Category: Membranes of the fetus and embryo
-

Connection (and difference) between buccal membrane and buccopharyngeal membrane
A Tale of Two Tissues Prepare yourself for a thrilling journey into the world of microscopic membranes! Today, we’re diving deep into the oral cavity to explore the buccal membrane and its embryonic cousin, the buccopharyngeal (aka oropharyngeal) membrane. It’s a story of similarities, differences, and developmental drama! Act I: The Buccal BombshellOur first star,…
-
embryonic intrigue that’ll make your buccopharyngeal membrane quiver with excitement!
Picture, if you will, the humble beginnings of life, where a thin membrane known as the buccopharyngeal membrane (or oropharyngeal membrane for those who like their words extra fancy) plays the role of the ultimate gatekeeper between the primitive mouth and pharynx. It’s like nature’s very own “You shall not pass!” moment, but with fewer…
-
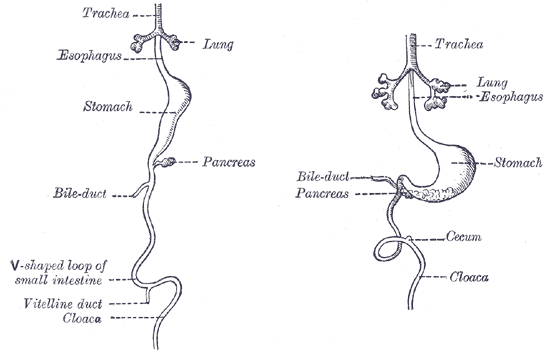
Vitelline duct connects the yolk sac to the small intestine. This duct obliterates when the embryo is about 6 weeks old. Complete failure of the duct to obliterate results in a fistula from the ileum to the umbilicus (vitelline fistula).
In the human embryo, the vitelline duct, also known as the vitellointestinal duct, the yolk stalk, the omphaloenteric duct, or the omphalomesenteric duct, is a long narrow tube that joins the yolk sac to the midgut lumen of the developing fetus. It appears at the end of the fourth week, when the yolk sac (also known as the umbilical vesicle) presents the appearance of a small pear-shaped vesicle. Function Obliteration Generally, the duct…
-
Cleavage (embryology)
In embryology, cleavage is the division of cells in the early development of the embryo, following fertilization. The zygotes of many species undergo rapid cell cycles with no significant overall growth, producing a cluster of cells the same size as the original zygote. The different cells derived from cleavage are called blastomeres and form a compact mass called the morula. Cleavage ends with the formation of the blastula, or of the blastocyst in…
-
Pulmonary neuroendocrine cells
Neuroendocrine cells are cells that receive neuronal input (through neurotransmitters released by nerve cells or neurosecretory cells) and, as a consequence of this input, release messenger molecules (hormones) into the blood. In this way they bring about an integration between the nervous system and the endocrine system, a process known as neuroendocrine integration. An example of a neuroendocrine cell is a cell…
-
Syncytiotrophoblast
Syncytiotrophoblast (from the Greek ‘syn’- “together”; ‘cytio’- “of cells”; ‘tropho’- “nutrition”; ‘blast’- “bud”) is the epithelial covering of the highly vascular embryonic placental villi, which invades the wall of the uterus to establish nutrient circulation between the embryo and the mother. It is a multi-nucleate, terminally differentiated syncytium, extending to 13 cm. It is the outer layer of the trophoblasts and actively invades the uterine wall, during implantation, rupturing maternal capillaries and thus establishing an interface between…
-
Cytotrophoblast
“Cytotrophoblast” is the name given to both the inner layer of the trophoblast (also called layer of Langhans) or the cells that live there. It is interior to the syncytiotrophoblast and external to the wall of the blastocyst in a developing embryo. The cytotrophoblast is considered to be the trophoblastic stem cell because the layer surrounding the blastocyst remains while daughter cells differentiate and proliferate…
Recent Posts
- 🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
- 🧂 Sodium Reduction and Sodium Replacement: A History of Reformulation and Exploding Diseases, Including Many Diseases Unheard of Before Deadly Sodium Policies
- 🧂 The DEADLY 1500 mg Sodium Recommendation predates the WHO’s formal global sodium reduction push by nearly a decade (and it’s even worse than that)
- 🧬 What Is Beta-Glucuronidase?
- When Sugar Was Salt: Crystalline Confusion and the Covenant of Sweetness
Tags
ADAM ASPARTAME Birds Blood Bones Brain Bugs Cancer Columba Cows crystallography Death Death cults Eggs Etymology Gastrin Gold Growth hormone History Hormones Insulin Liver Mere Perplexity Metal Monkey Business Mythology Paracetamol Plants Poison Pregnancy Protein Religion Reproduction Rocks Salt Slavery Snakes Sodium the birds and the bees Thiocyanate Tobacco Tylenol Underworld Venom zinc
