Category: The Science
-
Testican
Testican is a type of proteoglycan. Testican-1 is a highly conserved, multidomain proteoglycan that is most prominently expressed in the thalamus, and is upregulated in activated astroglial cells of the cerebrum. Several functions of this gene product have now been demonstrated in vitro including membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase inhibition, cathepsin L inhibition, and low-affinity calcium binding. The purified gene product has been shown to inhibit cell attachment…
-
Keratan sulfate (KS) aka keratosulfate
Not to be confused with Keratin. Keratan sulfate (KS), also called keratosulfate, is any of several sulfated glycosaminoglycans (structural carbohydrates) that have been found especially in the cornea, cartilage, and bone. It is also synthesized in the central nervous system where it participates both in development and in the glial scar formation following an injury. Keratan sulfates are large, highly hydrated molecules which in joints can act as a cushion to…
-
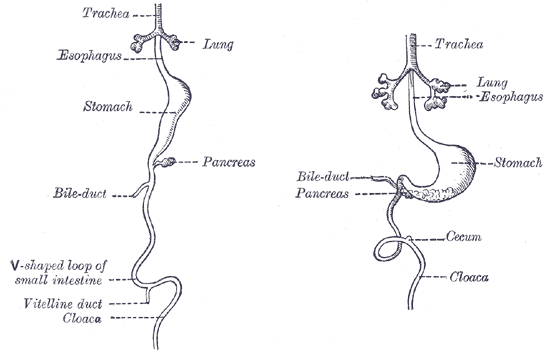
Vitelline duct connects the yolk sac to the small intestine. This duct obliterates when the embryo is about 6 weeks old. Complete failure of the duct to obliterate results in a fistula from the ileum to the umbilicus (vitelline fistula).
In the human embryo, the vitelline duct, also known as the vitellointestinal duct, the yolk stalk, the omphaloenteric duct, or the omphalomesenteric duct, is a long narrow tube that joins the yolk sac to the midgut lumen of the developing fetus. It appears at the end of the fourth week, when the yolk sac (also known as the umbilical vesicle) presents the appearance of a small pear-shaped vesicle. Function Obliteration Generally, the duct…
-
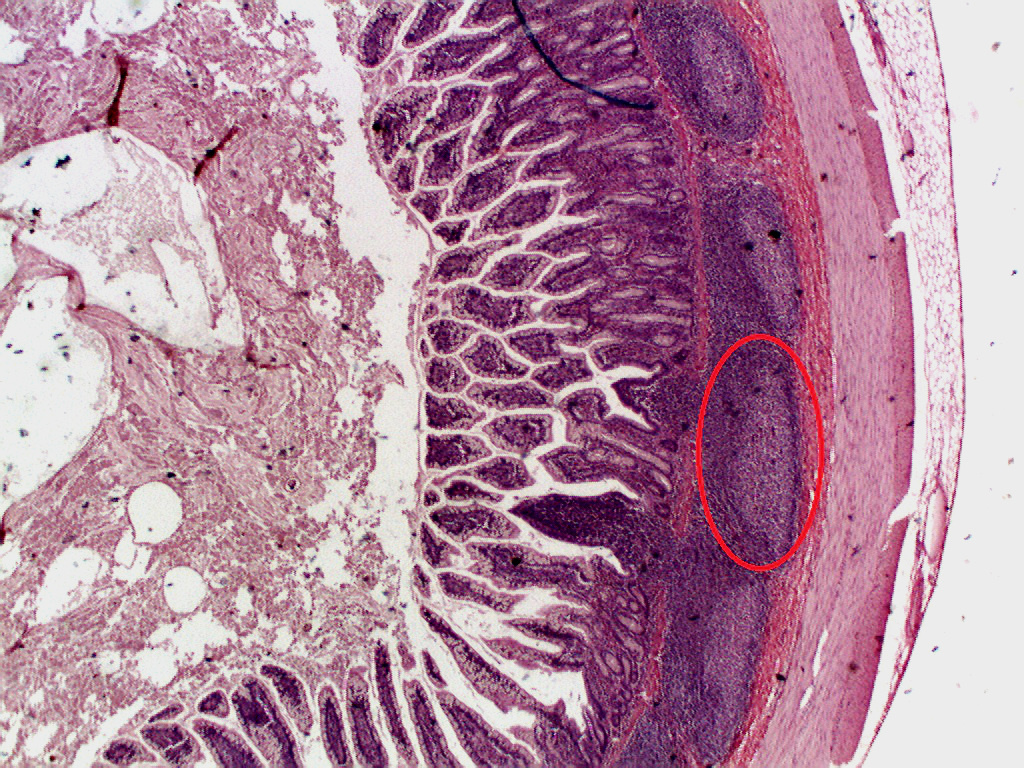
Peyer’s patches (aggregated lymphoid nodules)
Peyer’s patches (or aggregated lymphoid nodules) are organized lymphoid follicles, named after the 17th-century Swiss anatomist Johann Conrad Peyer. They are an important part of gut associated lymphoid tissue usually found in humans in the lowest portion of the small intestine, mainly in the distal jejunum and the ileum, but also could be detected in the duodenum. History Peyer’s patches had been observed and described by several anatomists…
-
Perivitellin-2 (PV2) is a pore-forming toxin present in the egg perivitelline fluid of apple snails
Perivitellin-2 (PV2) is a pore-forming toxin present in the egg perivitelline fluid of the apple snails Pomacea maculata (PmPV2) and Pomacea canaliculata (PcPV2). This protein, called perivitellin, is massively accumulated in the eggs (~20 % total protein). As a toxin PV2 protects eggs from predators, but it also nourishes the developing snail embryos. Structure and stability These ~172-kDa proteins are dimers of AB toxins, each composed of a carbohydrate-binding…
-
Perivitellins are egg proteins found in the perivitelline fluid of many gastropods
Perivitellins are multifunctional complexes providing the developing embryo with nutrition, protection from the environment, and defense against predators. Despite the central role perivitellins play in reproduction and development, there is little information about their role in gastropod Molluscs. Most studies of perivitellins have been performed in eggs of Ampullaridae, a family of freshwater snails (Caenogastropoda), notably the Pomacea genus, mostly…
-
Scalarin carries and stabilizes carotenoid pigments
Scalarin (PsSC) is the most abundant perivitellin of the perivitelline fluid from Pomacea scalaris eggs. This glyco-lipo-caroteno protein is an approx. 380 kDa multimer combining multiple copies of six different 24-35 kDa subunits. As part of the petivitelline fluid, PsSC is probably playing a role as a nutrient source for the developing embryo in Pomacea scalaris eggs. As its orthologous ovorubin and PmPV1, this protein carries and stabilizes carotenoid pigments. As…
-
Pomacea maculata perivitellin-1 (PmPV1) is a glyco-lipo-caroteno protein
Pomacea maculata perivitellin-1 (PmPV1) is the most abundant perivitellin found in the perivitelline fluid from Pomacea maculata snail eggs. This glyco-lipo-caroteno protein is an approx. 294 kDa multimer of a combination of multiple copies of six different ~30 kDa subunits. PmPV1 account >60% of the total proteins found in the Pomacea maculata eggs. PmPV1 is an orthologous of ovorubin and scalarin, sharing most of the structural features with the former protein…
-
Ovorubin
Ovorubin (PcOvo or PcPV1) is the most abundant perivitellin (>60 % total protein) of the perivitelline fluid from Pomacea canaliculata snail eggs. This glyco-lipo-caroteno protein complex is a approx. 300 kDa multimer of a combination of multiple copies of six different ~30 kDa subunits. Together with the other perivitellins from Pomacea canaliculata eggs, ovorubin serves a nutrient source for developing embryos, notably to the intermediate and late stages. Moreover, after hatching,…
-
The membrane attack complex (MAC) or terminal complement complex (TCC) is a complex of proteins typically formed on the surface of pathogen cell membranes as a result of the activation of the host’s complement system, and as such is an effector of the immune system
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia See also: MACPF The membrane attack complex (MAC) or terminal complement complex (TCC) is a complex of proteins typically formed on the surface of pathogen cell membranes as a result of the activation of the host’s complement system, and as such is an effector of the immune system. Antibody-mediated complement activation leads to MAC deposition on the surface of infected cells. Assembly…
-
Complement control protein are proteins that interact with components of the complement system
The complement system is tightly regulated by a network of proteins known as “regulators of complement activation (RCA)” that help distinguish target cells as “self” or “non-self.” A subset of this family of proteins, complement control proteins (CCP), are characterized by domains of conserved repeats that direct interaction with components of the complement system. These “Sushi” domains have…
-
A complement receptor is a membrane-bound receptor belonging to the complement system, which is part of the innate immune system
Complement receptors bind effector protein fragments that are produced in response to antigen-antibody complexes or damage-associated molecules. Complement receptor activation contributes to the regulation of inflammation, leukocyte extravasation, and phagocytosis; it also contributes to the adaptive immune response. Different complement receptors can participate in either the classical complement pathway, the alternative complement pathway, or both. Expression and function White blood cells, particularly monocytes and macrophages, express complement receptors on their surface.…
-
Rosetting
Erythrocyte rosetting or E-rosetting is a phenomenon seen through a microscope where red blood cells (erythrocytes) are arranged around a central cell to form a cluster that looks like a flower. The red blood cells surrounding the cell form the petal, while the central cell forms the stigma of the flower shape. This formation occurs due to an immunological reaction between an epitope on the central cell’s surface and…
-
Complement receptor type 1 (CR1)
Complement receptor type 1 (CR1) also known as C3b/C4b receptor or CD35 (cluster of differentiation 35) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CR1 gene. This gene is a member of the regulators of complement activation (RCA) family and is located in the ‘cluster RCA’ region of chromosome 1. The gene encodes a monomeric single-pass type I membrane glycoprotein found on erythrocytes, leukocytes, glomerular podocytes, hyalocytes, and splenic follicular dendritic…
-

A Mad Scientist’s Dream – Rumpless Chickens (and more)
Today, we delve into the bizarre phenomenon of rumpless chickens—a feathered marvel characterized by caudal dysplasia, or as some like to call it, the ultimate chicken makeover! These quirky birds are missing their pygostyle, that charming little appendage known as the “parson’s nose,” a mutation that defies nature itself. This peculiar trait is inherited through…
-
Effect of biotin deficiency on embryonic development in the domestic fowl (1944) with reference and cited by articles
The approximate biotin requirements of breeding hens have been established and the embryos examined for gross pathological symptoms and the approximate age at death are recorded. Cravens, W.W., W., & Sebesta, M.A. (1944). Effect of biotin deficiency on embryonic development in the domestic fowl. The Anatomical Record, 90. Reference articles Effect of Biotin on Reproduction in…
Recent Posts
- 🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
- 🧂 Sodium Reduction and Sodium Replacement: A History of Reformulation and Exploding Diseases, Including Many Diseases Unheard of Before Deadly Sodium Policies
- 🧂 The DEADLY 1500 mg Sodium Recommendation predates the WHO’s formal global sodium reduction push by nearly a decade (and it’s even worse than that)
- 🧬 What Is Beta-Glucuronidase?
- When Sugar Was Salt: Crystalline Confusion and the Covenant of Sweetness
Tags
ADAM ASPARTAME Birds Blood Bones Brain Bugs Cancer Columba Cows crystallography Death Death cults Eggs Etymology Gastrin Gold Growth hormone History Hormones Insulin Liver Mere Perplexity Metal Monkey Business Mythology Paracetamol Plants Poison Pregnancy Protein Religion Reproduction Rocks Salt Slavery Snakes Sodium the birds and the bees Thiocyanate Tobacco Tylenol Underworld Venom zinc
