Category: Complement
-
The NACHT domain consists of seven distinct conserved motifs, including the ATP/GTPase specific P-loop, the Mg2+-binding site (Walker A and B motifs, respectively) and five more specific motifs
The NACHT domain is an evolutionarily conserved protein domain. This NTPase domain is found in apoptosis proteins as well as those involved in MHC transcription. Its name reflects some of the proteins that contain it: NAIP (NLP family apoptosis inhibitor protein), CIITA (that is, C2TA or MHC class II transcription activator), HET-E (incompatibility locus protein from Podospora anserina) and TEP1 (that is, TP1 or telomerase-associated protein). The NACHT domain contains 300 to 400 amino acids. It is…
-
TRALI or ARDS: A Medical Game of “Who’s Who?”
Welcome to the thrilling world of post-transfusion respiratory distress, where distinguishing TRALI from ARDS is like trying to tell apart identical twins wearing the same outfit. Strap in, folks – it’s time for a wild ride through the land of bilateral infiltrates and hypoxemia! First things first: TRALI, or Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury, is the…
-
Osteopontin (OPN)
Osteopontin (OPN), also known as bone /sialoprotein I (BSP-1 or BNSP), early T-lymphocyte activation (ETA-1), secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1), 2ar and Rickettsia resistance (Ric), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPP1 gene (secreted phosphoprotein 1). The murine ortholog is Spp1. Osteopontin is a SIBLING (glycoprotein) that was first identified in 1986 in osteoblasts. The family of non-collagenous proteins known as SIBLING proteins, standing for small integrin-binding ligand, N-linked glycoprotein, are components of the extracellular matrix of bone and dentin. Evidence shows that these proteins play key…
-
Agrin is a large chimeric proteoglycan, a heparan sulfate and chondroitin proteoglycan, whose best-characterised role is in the development of the neuromuscular junction during embryogenesis
Agrin was originally found in the electric organ of Tarpedo california and in the basal lamina at the neuromuscular junction as a protein that directs the aggregation of acetylcholine receptors (AChR) and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) at synaptic sites. Tetronarce californica also known as the Pacific electric ray is a species of electric ray in the family Torpedinidae, endemic to the coastal waters of the northeastern Pacific Ocean from Baja California to British Columbia. It generally inhabits sandy flats, rocky reefs, and kelp forests from the surface…
-
Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) AKA the hepatic sinusoids
They form the lining of the smallest blood vessels in the liver
-
Juvenile hormone epoxide hydrolase (JHEH) is an enzyme that inactivates insect juvenile hormones
Juvenile hormone epoxide hydrolase (JHEH) is an enzyme that inactivates insect juvenile hormones. This inactivation is accomplished through hydrolysis of the epoxide functional group contained within these hormones into diols. JHEH is one of two enzymes involved in the termination of signaling properties of the various juvenile hormones. The other is juvenile-hormone esterase, or JHE. The first observation of activity from JHEH was in Rhodnius…
-
The conjugate (10S,11S) JH diol phosphate is the product of a two-step enzymatic process: conversion of JH to JH diol and then addition of a phosphate group to C10
The conjugate (10S,11S) JH diol phosphate is the product of a two-step enzymatic process: conversion of JH to JH diol and then addition of a phosphate group to C10. The enzyme responsible for the phosphorylation of JH diol is JH diol kinase (JHDK), which was first characterized from the Malpighian tubules of early fifth instars of M. sexta. The Malpighian tubule system is a type of excretory and osmoregulatory system found in…
-
Ku70
Ku70 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the XRCC6 gene.[5][6] Function Together, Ku70 and Ku80 make up the Ku heterodimer, which binds to DNA double-strand break ends and is required for the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway of DNA repair. It is also required for V(D)J recombination, which utilizes the NHEJ pathway to promote antigen diversity in the mammalian immune system. In addition to its role in NHEJ, Ku…
-
Ku80
Ku80 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the XRCC5 gene.[5] Together, Ku70 and Ku80 make up the Ku heterodimer, which binds to DNA double-strand break ends and is required for the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway of DNA repair. It is also required for V(D)J recombination, which utilizes the NHEJ pathway to promote antigen diversity in the mammalian immune system. In addition to its role in NHEJ, Ku is required…
-
The trefoil knot fold is a protein fold in which the protein backbone is twisted into a trefoil knot shape
“Shallow” knots in which the tail of the polypeptide chain only passes through a loop by a few residues are uncommon, but “deep” knots in which many residues are passed through the loop are extremely rare. Deep trefoil knots have been found in the SPOUT superfamily. including methyltransferase proteins involved in posttranscriptional RNA modification in all three domains of life, including bacterium Thermus thermophilus and…
-
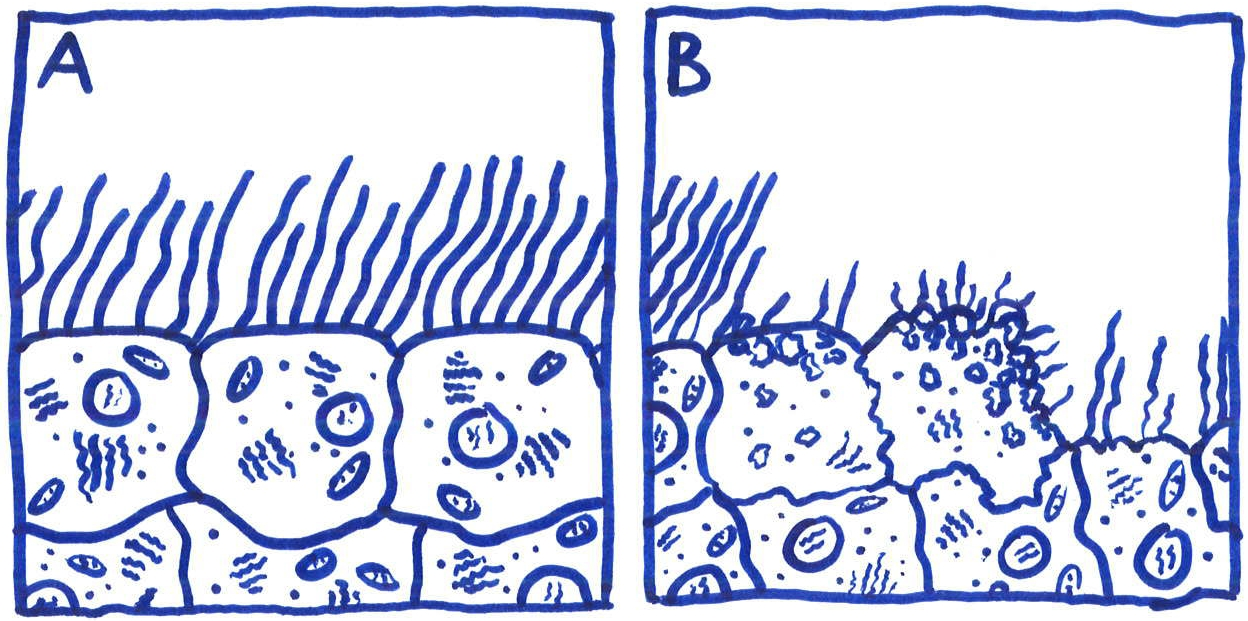
Tracheal cytotoxin (TCT) is a soluble piece of peptidoglycan (PGN) found in the cell wall of all gram-negative bacteria, but only some bacteria species release TCT including Bordetella pertussis, Vibrio fischeri, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Tracheal cytotoxin (TCT) is a 921 dalton glycopeptide released by Bordetella pertussis, Vibrio fischeri (as a symbiosis chemical), and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (among other peptidoglycan-derived cytotoxins it produces). It is a soluble piece of peptidoglycan (PGN) found in the cell wall of all gram-negative bacteria, but only some bacteria species release TCT due to inability to recycle this piece of anhydromuropeptide. History In 1980, it was discovered that B. pertussis could attach to hamster tracheal epithelial (HTE) cells, and also, that…
-
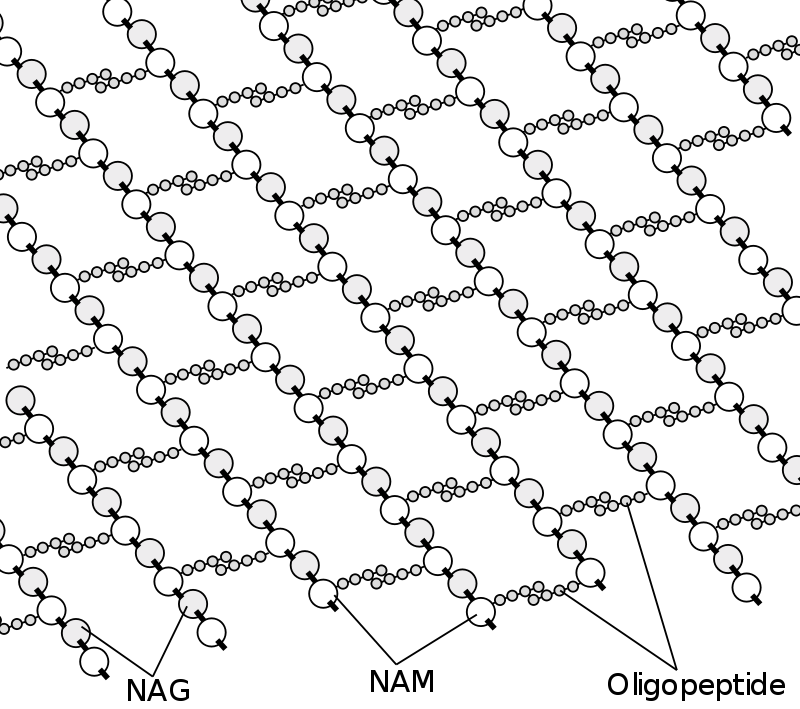
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane
Not to be confused with glycopeptide, proteoglycan, or glycoprotein Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane, the rigid cell wall (murein sacculus) characteristic of most bacteria (domain Bacteria). The sugar component consists of alternating residues of β-(1,4) linked N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM). Attached to the N-acetylmuramic acid is an oligopeptide chain made of three to five amino acids.…
-

Langgan 琅玕 is the ancient Chinese name of a gemstone which remains an enigma in the history of mineralogy; it has been identified, variously, as blue-green malachite, blue coral, white coral, whitish chalcedony, red spinel, and red jade
It is also the name of a mythological langgan tree of immortality found in the western paradise of Kunlun Mountain, and the name of the classic waidan alchemical elixir of immortality langgan huadan 琅玕華丹 “Elixir Efflorescence of Langgan”. Waidan, translated as ‘external alchemy‘ or ‘external elixir‘, is the early branch of Chinese alchemy that focuses upon compounding elixirs of immortality by heating minerals, metals, and other natural substances…
-

Sterol carrier proteins (aka nonspecific lipid transfer proteins)
These proteins are different from plant nonspecific lipid transfer proteins but structurally similar to small proteins of unknown function from Thermus thermophilus. This domain is involved in binding sterols. The human sterol carrier protein 2 (SCP2) is a basic protein that is believed to participate in the intracellular transport of cholesterol and various other lipids. Human…
-

Amygdalin and Laetrile
Amygdalin (from Ancient Greek: ἀμυγδαλή amygdalē “almond”) is a naturally occurring chemical compound found in many plants, most notably in the seeds (kernels) of apricots, bitter almonds, apples, peaches, cherries and plums, and in the roots of manioc. Amygdalin is classified as a cyanogenic glycoside, because each amygdalin molecule includes a nitrile group, which can be released as the toxic cyanide anion by the action of a beta-glucosidase. Eating amygdalin will cause it to release cyanide…
Recent Posts
- 🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
- 🧂 Sodium Reduction and Sodium Replacement: A History of Reformulation and Exploding Diseases, Including Many Diseases Unheard of Before Deadly Sodium Policies
- 🧂 The DEADLY 1500 mg Sodium Recommendation predates the WHO’s formal global sodium reduction push by nearly a decade (and it’s even worse than that)
- 🧬 What Is Beta-Glucuronidase?
- When Sugar Was Salt: Crystalline Confusion and the Covenant of Sweetness
Tags
ADAM ASPARTAME Birds Blood Bones Brain Bugs Cancer Columba Cows crystallography Death Death cults Eggs Etymology Gastrin Gold Growth hormone History Hormones Insulin Liver Mere Perplexity Metal Monkey Business Mythology Paracetamol Plants Poison Pregnancy Protein Religion Reproduction Rocks Salt Slavery Snakes Sodium the birds and the bees Thiocyanate Tobacco Tylenol Underworld Venom zinc

