Category: CREATURES
-
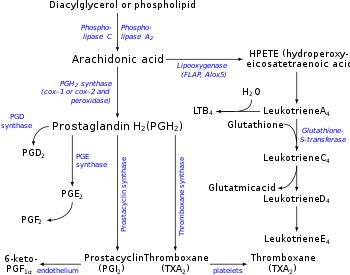
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1)
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1) or Prostaglandin E synthase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTGES gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a glutathione-dependent prostaglandin E synthase. The expression of this gene has been shown to be induced by proinflammatory cytokine interleukin 1 beta (IL1B). Its expression can also be induced by tumor suppressor protein TP53, and may be involved in…
-
Elastase
In molecular biology, elastase is an enzyme from the class of proteases (peptidases) that break down proteins. In particular, it is a serine protease. Forms and classification Eight human genes exist for elastase: Family Gene symbol Protein name EC number Approved Previous Approved Previous chymotrypsin-like CELA1 ELA1 chymotrypsin-like elastase family, member 1 elastase 1, pancreatic EC 3.4.21.36 CELA2A ELA2A chymotrypsin-like elastase family, member 2A elastase 2A, pancreatic EC 3.4.21.71 CELA2B…
-
β-Glucuronidases
For α-glucuronidase, see alpha-glucuronidase. β-Glucuronidase β-Glucuronidase asymmetric unit showing active site residues Glu451, Tyr504, and Glu540, along with the potentially supporting Asn450 residue Identifiers Symbol GUSB NCBI gene 2990 HGNC 4696 OMIM 611499 RefSeq NM_000181 UniProt P08236 Other data EC number 3.2.1.31 Locus Chr. 7 q11.21 β-Glucuronidases are members of the glycosidase family of enzymes that catalyze breakdown of complex carbohydrates. Human β-glucuronidase is…
-
Testican
Testican is a type of proteoglycan. Testican-1 is a highly conserved, multidomain proteoglycan that is most prominently expressed in the thalamus, and is upregulated in activated astroglial cells of the cerebrum. Several functions of this gene product have now been demonstrated in vitro including membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase inhibition, cathepsin L inhibition, and low-affinity calcium binding. The purified gene product has been shown to inhibit cell attachment…
-
Keratocan (KTN)
Keratocan (KTN) also known as keratan sulfate proteoglycan keratocan, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KERA gene. Keratan sulfate proteoglycans (KSPGs) are members of the small leucine-rich proteoglycan (SLRP) family. KSPGs, particularly keratocan, lumican and mimecan, are important to the transparency of the cornea. Mutations of the gene cause cornea plana 2. Cornea plana 2(CNA2) causes the cornea to flatten and the angle between the sclera and cornea to shrink. This…
-
Lumican aka LUM
Lumican, also known as LUM, is an extracellular matrix protein that, in humans, is encoded by the LUM gene on chromosome 12. Structure Lumican is a proteoglycan Class II member of the small leucine-rich proteoglycan (SLRP) family that includes decorin, biglycan, fibromodulin, keratocan, epiphycan, and osteoglycin. Like the other SLRPs, lumican has a molecular weight of about 40 kilodaltons and has four major intramolecular domains: There are four N-linked sites within…
-
Keratan sulfate (KS) aka keratosulfate
Not to be confused with Keratin. Keratan sulfate (KS), also called keratosulfate, is any of several sulfated glycosaminoglycans (structural carbohydrates) that have been found especially in the cornea, cartilage, and bone. It is also synthesized in the central nervous system where it participates both in development and in the glial scar formation following an injury. Keratan sulfates are large, highly hydrated molecules which in joints can act as a cushion to…
-
Microfold cells (or M cells)
Microfold cells (or M cells) are found in the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) of the Peyer’s patches in the small intestine, and in the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) of other parts of the gastrointestinal tract. These cells are known to initiate mucosal immunity responses on the apical membrane of the M cells and allow for transport of microbes and particles across the epithelial cell layer from the gut lumen to the lamina…
-
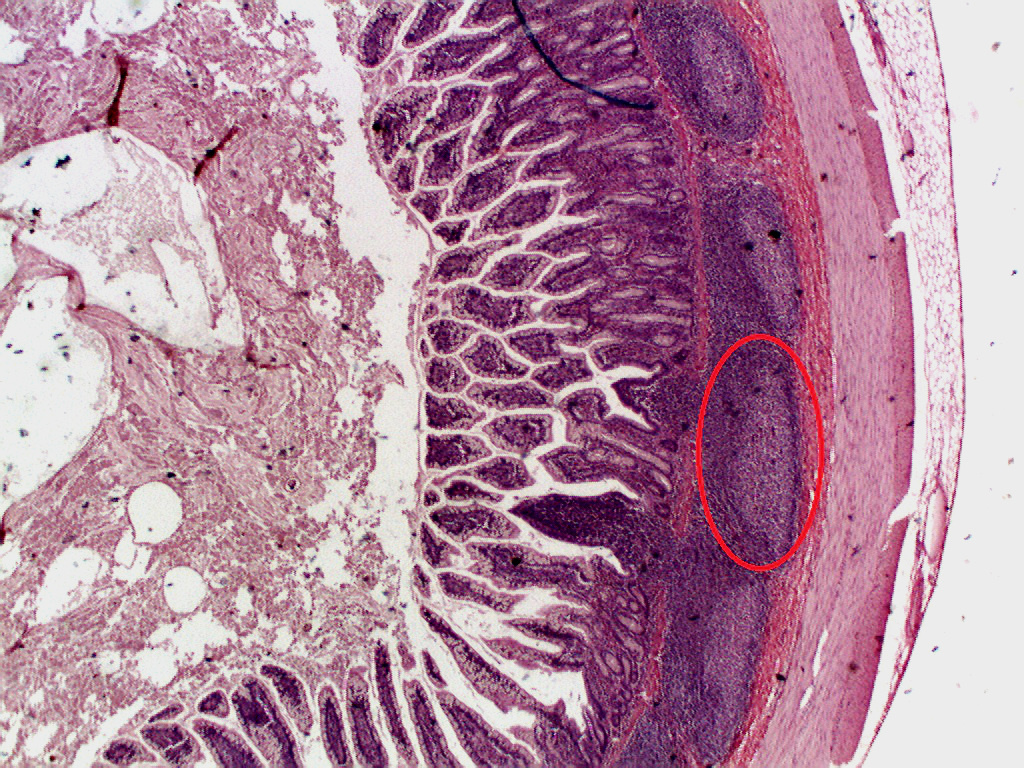
Peyer’s patches (aggregated lymphoid nodules)
Peyer’s patches (or aggregated lymphoid nodules) are organized lymphoid follicles, named after the 17th-century Swiss anatomist Johann Conrad Peyer. They are an important part of gut associated lymphoid tissue usually found in humans in the lowest portion of the small intestine, mainly in the distal jejunum and the ileum, but also could be detected in the duodenum. History Peyer’s patches had been observed and described by several anatomists…
-
Perivitellin-2 (PV2) is a pore-forming toxin present in the egg perivitelline fluid of apple snails
Perivitellin-2 (PV2) is a pore-forming toxin present in the egg perivitelline fluid of the apple snails Pomacea maculata (PmPV2) and Pomacea canaliculata (PcPV2). This protein, called perivitellin, is massively accumulated in the eggs (~20 % total protein). As a toxin PV2 protects eggs from predators, but it also nourishes the developing snail embryos. Structure and stability These ~172-kDa proteins are dimers of AB toxins, each composed of a carbohydrate-binding…
-
Perivitellins are egg proteins found in the perivitelline fluid of many gastropods
Perivitellins are multifunctional complexes providing the developing embryo with nutrition, protection from the environment, and defense against predators. Despite the central role perivitellins play in reproduction and development, there is little information about their role in gastropod Molluscs. Most studies of perivitellins have been performed in eggs of Ampullaridae, a family of freshwater snails (Caenogastropoda), notably the Pomacea genus, mostly…
-
Scalarin carries and stabilizes carotenoid pigments
Scalarin (PsSC) is the most abundant perivitellin of the perivitelline fluid from Pomacea scalaris eggs. This glyco-lipo-caroteno protein is an approx. 380 kDa multimer combining multiple copies of six different 24-35 kDa subunits. As part of the petivitelline fluid, PsSC is probably playing a role as a nutrient source for the developing embryo in Pomacea scalaris eggs. As its orthologous ovorubin and PmPV1, this protein carries and stabilizes carotenoid pigments. As…
-
Pomacea maculata perivitellin-1 (PmPV1) is a glyco-lipo-caroteno protein
Pomacea maculata perivitellin-1 (PmPV1) is the most abundant perivitellin found in the perivitelline fluid from Pomacea maculata snail eggs. This glyco-lipo-caroteno protein is an approx. 294 kDa multimer of a combination of multiple copies of six different ~30 kDa subunits. PmPV1 account >60% of the total proteins found in the Pomacea maculata eggs. PmPV1 is an orthologous of ovorubin and scalarin, sharing most of the structural features with the former protein…
-
Ovorubin
Ovorubin (PcOvo or PcPV1) is the most abundant perivitellin (>60 % total protein) of the perivitelline fluid from Pomacea canaliculata snail eggs. This glyco-lipo-caroteno protein complex is a approx. 300 kDa multimer of a combination of multiple copies of six different ~30 kDa subunits. Together with the other perivitellins from Pomacea canaliculata eggs, ovorubin serves a nutrient source for developing embryos, notably to the intermediate and late stages. Moreover, after hatching,…
-
Clusterin (apolipoprotein J)
Clusterin (apolipoprotein J) is a 75-80 kDa disulfide-linked heterodimeric protein associated with the clearance of cellular debris and apoptosis. In humans, clusterin is encoded by the CLU gene on chromosome 8. CLU is a molecular chaperone responsible for aiding protein folding of secreted proteins, and its three isoforms have been differentially implicated in pro- or antiapoptotic processes. Through this function, CLU is involved in many diseases related to oxidative stress, including neurodegenerative diseases, cancers, inflammatory diseases, and aging. Structure The CLU gene contains…
-
The Membrane Attack Complex/Perforin (MACPF) superfamily aka MACPF/CDC superfamily
See also: Complement membrane attack complex The Membrane Attack Complex/Perforin (MACPF) superfamily, sometimes referred to as the MACPF/CDC superfamily, is named after a domain that is common to the membrane attack complex (MAC) proteins of the complement system (C6, C7, C8α, C8β and C9) and perforin (PF). Members of this protein family are pore-forming toxins (PFTs). In eukaryotes, MACPF proteins play a role in immunity and development. Archetypal members of the family…
Recent Posts
- 🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
- 🧂 Sodium Reduction and Sodium Replacement: A History of Reformulation and Exploding Diseases, Including Many Diseases Unheard of Before Deadly Sodium Policies
- 🧂 The DEADLY 1500 mg Sodium Recommendation predates the WHO’s formal global sodium reduction push by nearly a decade (and it’s even worse than that)
- 🧬 What Is Beta-Glucuronidase?
- When Sugar Was Salt: Crystalline Confusion and the Covenant of Sweetness
Tags
ADAM ASPARTAME Birds Blood Bones Brain Bugs Cancer Columba Cows crystallography Death Death cults Eggs Etymology Gastrin Gold Growth hormone History Hormones Insulin Liver Mere Perplexity Metal Monkey Business Mythology Paracetamol Plants Poison Pregnancy Protein Religion Reproduction Rocks Salt Slavery Snakes Sodium the birds and the bees Thiocyanate Tobacco Tylenol Underworld Venom zinc
