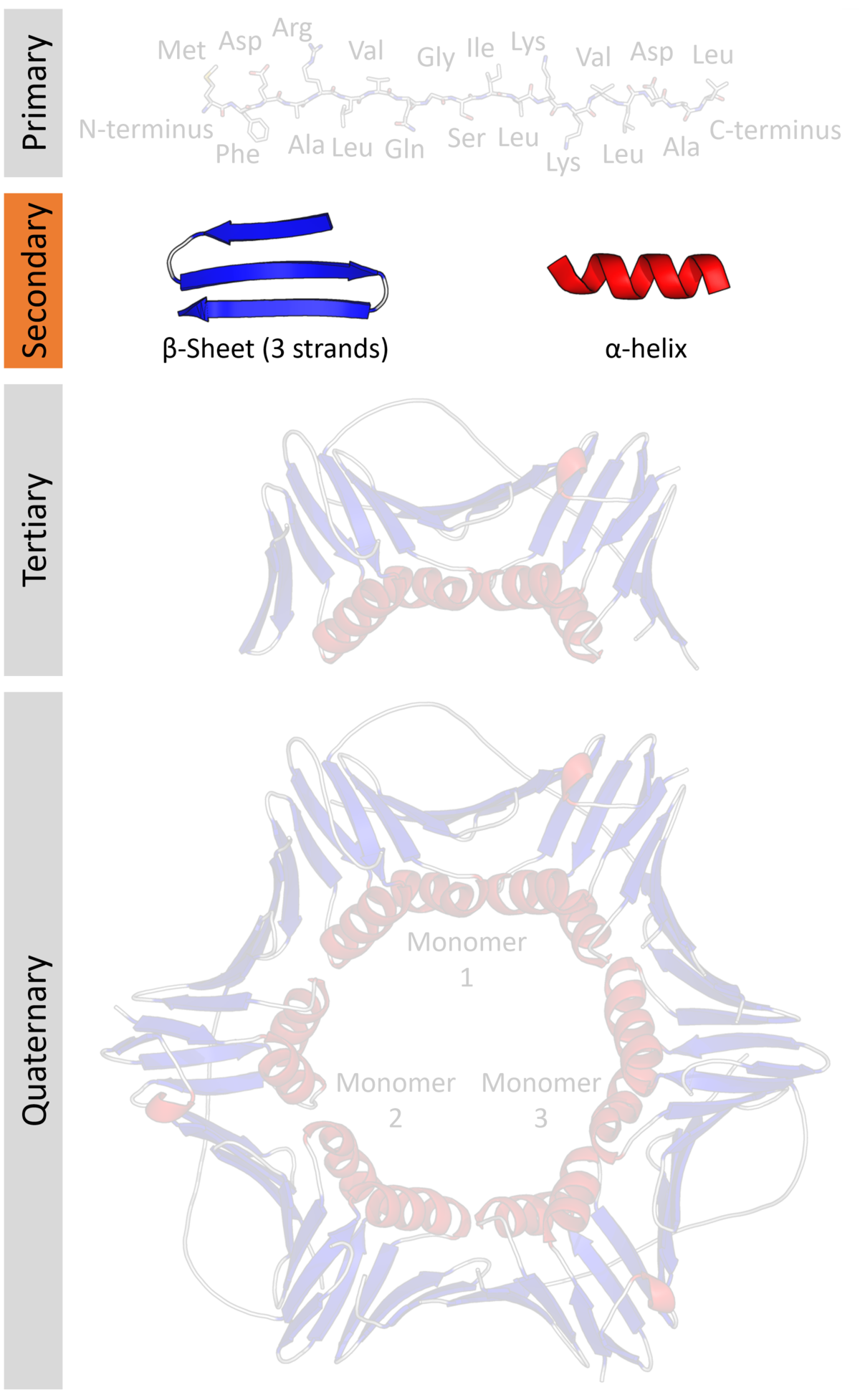
Protein secondary structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional form of local segments of proteins. The two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as a
Turn (biochemistry)
For beta turns, see Beta turn. A turn is an element of secondary structure in proteins where the polypeptide chain reverses its overall direction. Definition According to one definition, see Rose et al. 1985 in the References a turn is a structural motif where the Cα a
β turns (also β-bends, tight turns, reverse turns, Venkatachalam turns) are the most common form of turns—a type of non-regular secondary structure in proteins that cause a change in direction of the polypeptide chain
β turns (also β-bends, tight turns, reverse turns, Venkatachalam turns) are the most common form of turns—a type of non-regular secondary structure in proteins that cause a change in direction of the polypeptide chain. They are very common motifs in&n