Sun
-
Chrysiasis
Chrysiasis is a dermatological condition induced by the parenteral administration of gold salts, usually for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Such treatment has been superseded as the best practice for treating the disease because of “numerous… Read more.
-
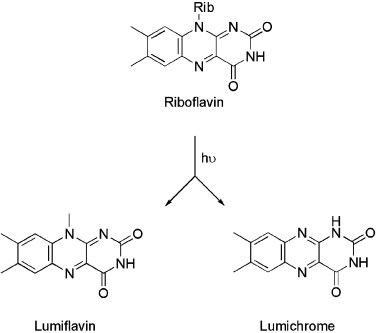
Riboflavin and its breakdown products interact with DNA, making this system attractive in the photodisinfection of blood and blood products
The application of photosensitisers to tropical pathogens in the blood supply Mark Wainwright PhD, Mauricio S. Baptista, in Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy, 2011 Riboflavin As vitamin B2, riboflavin (Fig. 5) is an essential nutrient in humans. The Mirasol system… Read more.
-
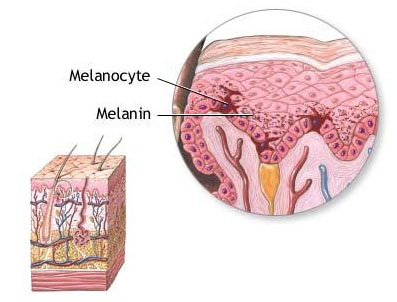
Cells in the APUD system may include melanocytes
Melanocytes are melanin-producing neural crest-derived cells located in the bottom layer (the stratum basale) of the skin’s epidermis, the middle layer of the eye (the uvea), the inner ear, vaginal epithelium, meninges, bones, and heart. Melanin is a dark pigment primarily responsible for skin color. Once synthesized, melanin is contained in… Read more.
-
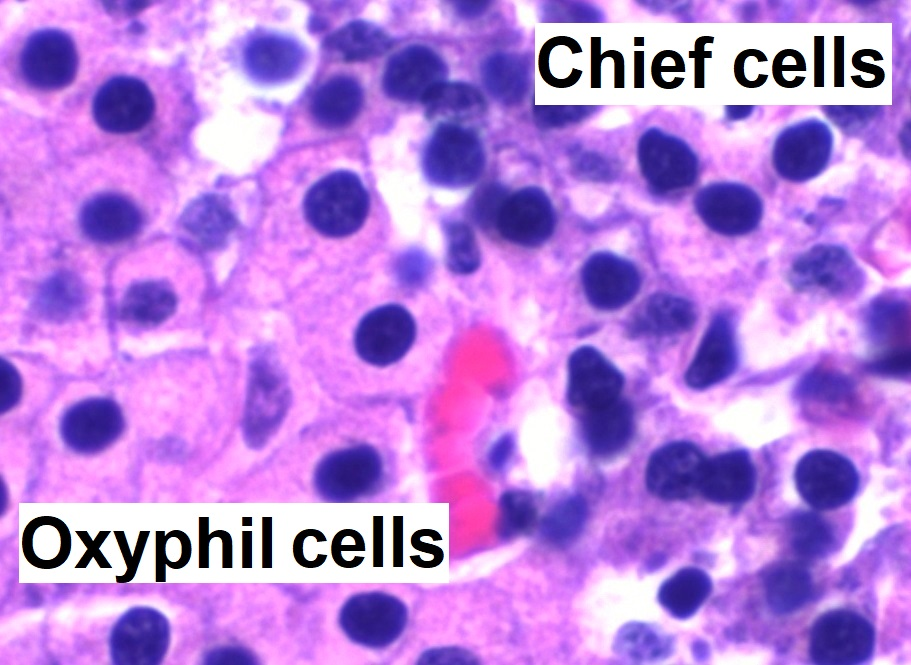
The chief cells of the parathyroid glands sense the amount of calcium in the blood, and release the calcium-increasing hormone parathyroid hormone (PTH) accordingly
Parathyroid chief cells (also called parathyroid principal cells or simply parathyroid cells) are one of the two cell types of the parathyroid glands, along with oxyphil cells. The chief cells are much more prevalent in the… Read more.