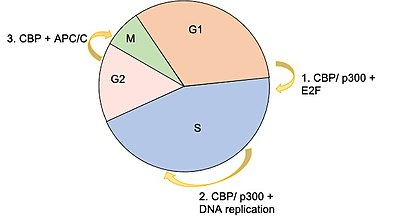
CBP and p300 are critical for normal embryonic development
Mouse models CBP and p300 are critical for normal embryonic development, as mice completely lacking either CBP or p300 protein, die at an early embryonic stage. In addition, mice which lack one functional copy (allele) of both the CBP and p300 genes (i.e. are heterozygous for both CBP and p300) and thus haveContinue Reading