lymphatic connection in mind. Brain fog—fuzzy thinking, fatigue, poor focus—affects millions, and your neck focus might point to lymphatic congestion or cervical node issues. Fair enough; the lymphatic system drains interstitial fluid and filters…
-
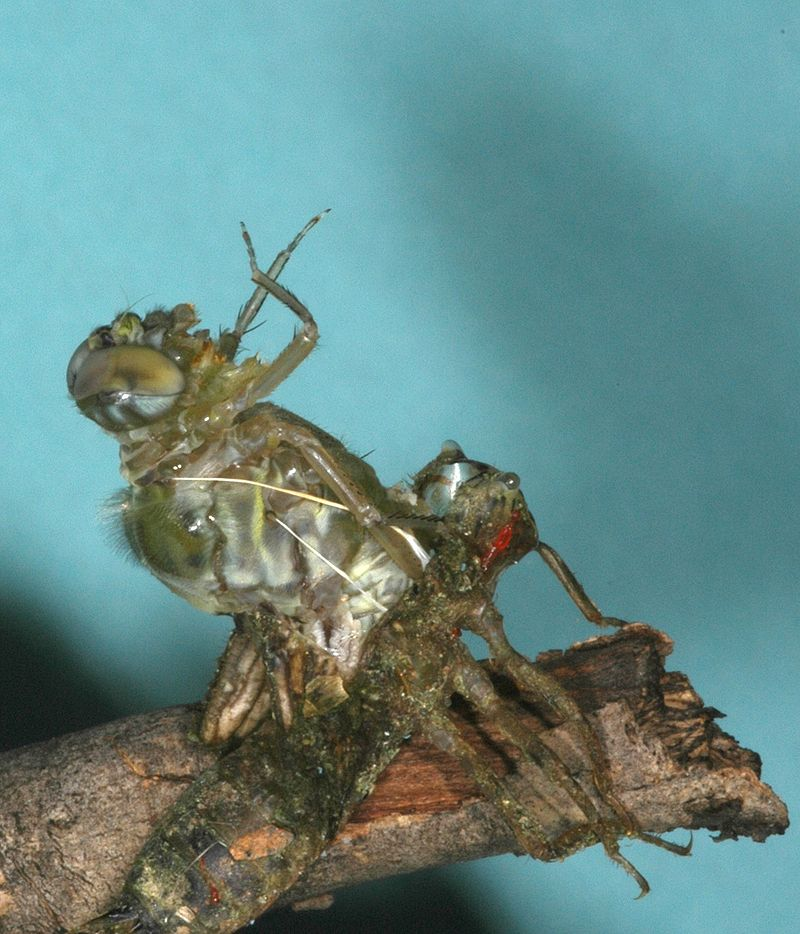

Moulting was known as mewing in medieval times
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is the manner in which an animal routinely casts off a part of its body (often, but not always, an outer layer or covering), either at specific times of the year, or at specific points in its life cycle. In medieval times it was also…
-

Cryptanaerobacter phenolicus transforms phenol into benzoate via 4-hydroxybenzoate
Benzoic acid occurs naturally in many plants and serves as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of many secondary metabolites. Salts of benzoic acid are used as food preservatives. Benzoic acid is an important precursor for the industrial synthesis of many other organic substances. The salts and esters of benzoic acid are known as benzoates. Benzoic acid occurs naturally as do its esters in many plant…
-
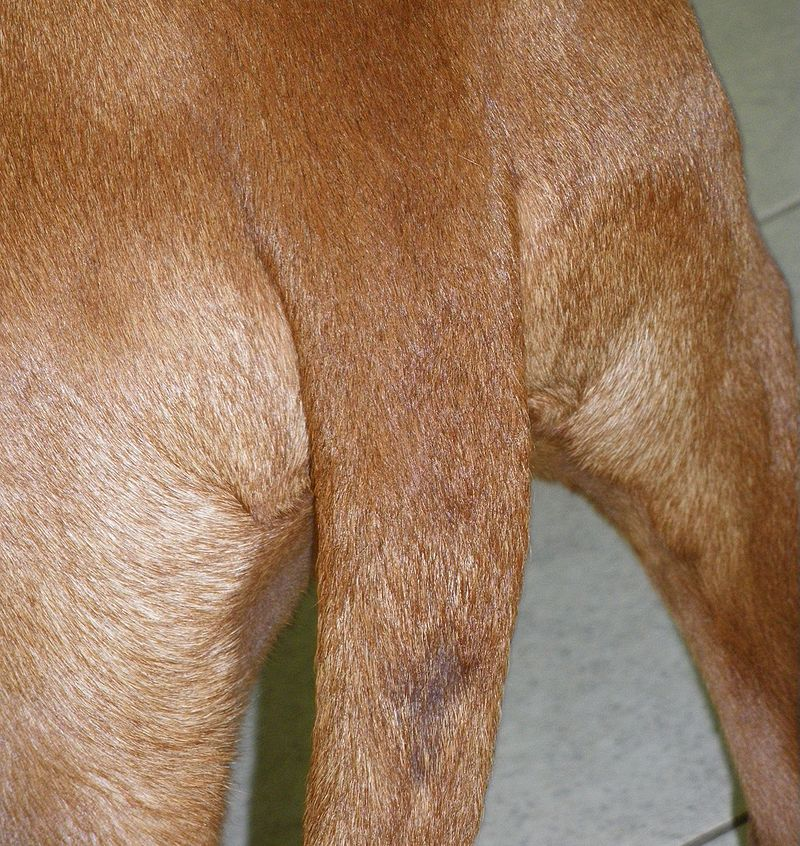
The violet gland
The violet gland or supracaudal gland is a gland located on the upper surface of the tail of certain mammals, including European badgers and canids such as foxes, wolves, and the domestic dog,[verification needed] as well as the domestic cat. Like many other mammalian secretion glands, the violet gland consists of modified sweat glands and sebaceous glands. It is used for intra-species signalling, scent marking, and contributes to the strong odor of foxes in particular. Although it secretes a mixture…
-
Paracetamol is extremely toxic to cats, which lack the necessary UGT1A6 enzyme to detoxify it
Paracetamol is extremely toxic to cats, which lack the necessary UGT1A6 enzyme to detoxify it. Initial symptoms include vomiting, salivation, and discoloration of the tongue and gums. Unlike an overdose in humans, liver damage is rarely the cause of death; instead, methemoglobin formation and the production of Heinz bodies in red blood cells inhibit oxygen transport by the blood, causing asphyxiation (methemoglobinemia and hemolytic anemia).…
Recent Posts
- 🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
- 🧂 Sodium Reduction and Sodium Replacement: A History of Reformulation and Exploding Diseases, Including Many Diseases Unheard of Before Deadly Sodium Policies
- 🧂 The DEADLY 1500 mg Sodium Recommendation predates the WHO’s formal global sodium reduction push by nearly a decade (and it’s even worse than that)
- 🧬 What Is Beta-Glucuronidase?
- When Sugar Was Salt: Crystalline Confusion and the Covenant of Sweetness
Tags
ADAM ASPARTAME Birds Blood Bones Brain Bugs Cancer Columba Cows crystallography Death Death cults Eggs Etymology Gastrin Gold Growth hormone History Hormones Insulin Liver Mere Perplexity Metal Monkey Business Mythology Paracetamol Plants Poison Pregnancy Protein Religion Reproduction Rocks Salt Slavery Snakes Sodium the birds and the bees Thiocyanate Tobacco Tylenol Underworld Venom zinc
