Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic disease
-
Parafollicular cells aka C cells secrete calcitonin and several neuroendocrine peptides
Parafollicular cells, also called C cells, are neuroendocrine cells in the thyroid. The primary function of these cells is to secrete calcitonin. They are located adjacent to the thyroid follicles and reside in the connective… Read more.
-
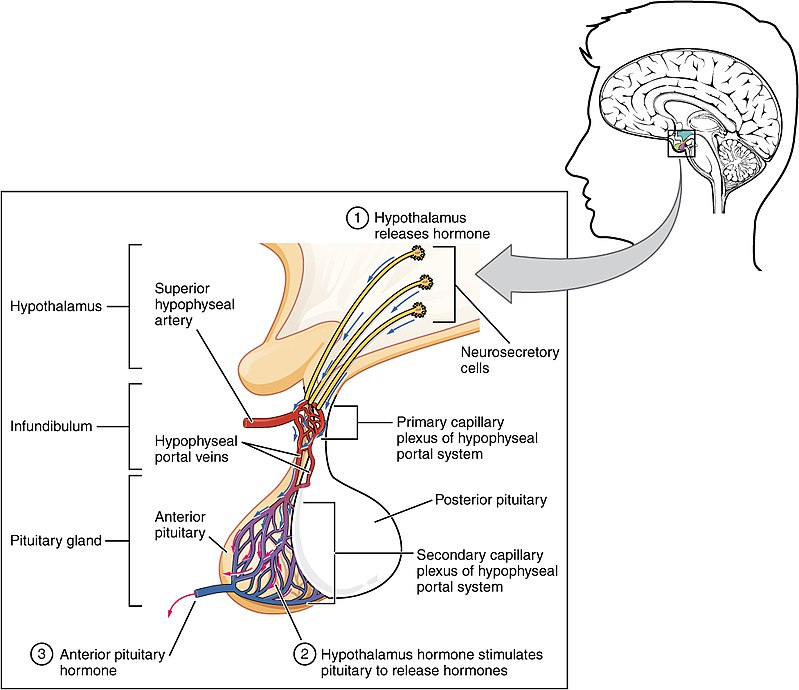
Adenohypophysis regulates several physiological processes, including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation
A major organ of the endocrine system, the anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis or pars anterior) is the glandular, anterior lobe that together with the posterior lobe (posterior pituitary, or the neurohypophysis) makes up the pituitary gland (hypophysis). The anterior pituitary regulates several physiological processes, including stress, growth, reproduction,… Read more.
-
Inborn error of purine–pyrimidine metabolism
Inborn errors of purine–pyrimidine metabolism are a class of inborn error of metabolism disorders specifically affecting purine metabolism and pyrimidine metabolism. An example is Lesch–Nyhan syndrome. Urine tests may be of use in identifying some of these… Read more.