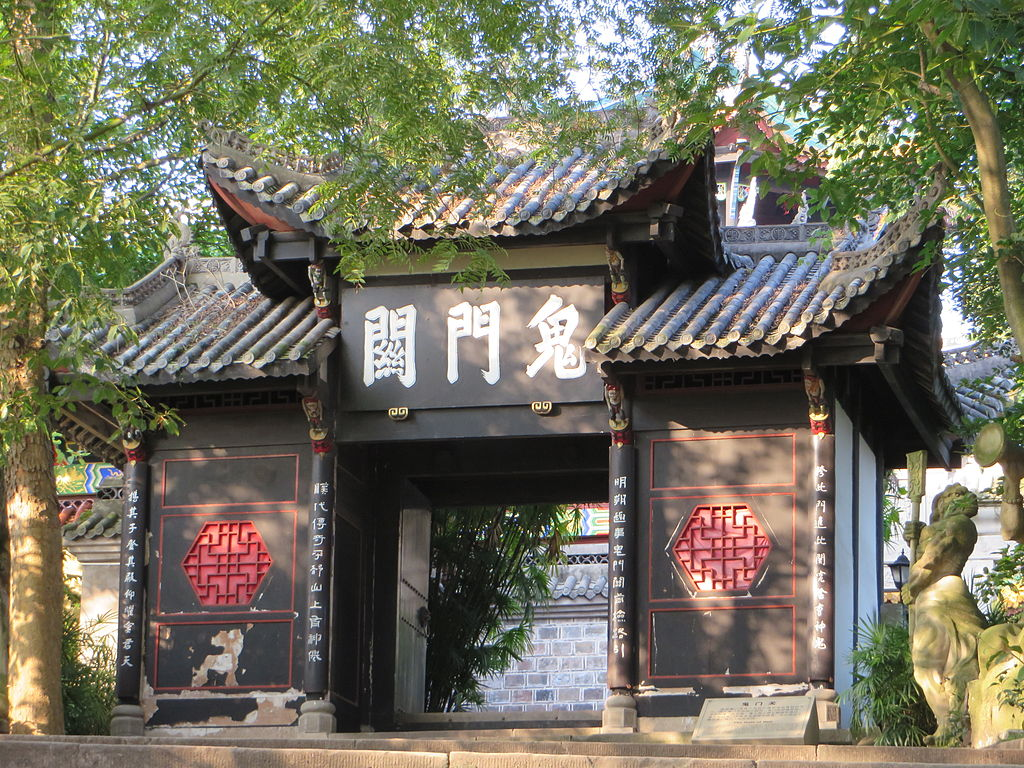
Gate of the Ghosts
The Gate of the Ghosts (simplified: 鬼门关; traditional: 鬼門關), or Devil’s Gate, Demon Gate, known as Guimen guan in Chinese, is a pass in the Underworld in Chinese mythology. The gate is a pailou (also known as a paifang, a traditional style of Chinese architectural arch or…
Diyu (‘earth prison’) is the realm of the dead in Chinese mythology
Diyu (simplified Chinese: 地狱; traditional Chinese: 地獄; pinyin: dìyù; lit. ‘earth prison’) is the realm of the dead or “hell” in Chinese mythology. It is loosely based on a combination of the Buddhist concept of Naraka, traditional Chinese beliefs about…
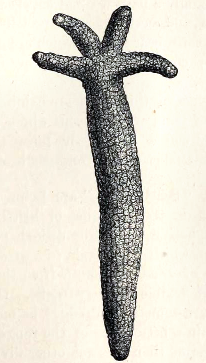
Echinoderm reproduction and pluteus larva
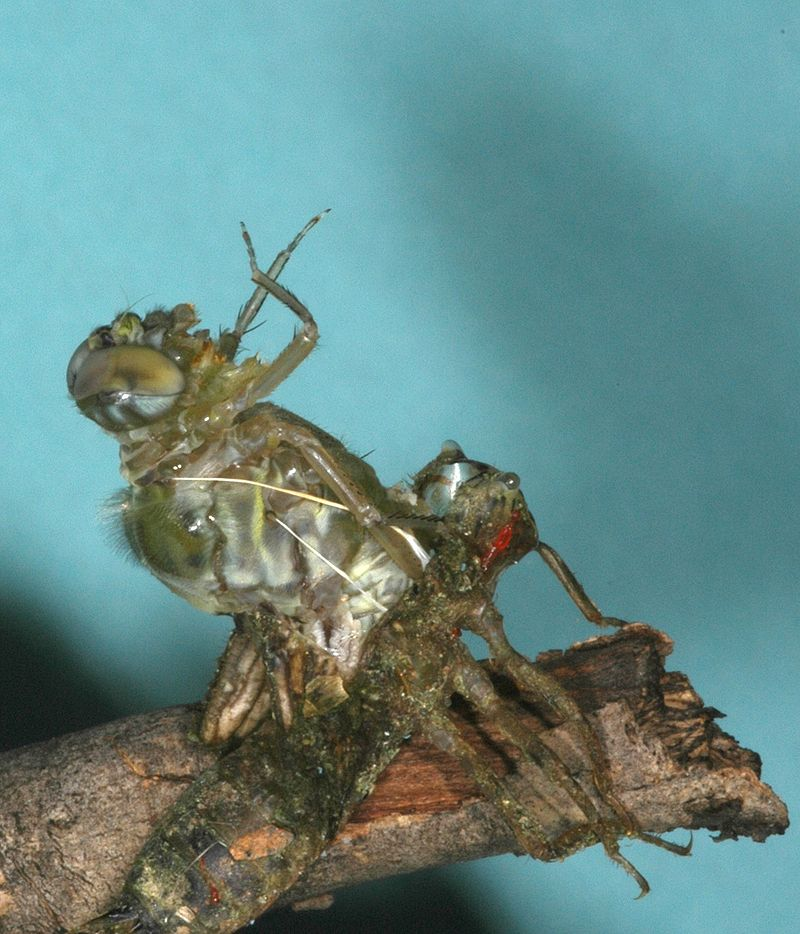
An echinoderm is any member of the phylum Echinodermata. The adults are recognisable by their (usually five-point) radial symmetry, and include starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers, as well as the sea lilies or “stone lilies”. Adult echinoderms…
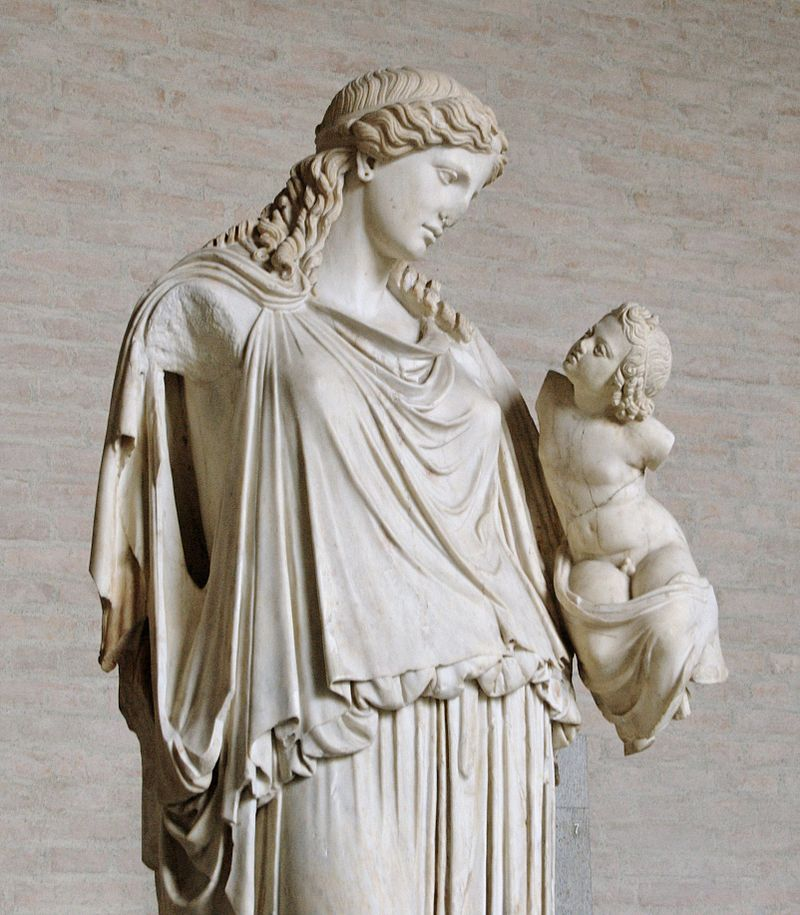
Plutus Notes
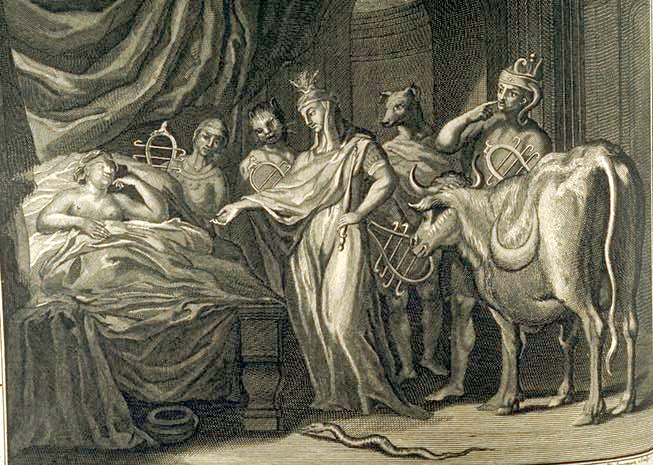
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Plutus (Ploûtos, lit. “wealth”) is the god and the personification of wealth, and the son of the goddess of agriculture Demeter and the mortal Iasion. Family Plutus is most commonly the son of Demeter and Iasion, with whom she lay in a…
Acharaca was a village of ancient Lydia with a Ploutonion or a temple of Pluto and a cave named Charonium
Acharaca was a village of ancient Lydia, Anatolia on the road from Tralles (modern Aydın, Turkey) to Nysa on the Maeander, with a Ploutonion or a temple of Pluto, and a cave, named Charonium (Ancient Greek: Χαρώνειον άντρον), where the…
Charonium at Aornum
Aornum was an oracle in Ancient Greece, located in Thesprotia in a cave called Charonium (Χαρώνειον ἄντρον or χάσμα) which gave forth poisonous vapours. The name of the cave, “Charon‘s Cave”, reflects the belief that it was…
Iphis Notes
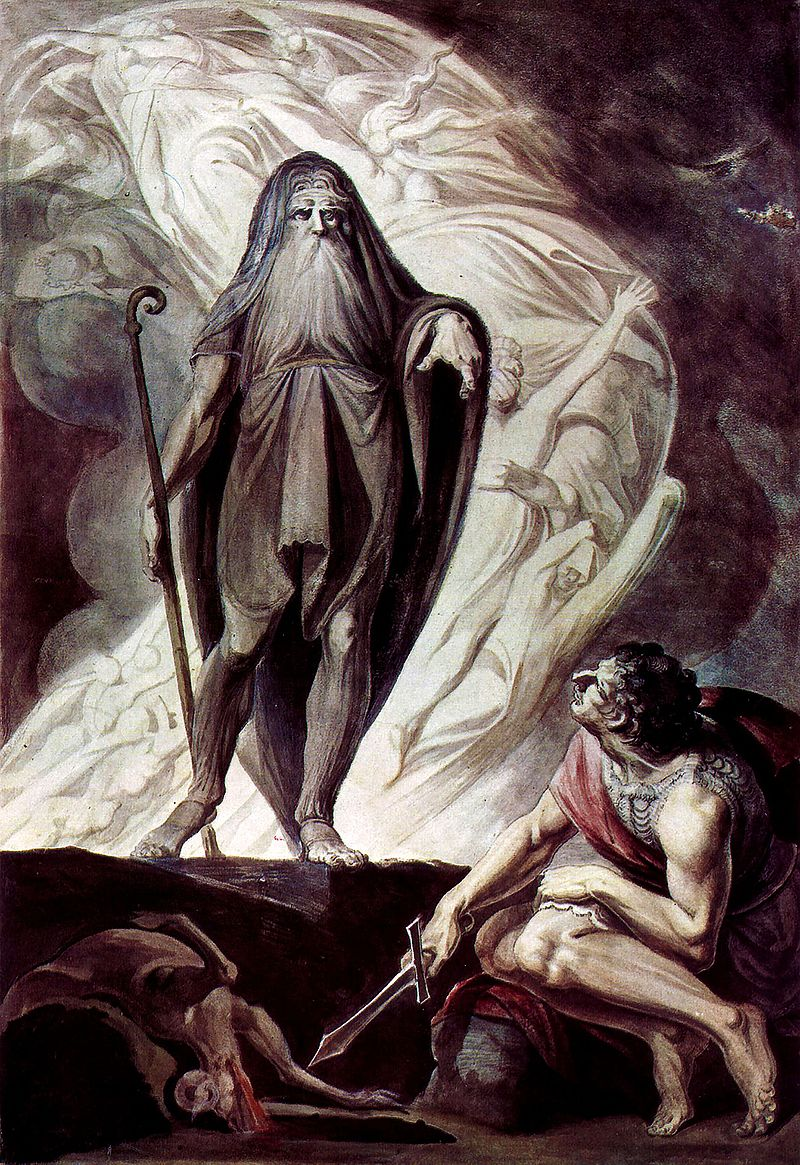
In Greek and Roman mythology, Iphis or Iphys was a child of Telethusa and Ligdus in Crete, born female and raised male, who was later transformed by the goddess Isis into a man. (/ˈaɪfɪs/ EYE-fis, /ˈɪfɪs/ IF-iss; Ancient Greek: Ἶφις Îphis [íi.pʰis], gen. Ἴφιδος Ī́phidos) Mythology According to the Roman poet Ovid‘s Metamorphoses,…
Mews derives from the French muer, ‘to moult’
A mews is a row or courtyard of stables and carriage houses with living quarters above them, built behind large city houses before motor vehicles replaced horses in the early twentieth century. Mews are usually located…