Category: Bad Food
-

Institut für Sexualwissenschaft
The Institut für Sexualwissenschaft was an early private sexology research institute in Germany from 1919 to 1933. The name is variously translated as Institute of Sex Research, Institute of Sexology, Institute for Sexology or Institute for the Science of Sexuality. The Institute was a non-profit foundation situated in Tiergarten, Berlin. It was the first sexology research center in the world. The Institute was headed by Magnus Hirschfeld, who since 1897 had run…
-
Experts warn of fatty liver disease ‘epidemic’ in young people
In Bristol University‘s study Children of the 90s, 2.5% of 4,000 people born in 1991 and 1992 were found by ultrasound scanning at the age of 18 to have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; five years later transient elastography (fibroscan) found over 20% to have the fatty deposits on the liver of steatosis, indicating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; half of those…
-

Aetokthonotoxin (AETX) aka ‘eagle toxin’ discovered in 2021
Aetokthonotoxin (AETX), colloquially ‘eagle toxin’, was discovered in 2021 as the cyanobacterial neurotoxin causing vacuolar myelinopathy (VM) in eagles in North America. Avian vacuolar myelinopathy (AVM) is a fatal neurological disease that affects various waterbirds and raptors. It is most common in the bald eagle and American coot, and it is known in the killdeer, bufflehead, northern shoveler, American wigeon, Canada goose, great horned owl, mallard, and ring-necked duck. Avian vacuolar myelinopathy is a newly discovered disease that…
-
β-Methylamino-L-alanine, or BMAA
β-Methylamino-L-alanine, or BMAA, is a non-proteinogenic amino acid produced by cyanobacteria. BMAA is a neurotoxin and its potential role in various neurodegenerative disorders is the subject of scientific research. Structure and properties BMAA is a derivative of the amino acid alanine with a methylamino group on the side chain. This non-proteinogenic amino acid is classified as a polar base. Sources and detection BMAA is produced by cyanobacteria in marine, freshwater, and terrestrial environments. In…
-
Lytico-bodig disease, Guam disease, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-parkinsonism-dementia (ALS-PDC) is a neurodegenerative disease or all of them
Lytico-bodig (also Lytigo-bodig) disease, Guam disease, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-parkinsonism-dementia (ALS-PDC) is a neurodegenerative disease of uncertain etiology endemic to the Chamorro people of the island of Guam in Micronesia. Lytigo and bodig are Chamorro language words for two different manifestations of the same condition. ALS-PDC, a term coined by Asao Hirano and colleagues in 1961, reflects its resemblance to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease. First reports of the disease surfaced in three death certificates on Guam in 1904 which made…
-

The Amazonian legend of Maní is related to the cult of Manioc, the native staple food that sprang from her grave
Maní, a Tupí myth of origins, is the name of an indigenous girl with very fair complexion. The Amazonian legend of Maní is related to the cult of Manioc, the native staple food that sprang from her grave. The legend The daughter of a Tupí chief became pregnant. Her father wanted to take revenge on the man who brought shame to…
-
Cassava (tapioca) chips have become a major source of ethanol production
In many countries, significant research has begun to evaluate the use of cassava as an ethanol biofuel feedstock. Under the Development Plan for Renewable Energy in the Eleventh Five-Year Plan in the People’s Republic of China, the target was to increase the production of ethanol fuel from nongrain feedstock to 2 million metric tons (2,000,000 long tons; 2,200,000 short tons), and…
-
Cassava is used in a number of commercially available laundry products
Cassava is also used in a number of commercially available laundry products, especially as starch for shirts and other garments. Using cassava starch diluted in water and spraying it over fabrics before ironing helps stiffen collars.
-
Malnutrition may play a role in Tropical ataxic neuropathy (TAN) aka Strachan-Scott Syndrome and prisoners of war neuropathy
Tropical ataxic neuropathy (TAN, also known as Strachan-Scott Syndrome and prisoners of war neuropathy) is a disease or category of diseases that commonly causes disability and increases mortality. The causes of TAN are not understood; there is no generally accepted treatment, and the reported outcomes are inconsistent. The disease affects poor tropical populations; there are no good statistics on how…
-
Cause and Prevention of Konzo
The character of the neurological injury is not clear. The disease onset is associated with high intake of cyanide from a diet of mostly bitter cassava, which is low in protein, particularly sulfur amino acids. These are essential for the detoxification in the body of cyanide to thiocyanate, which is removed in the urine. A…
-
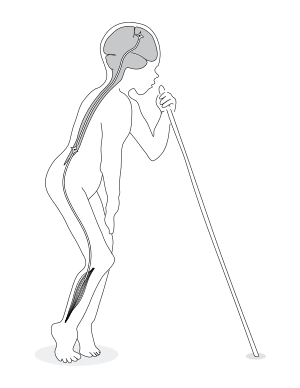
Signs and symptoms of Konzo
The onset of paralysis (spastic paraparesis) is sudden and symmetrical and affects the legs more than the arms. The resulting disability is permanent but does not progress. Typically, a patient is standing and walking on the balls of the feet with rigid legs and often with ankle clonus. Initially, most patients experience generalized weakness during the first…
-
Differential diagnoses for Konzo are lathyrism and paraparesis apparently caused by geographical location or bad genes…go figure
The clinical symptoms are strikingly similar to those of lathyrism and also similar to tropical spastic paraparesis and hereditary spastic paraparesis, only that the latter two disorders have a slow onset. Konzo is distinct from polio which is a flaccid paralysis and most often affects a person asymmetrically.[citation needed] Konzo is one of several tropical neuropathies. A distinct myeloneuropathy also associated to cyanogen intake from cassava is tropical ataxic…
-

Konzo is an epidemic paralytic disease reportedly from simultaneous malnutrition and high dietary cyanide intake
Konzo is an epidemic paralytic disease occurring among hunger-stricken rural populations in Africa where a diet dominated by insufficiently processed cassava results in simultaneous malnutrition and high dietary cyanide intake. Konzo was first described by Giovanni Trolli in 1938 who compiled the observations from eight doctors working in the Kwango area of the Belgian Congo (now Democratic Republic of the Congo). “Konzo” means “tied legs” in…
-
Carbazochrome is an antihemorrhagic or hemostatic agent
Carbazochrome is an antihemorrhagic, or hemostatic, agent that will cease blood flow by causing the aggregation and adhesion of platelets in the blood to form a platelet plug, ceasing blood flow from an open wound. It is hoped that this drug can be used in the future for preventing excessive blood flow during surgical operations and the treatment…
-
CBP has intrinsic acetyltransferase functions
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate Response Element Binding protein Binding Protein (CREB-binding protein), also known as CREBBP or CBP or KAT3A, is a coactivator encoded by the CREBBP gene in humans, located on chromosome 16p13.3. CBP has intrinsic acetyltransferase functions; it is able to add acetyl groups to both transcription factors as well as histone lysines, the latter of which has been shown to alter chromatin structure making genes more accessible for transcription. This relatively…
-

Ira Remsen (1846 – 1927) discovered artificial sweetener saccharin along with Constantin Fahlberg
Ira Remsen was an American chemist who discovered the artificial sweetener saccharin along with Constantin Fahlberg. He was the second president of Johns Hopkins University. Early life Ira Remsen was born in New York City on February 10, 1846. He is the son of James Vanderbelt Remsen (1818–1892) and Rosanna Secor (1823–1856). He married Elisabeth Hilleard Mallory on Apr 3, 1875, in New York…
Recent Posts
- 🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
- 🧂 Sodium Reduction and Sodium Replacement: A History of Reformulation and Exploding Diseases, Including Many Diseases Unheard of Before Deadly Sodium Policies
- 🧂 The DEADLY 1500 mg Sodium Recommendation predates the WHO’s formal global sodium reduction push by nearly a decade (and it’s even worse than that)
- 🧬 What Is Beta-Glucuronidase?
- When Sugar Was Salt: Crystalline Confusion and the Covenant of Sweetness
Tags
ADAM ASPARTAME Birds Blood Bones Brain Bugs Cancer Columba Cows crystallography Death Death cults Eggs Etymology Gastrin Gold Growth hormone History Hormones Insulin Liver Mere Perplexity Metal Monkey Business Mythology Paracetamol Plants Poison Pregnancy Protein Religion Reproduction Rocks Salt Slavery Snakes Sodium the birds and the bees Thiocyanate Tobacco Tylenol Underworld Venom zinc
