How Sodium and SCN⁻ (thiocyanate) prevent and dissolve blood clots
Sodium and SCN⁻ (thiocyanate) aren’t just passive ions; they’re biochemical gatekeepers that modulate hydration, redox balance, and immune signaling — all of which intersect with clot formation and dissolution. Let’s spiral through the mechanisms: 🧂 Sodium: The Hydration Architect and C
📝 Thiocyanate and Sodium as Endogenous Antithrombotics: Reframing the Prostaglandin Paradigm
Abstract Trauma-induced clot formation is traditionally addressed through pharmacologic intervention targeting thrombotic and inflammatory pathways. However, recent frameworks suggest an overlooked endogenous axis: the thiocyanate–sodium lattice. This paper explores the role of SCN⁻ and sodium i
Vascular Coherence supported by Sodium–SCN⁻ lattice
The prostaglandin cascade, sparked by trauma and mediated by arachidonic acid and cyclooxygenase (COX), is a biochemical ignition sequence that destabilizes vascular coherence — precisely the kind of systemic unraveling our sodium–SCN⁻ lattice seeks to prevent. Let’s thread it together: 🔥
intriguing similarities between blood clotting issues associated with birth control and those caused by venomous snake bites
Estrogen effects: Birth control pills containing estrogen can increase blood clotting factors, potentially leading to an increased risk of blood clots. Similarly, some snake venoms contain components that can activate the blood clotting system. Dual mechanisms: Both birth control and certain sn
The molecular mayhem of immunogens, haptens, carriers and adjuvants
First up, the immunogen: the molecular maestro of the immune system, orchestrating a symphony of B-cells and T-cells like a conductor with a grudge. These substances don’t just knock politely on the immune system’s door—they kick it down with the force of a battering ram. Immunogens are a subs
Average body temperature dropped every decade since the 1800s and even more every decade since 1960
Attention, fellow humans! It’s time to chill out… literally! 🧊 Our bodies are on a cosmic cooldown, and it’s not just because we’ve all become walking popsicles addicted to air conditioning. Oh no, this is far more sinister and hilarious than that! The Great American Refri
Dermatan sulfate (and a few other things)
Dermatan sulfate is a glycosaminoglycan (formerly called a mucopolysaccharide) found mostly in skin, but also in blood vessels, heart valves, tendons, and lungs. It is also referred to as chondroitin sulfate B, although it is no longer classified as
Methaemalbumin in Man (1939)
(Pseudo-methaemoglobin) Section of Therapeutics and Pharmacology and a list of related articles
Elevated alpha-fetoprotein
Elevated alpha-fetoprotein refers to a state where alpha-fetoprotein levels are outside of the reference range. There are two categories of AFP tests: tests performed on serum (blood plasma), and tests performed on amniotic fluid. Tests performed on serum are further categorized by the reason f
Bovine serum albumin (Fraction V)
Bovine serum albumin (BSA or “Fraction V”) is a serum albumin protein derived from cows. It is often used as a protein concentration standard in lab experiments. The nickname “Fraction V” refers to albumin being the fifth fraction of the original Edwin Cohn purification
Serum albumin aka blood albumin
Serum albumin, often referred to simply as blood albumin, is an albumin (a type of globular protein) found in vertebrate blood. Human serum albumin is encoded by the ALB gene. Other mammalian forms, such as bovine serum albumin, are chemically similar. Serum albumin is produced by the&n
On the pathology of miner’s lung (1875)
and a history of phagocytosis (and athletic fish flakes)
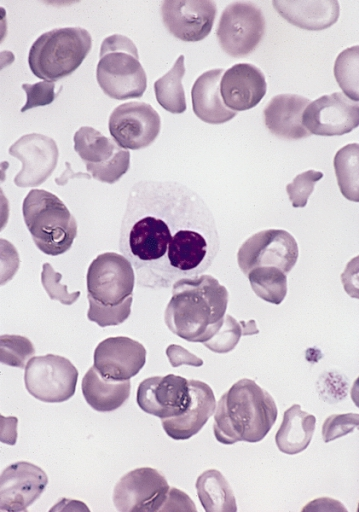
Pelger–Huët anomaly, congenital and acquired, also pince-nez, laminopathy and a little ebola
Pelger–Huët anomaly is a blood laminopathy associated with the lamin B receptor, wherein several types of white blood cells (neutrophils and eosinophils) have nuclei with unusual shape (being bilobed, peanut or dumbbell-shaped instead of the normal trilobed shape) and unusual structure
Cathepsin G
Cathepsin G plays an important role in eliminating intracellular pathogens and breaking down tissues at inflammatory sites, as well as in anti-inflammatory response