Embryology
-
Connection (and difference) between buccal membrane and buccopharyngeal membrane
A Tale of Two Tissues Prepare yourself for a thrilling journey into the world of microscopic membranes! Today, we’re diving deep into the oral cavity to explore the buccal membrane… Read more.
-
embryonic intrigue that’ll make your buccopharyngeal membrane quiver with excitement!
Picture, if you will, the humble beginnings of life, where a thin membrane known as the buccopharyngeal membrane (or oropharyngeal membrane for those who like their words extra fancy) plays… Read more.
-
Sex-determining region Y protein (SRY), or testis-determining factor (TDF)
Sex-determining region Y protein (SRY), or testis-determining factor (TDF), is a DNA-binding protein (also known as gene-regulatory protein/transcription factor) encoded by the SRY gene that is responsible for the initiation of male sex determination in therian mammals (placental mammals and marsupials). SRY is an intronless sex-determining gene on… Read more.
-
DAX1
DAX1 (dosage-sensitive sex reversal, adrenal hypoplasia critical region, on chromosome X, gene 1) is a nuclear receptor protein that in humans is encoded by the NR0B1 gene (nuclear receptor subfamily 0, group B, member 1). The NR0B1 gene is… Read more.
-
Steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) protein and a few related things
The steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) protein is a transcription factor involved in sex determination by controlling the activity of genes related to the reproductive glands or gonads and adrenal glands. This protein is encoded by the NR5A1 gene, a member of the nuclear receptor subfamily, located… Read more.
-
Structure of DNA repair protein XRCC4 aka X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 4
XRCC4 protein is a TETRAMER that resembles the shape of a DUMBBELL containing two globular ends separated by a long, thin stalk. The tetramer is composed of two dimers, and each dimer… Read more.
·
-
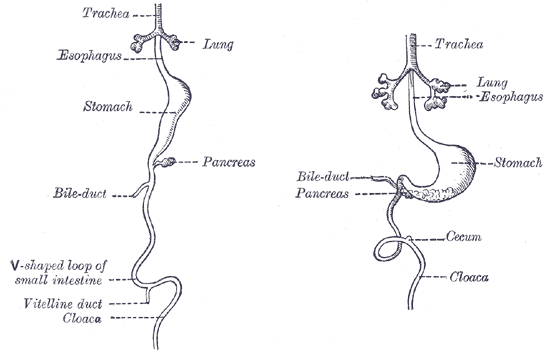
Vitelline duct connects the yolk sac to the small intestine. This duct obliterates when the embryo is about 6 weeks old. Complete failure of the duct to obliterate results in a fistula from the ileum to the umbilicus (vitelline fistula).
In the human embryo, the vitelline duct, also known as the vitellointestinal duct, the yolk stalk, the omphaloenteric duct, or the omphalomesenteric duct, is a long narrow tube that joins the yolk sac to the midgut lumen of the developing fetus. It appears at the end of… Read more.
-
A Mad Scientist’s Dream – Rumpless Chickens (and more)
Today, we delve into the bizarre phenomenon of rumpless chickens—a feathered marvel characterized by caudal dysplasia, or as some like to call it, the ultimate chicken makeover! These quirky birds… Read more.
-
Prenatal exposure to paracetamol/acetaminophen and precursor aniline impairs masculinisation of male brain and behaviour
Paracetamol/acetaminophen (N-Acetyl-p-Aminophenol; APAP) is the preferred analgesic for pain relief and fever during pregnancy. It has therefore caused concern that several studies have reported that prenatal exposure to APAP results… Read more.
-
Agrin is a large chimeric proteoglycan, a heparan sulfate and chondroitin proteoglycan, whose best-characterised role is in the development of the neuromuscular junction during embryogenesis
Agrin was originally found in the electric organ of Tarpedo california and in the basal lamina at the neuromuscular junction as a protein that directs the aggregation of acetylcholine receptors (AChR) and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) at synaptic sites. Tetronarce californica also known as… Read more.