Xylose is the first saccharide added to the serine or threonine in the proteoglycan type O-glycosylation
Xylose is the first saccharide added to the serine or threonine in the proteoglycan type O-glycosylation, and, so, it is the first saccharide in biosynthetic pathways of most anionic polysaccharides such as heparan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate. Buskas, Therese; Ingale, Sampat; Boons, Geert-Jan (2006), "Glycopeptides as versatile tool for glycobiology", Glycobiology, 16 (8): 113R–36R, doi:10.1093/glycob/cwj125, PMID 16675547 Definitions Proteoglycans are proteins that are heavily glycosylated.
In supramolecular assembly
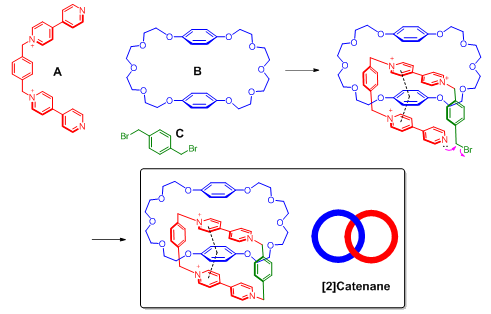
π systems are important building blocks in supramolecular assembly because of their versatile noncovalent interactions with various functional groups. A notable example of applying π–π interactions in supramolecular assembly is the synthesis of catenane. The major challenge for the synthesis of catenane is
Addition in pharmacological active compounds
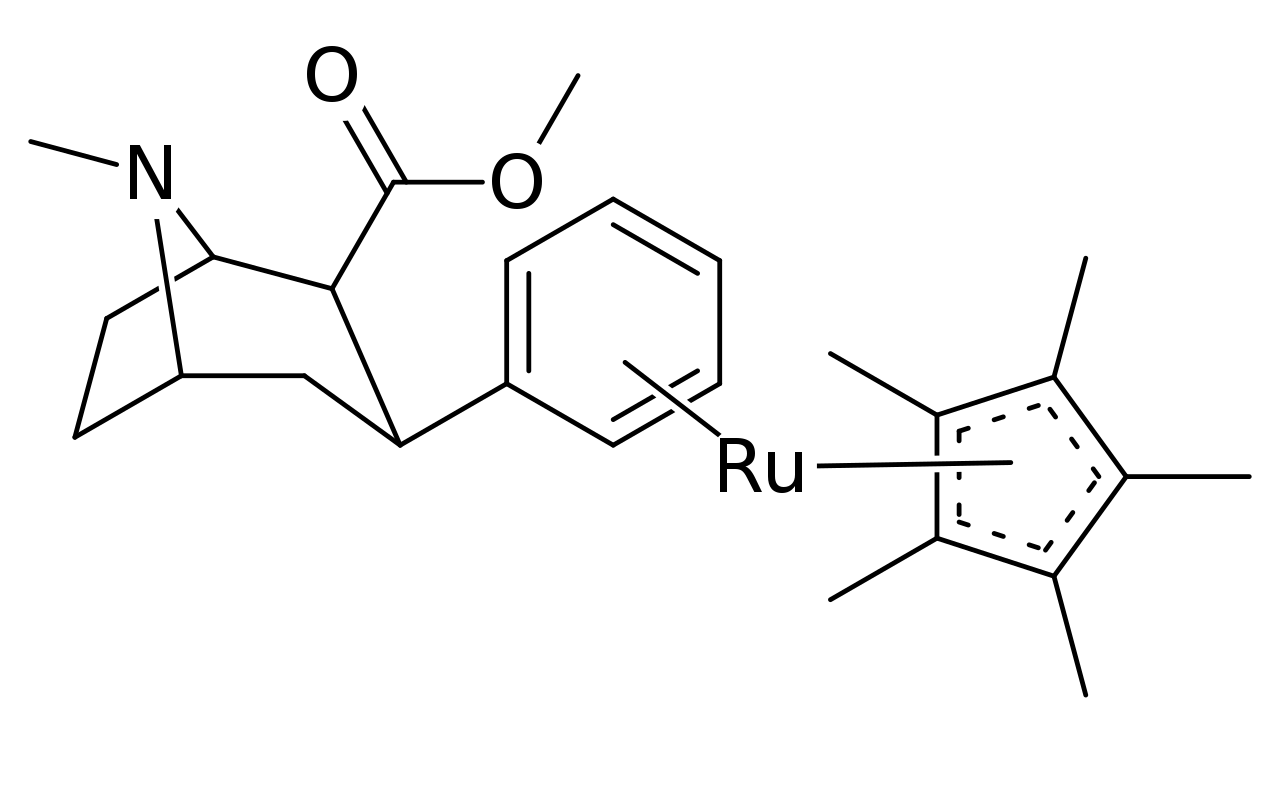
Several variants of pi coordinated phenyls have even been tested using transition metals for stacking η6-phenyltropanes, using cyclopentadienyl and tricarbonyl in place of a benzene. Which in the case of the tricarbonyl doubled the compound's affinity for its intended ligand site
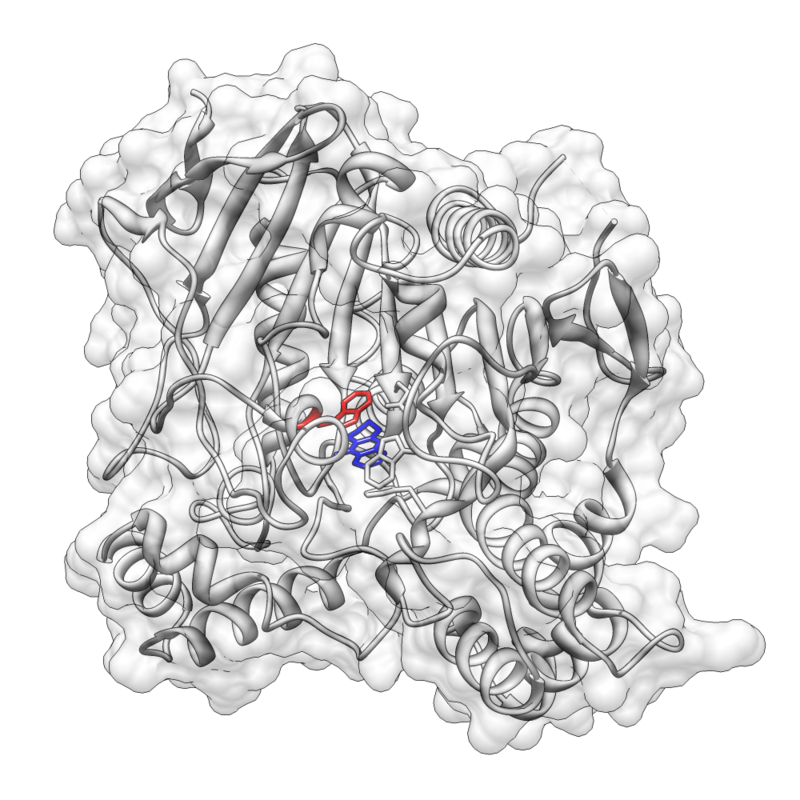
Pi stacking is prevalent in protein crystal structures and also contributes to the interactions between small molecules and proteins
As a result, pi–pi and cation–pi interactions are important factors in rational drug design. Babine RE, Bender SL (August 1997). "Molecular Recognition of Proteinminus signLigand Complexes: Applications to Drug Design". Chemical Reviews. 97 (5): 1359–1472. doi:10.1021/cr960370z. PMID 11851455. Crystal structure of Tacrine bound to acetylcholinesterase (PDB accession: 1ACJ)
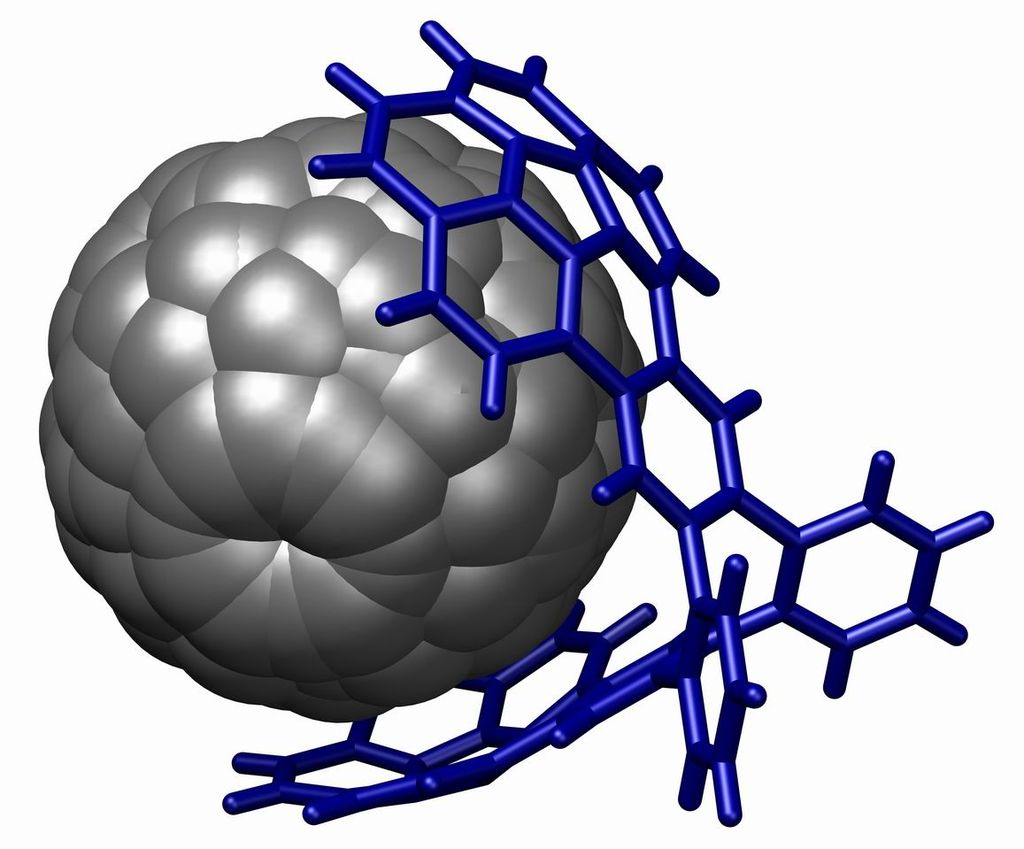
A powerful demonstration of stacking is found in the buckycatcher
A fullerene bound in a buckycatcher through aromatic stacking interactions. This is a picture generated from a crystal structure data reported by Andrzej Sygula, Frank R. Fronczek, Renata Sygula, Peter W. Rabideau, and Marilyn M. Olmstead in the Journal of the American Chemical Society
Requirement of aromaticity
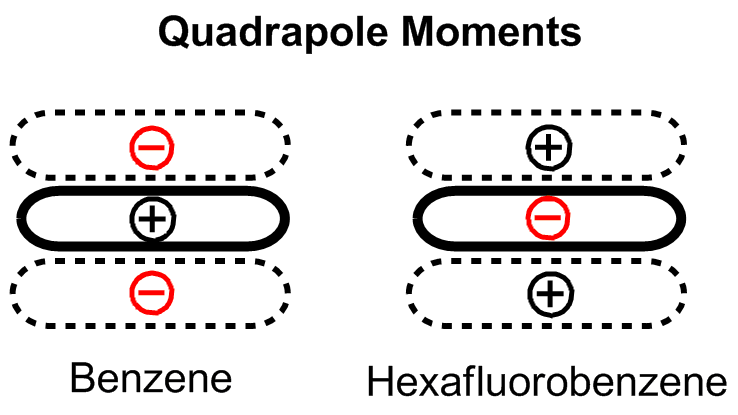
The conventional understanding of pi stacking involves quadrupole interactions between delocalized electrons in p-orbitals. In other words, aromaticity should be required for this interaction to occur. However, several groups have provided contrary evidence, calling into question whether pi stacking is
Direct interaction model (substituent effects)
The Hunter–Sanders model has been criticized by numerous research groups offering contradictory experimental and computational evidence of pi stacking interactions that are not governed primarily by electrostatic effects. The clearest experimental evidence against electrostatic substituent effects was reported by Rashkin and
Electrostatic model (substituent effects)
An early model for the role of substituents in pi stacking interactions was proposed by Hunter and Sanders. Hunter CA, Sanders JK (1990). "The nature of π–π Interactions". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 112 (14): 5525–5534. doi:10.1021/ja00170a016. They used a simple mathematical model based on sigma and
Substituent effects
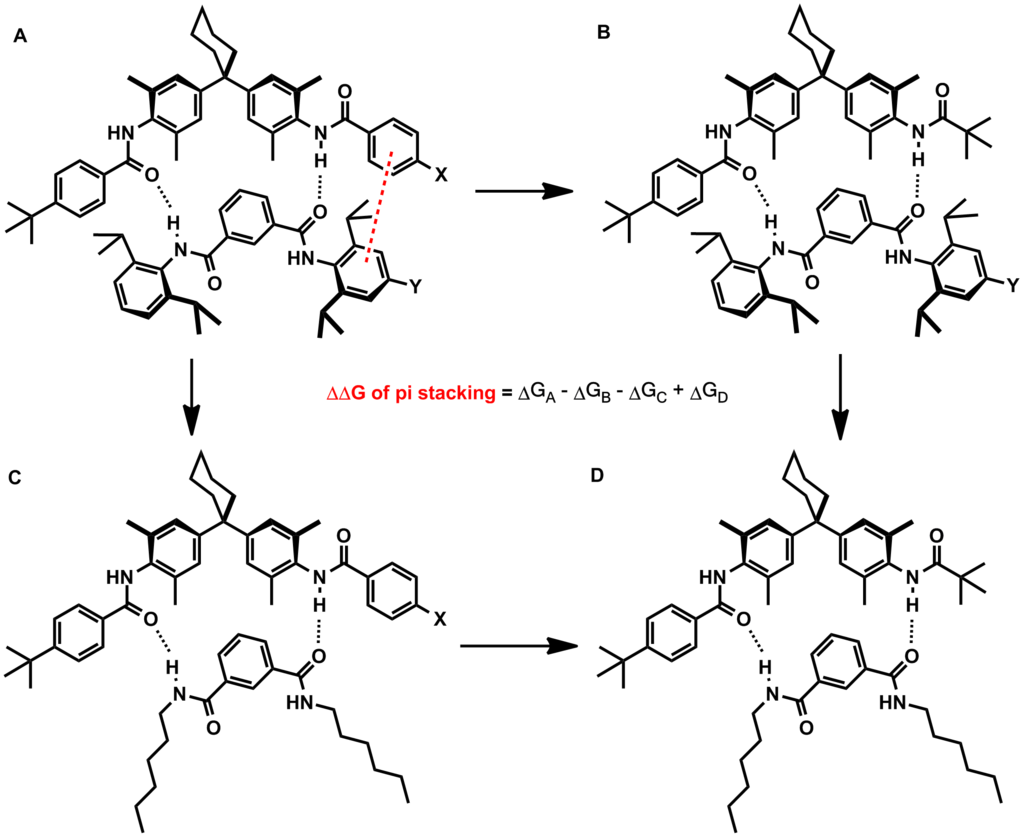
The ability to fine-tune pi stacking interactions would be useful in numerous synthetic efforts. One example would be to increase the binding affinity of a small-molecule inhibitor to an enzyme pocket containing aromatic residues. The effects of heteroatoms and substituents on
Geometric configurations
The preferred geometries of the benzene dimer have been modeled at a high level of theory with MP2-R12/A computations and very large counterpoise-corrected aug-cc-PVTZ basis sets. Sinnokrot MO, Valeev EF, Sherrill CD (September 2002). "Estimates of the ab initio limit for
Evidence against pi stacking
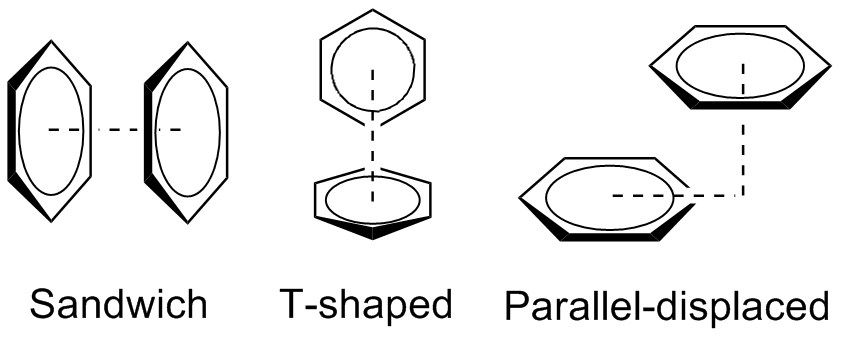
The benzene dimer is the prototypical system for the study of pi stacking, and is experimentally bound by 8–12 kJ/mol (2–3 kcal/mol) in the gas phase with a separation of 4.96 Å between the centers of mass for the T-shaped dimer. The
Pi stacking aka π–π stacking
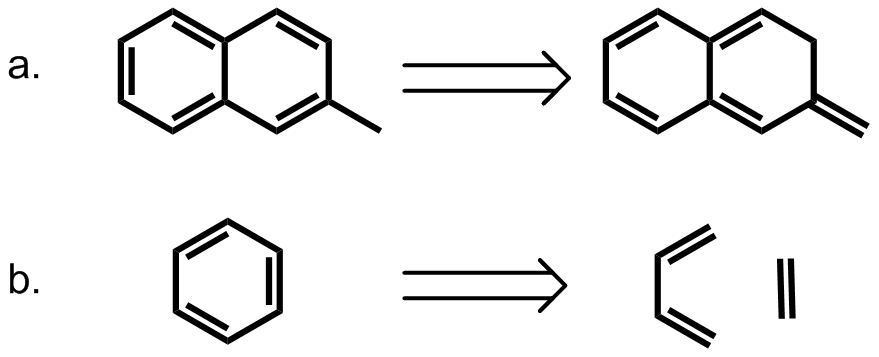
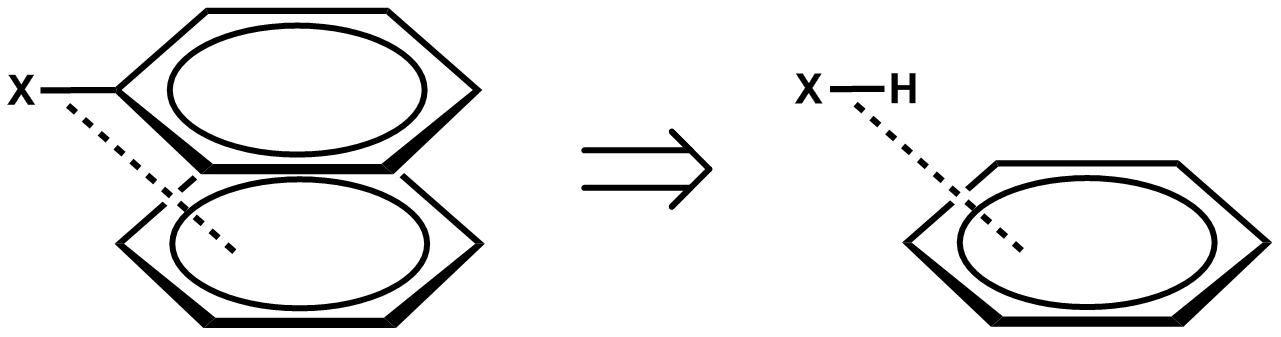
In chemistry, pi stacking (also called π–π stacking) refers to the presumptive attractive, noncovalent pi interactions (orbital overlap) between the pi bonds of aromatic rings. However this is a misleading description of the phenomena since direct stacking of aromatic rings (the "sandwich interaction") is electrostatically repulsive. What is more commonly observed (see figure below)
Conductive ink
Silver nanoparticle conductive ink FlowMetal™ | BANDO Conductive ink is an ink that results in a printed object which conducts electricity. It is typically created by infusing graphite or other conductive materials into ink. Steven Osborn (17 September 2013). Makers at Work: Folks Reinventing the World One Object Or
Carboxypeptidases function in blood clotting, growth factor production, wound healing, reproduction, and many other processes
A carboxypeptidase (EC number 3.4.16 - 3.4.18) is a protease enzyme that hydrolyzes (cleaves) a peptide bond at the carboxy-terminal (C-terminal) end of a protein or peptide. This is in contrast to an aminopeptidases, which cleave peptide bonds at the N-terminus of proteins. Humans, animals, bacteria and plants contain several types of carboxypeptidases that have diverse functions ranging
Arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) and both the amino and guanidino groups are protonated, resulting in a cation. Only