Category: The Other Things
-
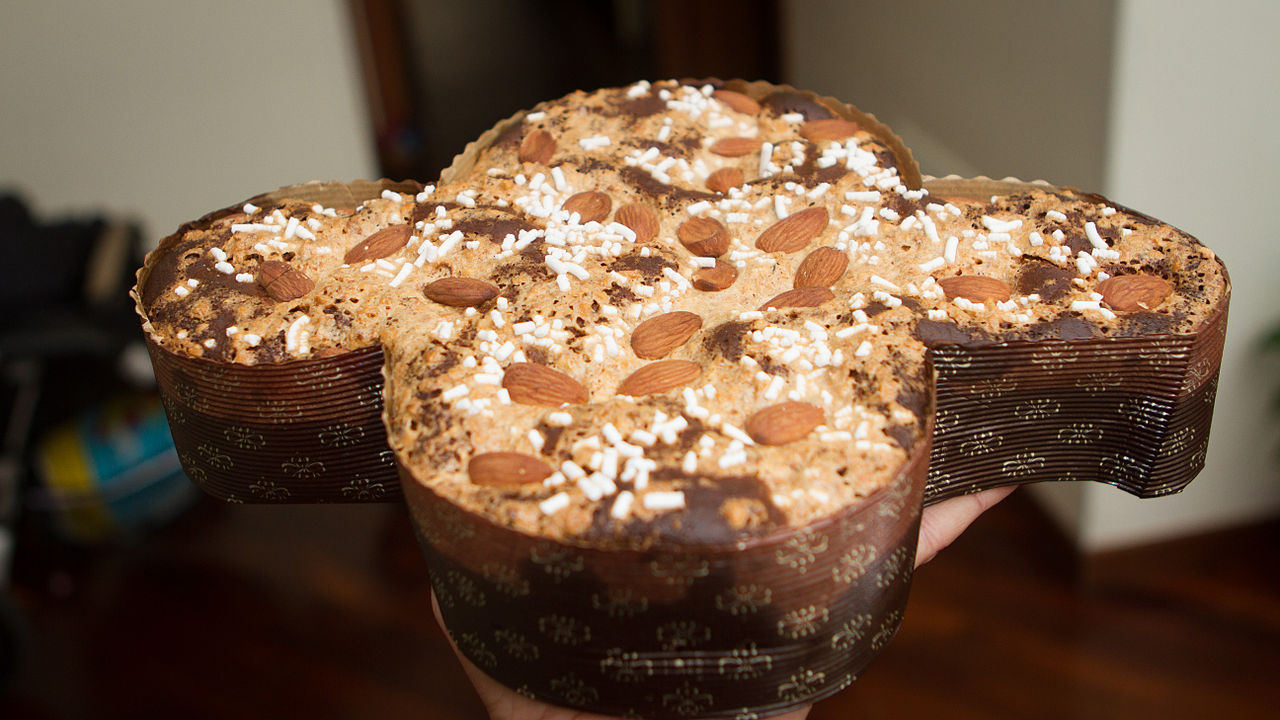

Colomba pasquale, Italian Easter bread
Colomba pasquale [koˈlomba paˈskwaːle] or colomba di Pasqua [koˈlomba di ˈpaskwa] (“Easter Dove” in English) is an Italian traditional Easter bread, the counterpart of the two well-known Italian Christmas desserts, panettone and pandoro. The dough for the colomba is made in a similar manner to panettone, with flour, eggs, sugar, natural yeast and butter; unlike panettone, it usually contains candied peel and no raisins. The dough is then fashioned into a dove shape (colomba in Italian) and finally…
-
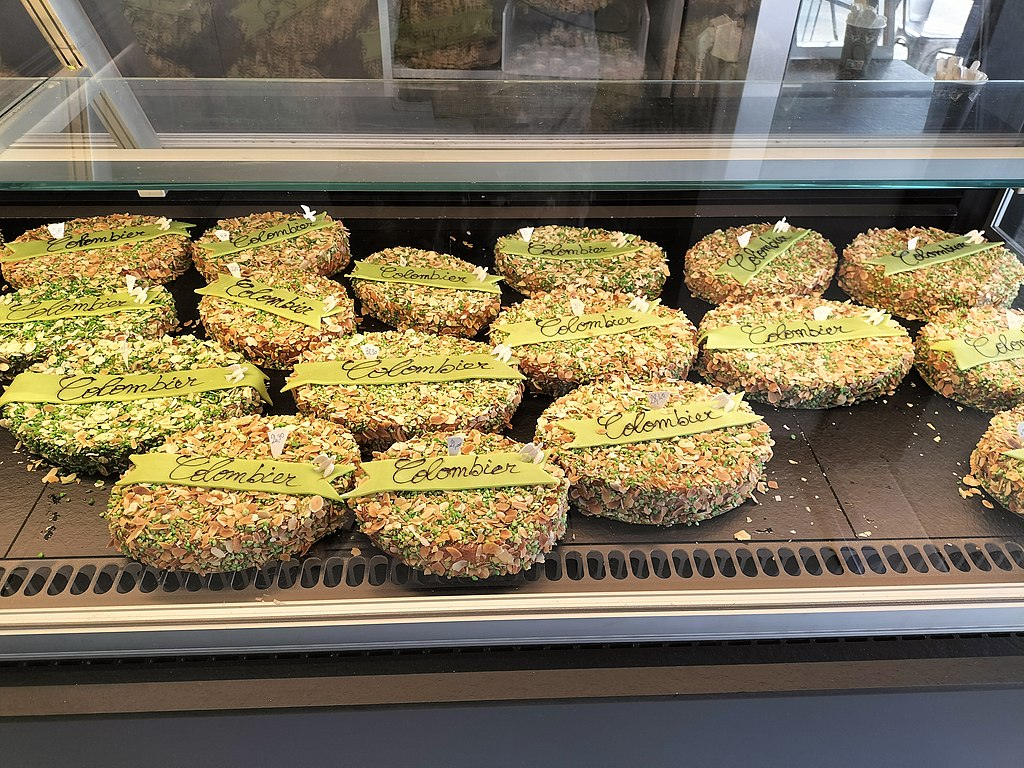

Dovecote cake and the founding myth of Marseille
In Marseille tradition, the dovecote is a cake offered by pastry chefs at the time of Pentecost: cake made from almonds and melon, covered with sugar, generously colored, flavored with kirsch and inside is hidden a dove. This oval-shaped cake is adorned with a strip of marzipan on which is written: “whoever the dove will have in the year will marry”. This typically Marseilles tradition,…
-
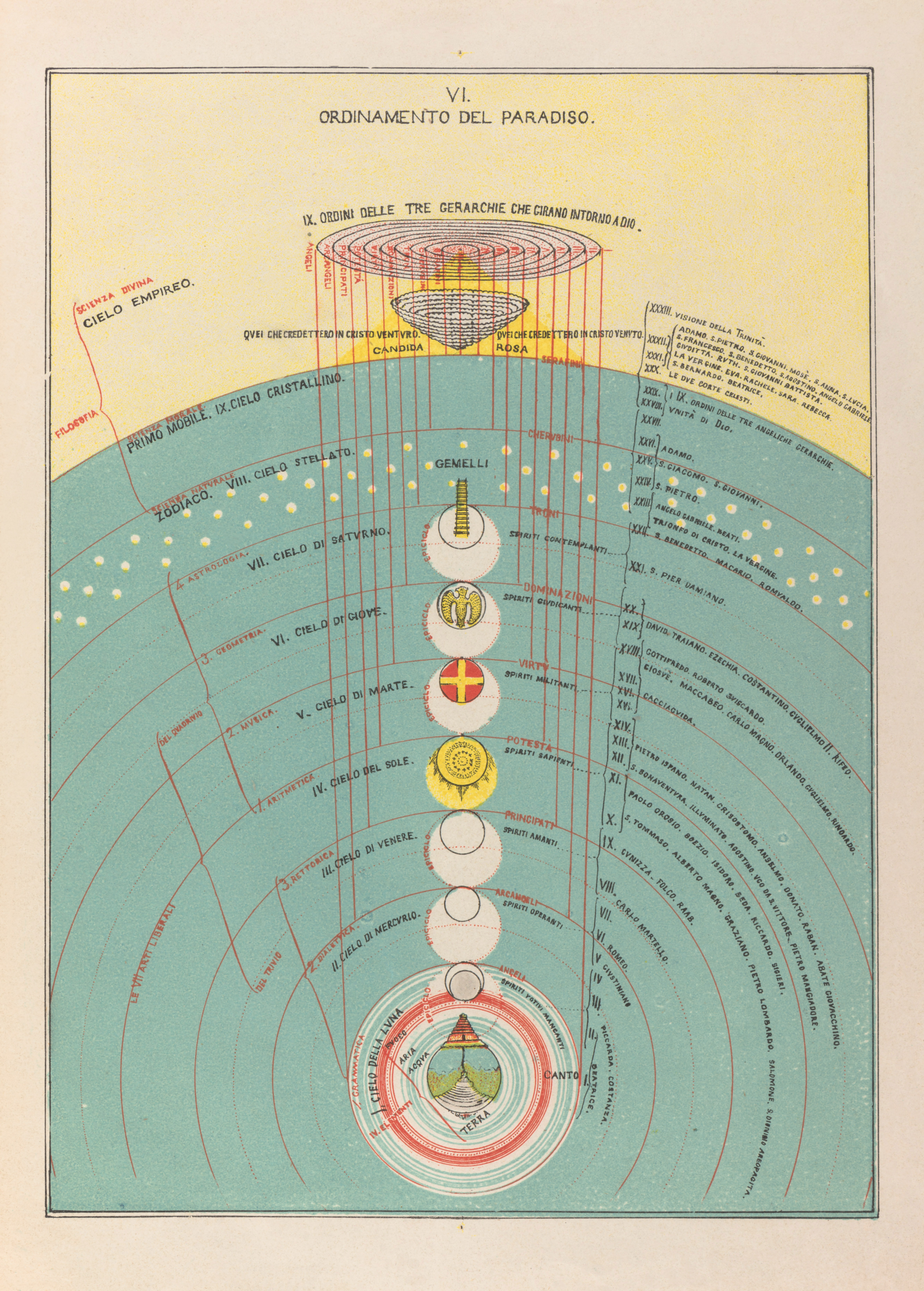
Seven heavens notes
In religious or mythological cosmology, the seven heavens refer to seven levels or divisions of the Heavens. The concept, also found in the ancient Mesopotamian religions, can be found in Judaism, Christianity, and Islam; a similar concept is also found in some other religions such as Hinduism. Some of these traditions, including Jainism, also have a concept of seven earths or seven underworlds both with the metaphysical realms of deities and with observed…
-
In Judaism, The Guf or Treasury of Souls is sometimes described as a columbarium
In post-biblical Judaism, souls are envisioned as bird-like (Bahir 119), a concept that may be derived from the Biblical notion that dead spirits “chirp” (Isa. 29:4). The Guf, or Treasury of Souls, is sometimes described as a columbarium, a dovecote. This connects it to a related legend: the “Palace of the Bird’s Nest”, the dwelling place of the…
-
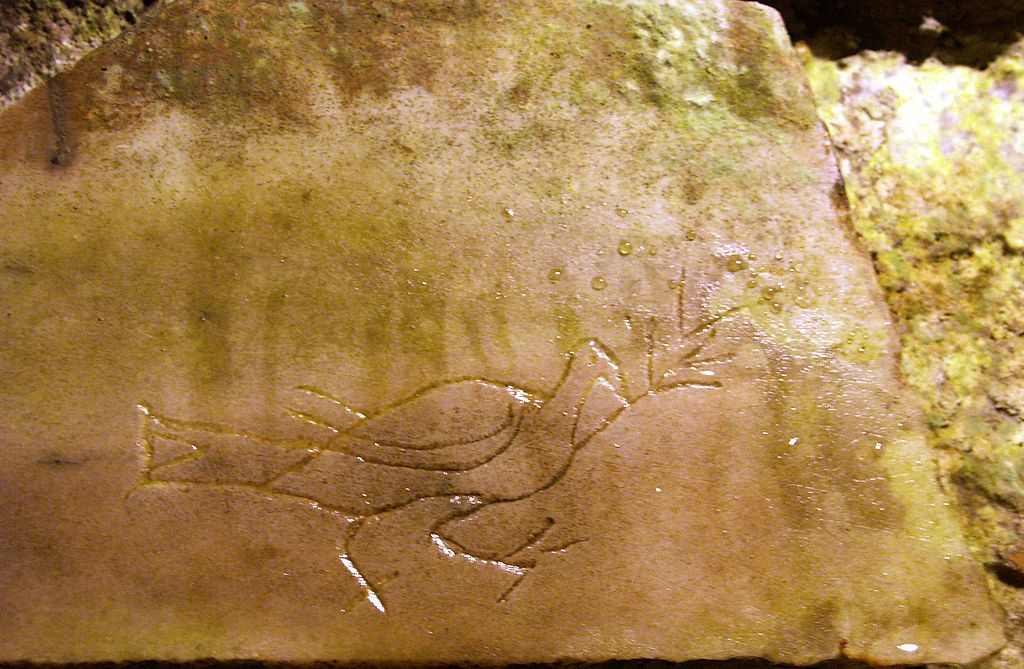

The dove and the raven and the flood notes
According to the biblical story (Genesis 8:11), a dove was released by Noah after the Flood in order to find land; it came back carrying a freshly plucked olive leaf (Hebrew: עלה זית alay zayit),[Gen 8:11] a sign of life after the Flood and of God’s bringing Noah, his family and the animals to land. Rabbinic literature interpreted the olive leaf as “the young shoots of…
-
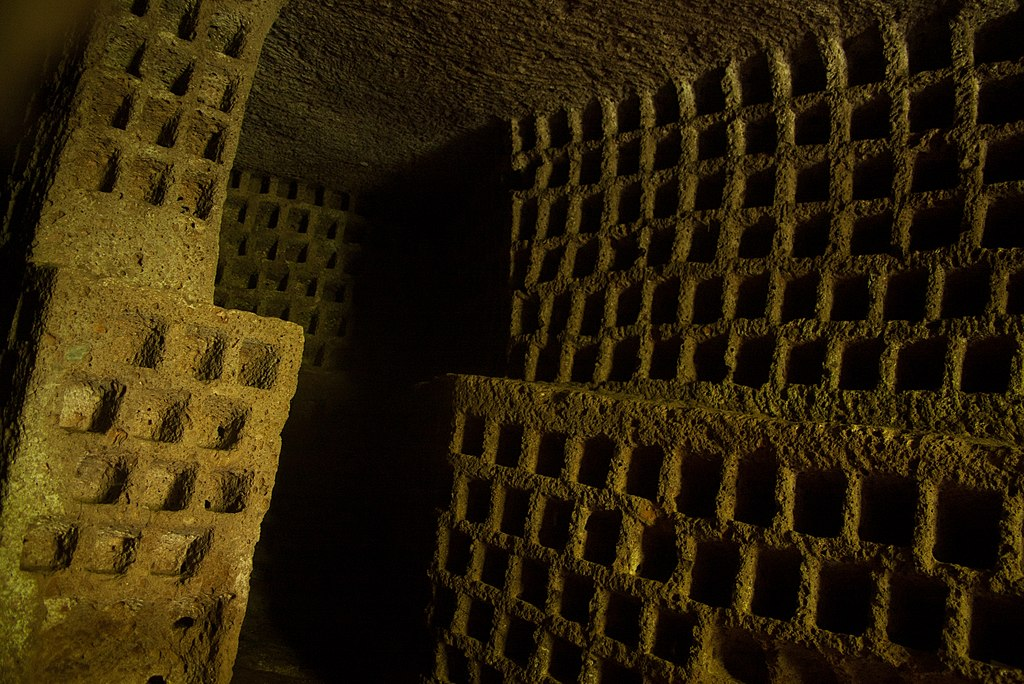

A columbarium is a structure for the reverential and usually public storage of funerary urns holding cremains of the dead
A columbarium (pl. columbaria) is a structure for the reverential and usually public storage of funerary urns holding cremains of the dead. The term comes from the Latin columba (dove) and originally solely referred to compartmentalized housing for doves and pigeons, also called dovecotes. Background Roman columbaria were often built partly or completely underground. The Columbarium of Pomponius Hylas is an ancient Roman example, rich in frescoes, decorations, and…
-
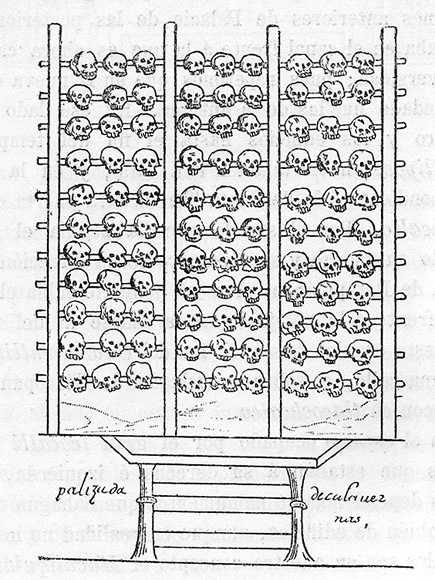
A tzompantli or skull rack was used for the public display of human skulls, typically of war captives or sacrificial victims
A tzompantli (Nahuatl pronunciation: [t͡somˈpant͡ɬi]) or skull rack was a type of wooden rack or palisade documented in several Mesoamerican civilizations, which was used for the public display of human skulls, typically those of war captives or other sacrificial victims. It is a scaffold-like construction of poles on which heads and skulls were placed after holes had been made in them. Many have been documented throughout Mesoamerica,…
-
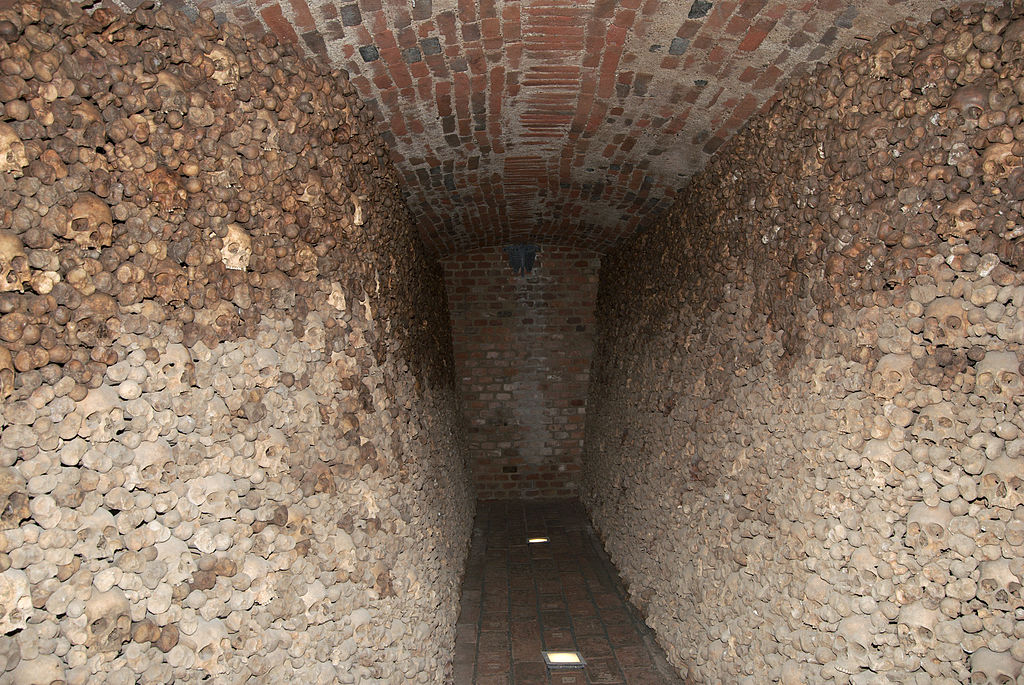

Brno Ossuary holds the remains of over 50 thousand people
Brno Ossuary is an underground ossuary in Brno, Czech Republic. It was rediscovered in 2001 in the historical centre of the city, partially under the Church of St. James. It is estimated that the ossuary holds the remains of over 50 thousand people which makes it the second-largest ossuary in Europe, after the Catacombs of Paris. The ossuary was founded in the 17th century,…
-
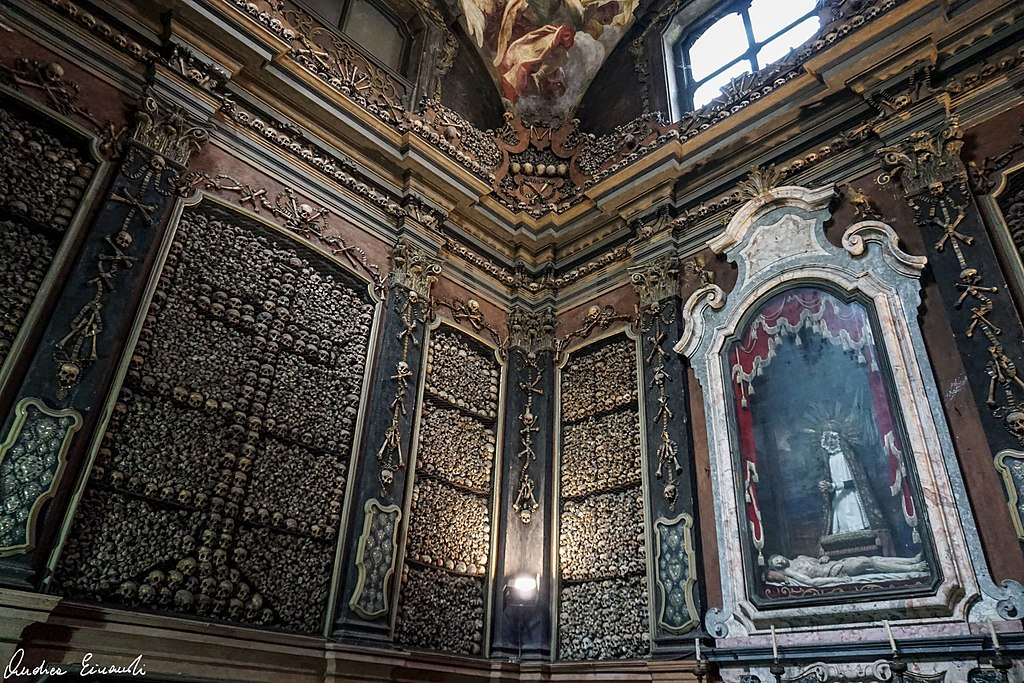

San Bernardino alle Ossa, Milan
San Bernardino alle Ossa is a church in Milan, northern Italy, best known for its ossuary, a small side chapel decorated with numerous human skulls and bones. In 1210, when an adjacent cemetery ran out of space, a room was built to hold bones. A church was attached in 1269. Renovated in 1679, it was destroyed by a…
-
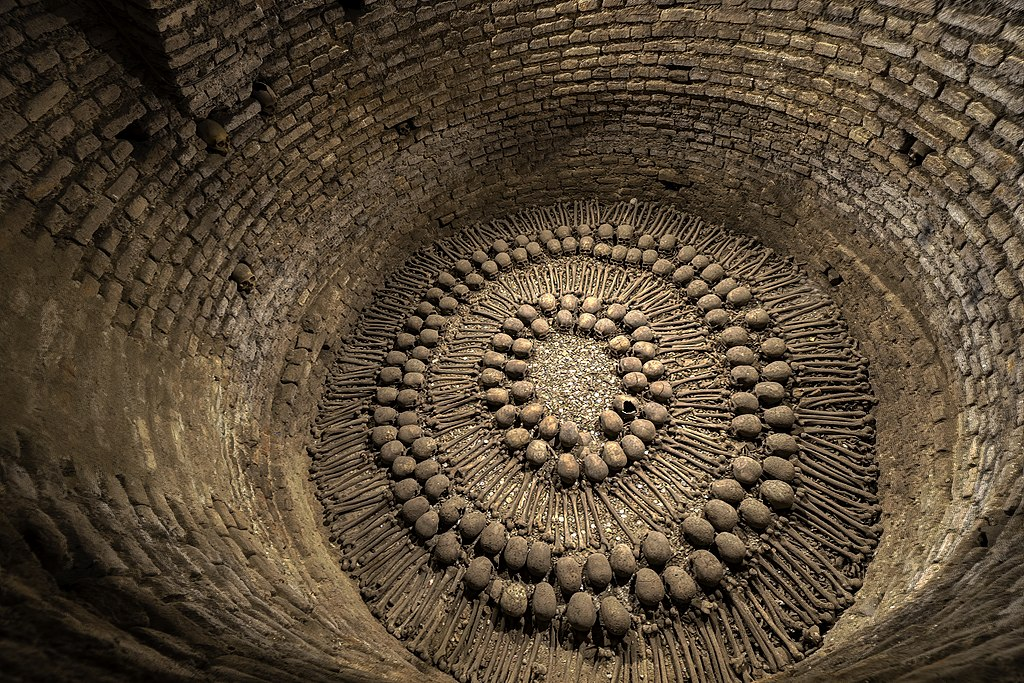

Catacombs of Lima, Peru
The Catacombs of Lima (Spanish: Catacumbas de Lima) are underground ossuaries in the historic centre of Lima, Peru. The catacombs were built under the Basilica and Convent of San Francisco and currently function as a museum. History In 1546, the Franciscan order began construction of the Basilica and Convent of San Francisco in Lima, which included the catacombs, built to support the convent in the event of an earthquake. The crypt’s use as a cemetery continued for almost…
-
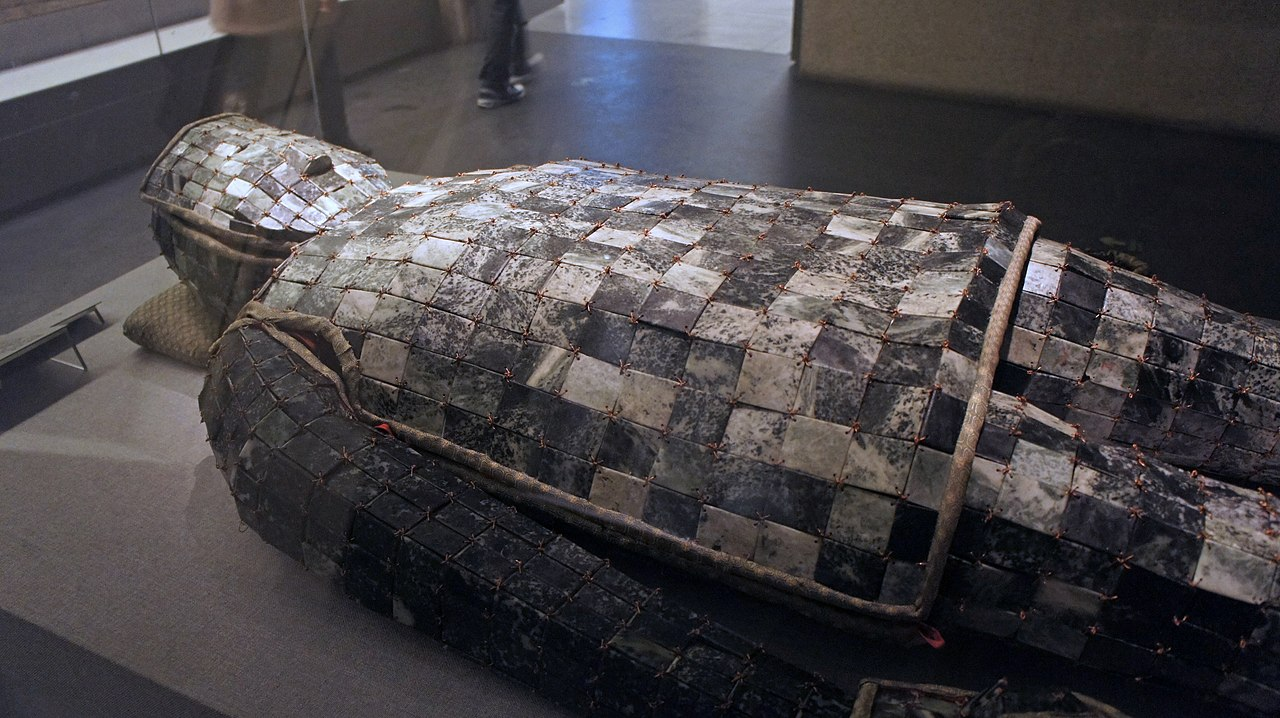

Jade burial suit
A jade burial suit (Chinese: 玉衣; pinyin: yù yī; lit. ‘jade clothing’) is a ceremonial suit made of pieces of jade in which royal members in Han dynasty China were buried. Construction Of the jade suits that have been found, the pieces of jade are mostly square or rectangular in shape, though triangular, trapezoid and rhomboid plaques have also been found. Plaques are often joined by means of…
-
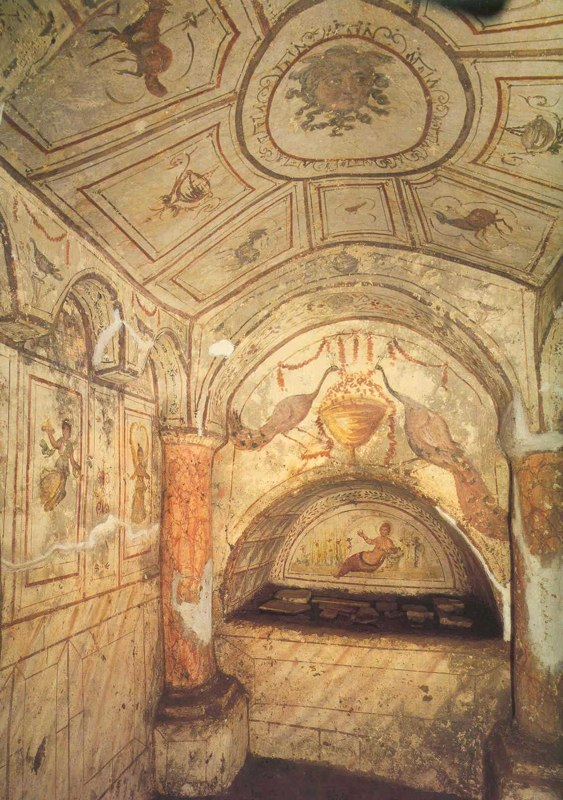

An arcosolium is an arched recess used as a place of entombment
An arcosolium, plural arcosolia, is an arched recess used as a place of entombment. The word is from Latin arcus, “arch”, and solium, “throne” (literally “place of state”) or post-classical “sarcophagus“.[dubious – discuss] Early arcosolia were carved out of the living rock in catacombs. In the very earliest of these, the arched recess was cut to ground level. Then a low wall would be…
-
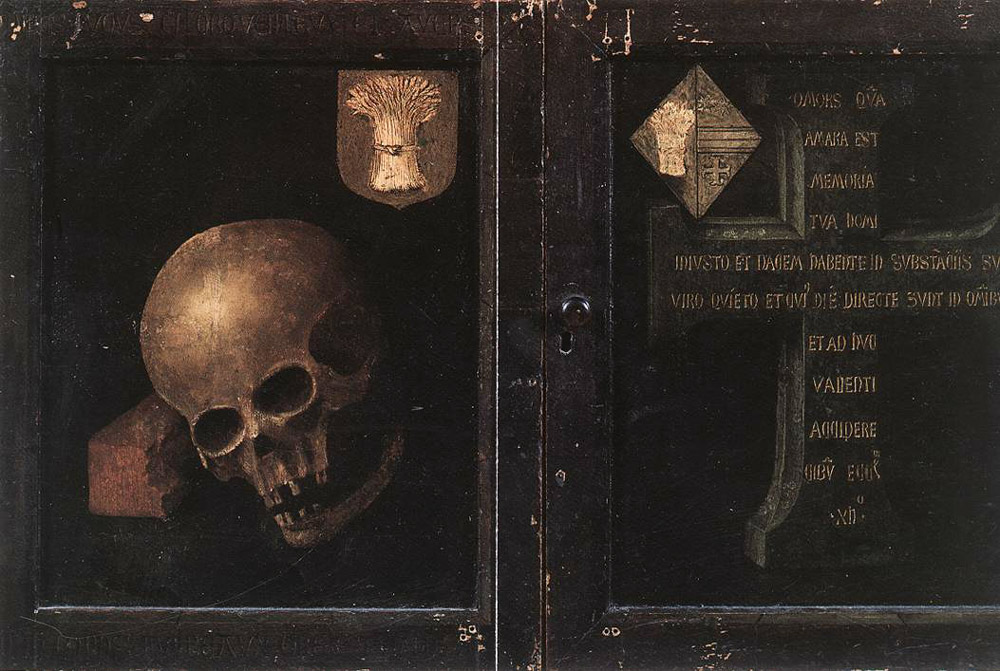

Memento mori (symbolic trope)
Memento mori (Latin for ‘remember that you [have to] die’) is an artistic or symbolic trope acting as a reminder of the inevitability of death. The concept has its roots in the philosophers of classical antiquity and Christianity, and appeared in funerary art and architecture from the medieval period onwards. The most common motif is a skull, often accompanied by one or more bones. Often this alone is…
-

Chapel of Bones (Faro, Portugal)
The Capela dos Ossos (English: Chapel of Bones) is an ossuary chapel in Faro, Portugal, which belongs to the 18th century Carmelite church Nossa Senhora do Carmo. Above the entrance, there is the following inscription: Pára aqui a considerar que a este estado hás-de chegar which translates to Stop here and consider, that you will reach this state too. The 4 by 6 meter…
-
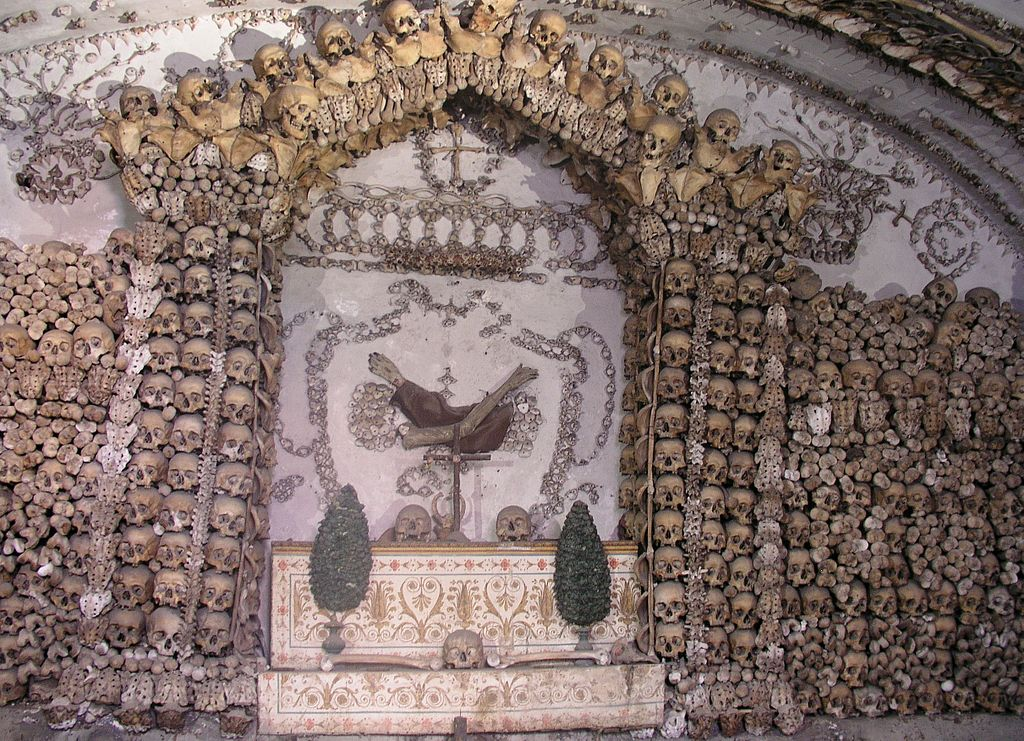

The Capuchin Crypt, Rome
The Capuchin Crypt is a small space comprising several tiny chapels located beneath the church of Santa Maria della Concezione dei Cappuccini on the Via Veneto near Piazza Barberini in Rome, Italy. It contains the skeletal remains of 3,700 bodies believed to be Capuchin friars buried by their order. The Catholic order insists that the display is not meant to be macabre, but a silent reminder of the swift passage of…
-
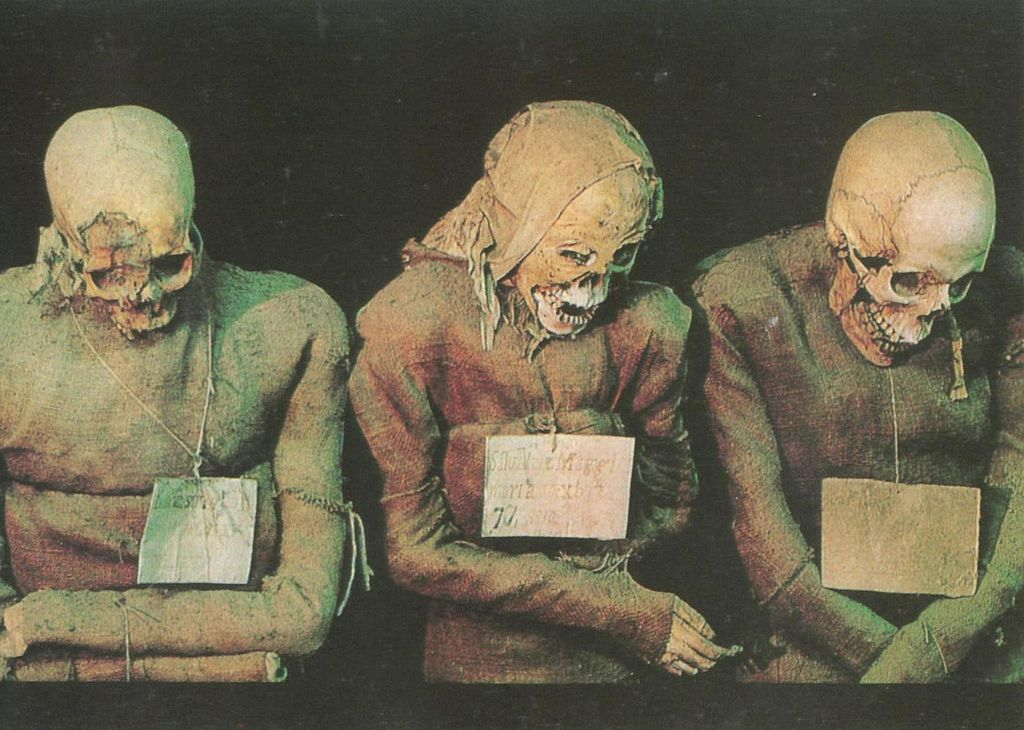

The Capuchin Catacombs of Palermo
The Capuchin Catacombs of Palermo (also Catacombe dei Cappuccini or Catacombs of the Capuchins) are burial catacombs in Palermo, Sicily, southern Italy. Today they provide a somewhat macabre tourist attraction as well as an extraordinary historical record. Historical background Palermo’s Capuchin monastery outgrew its original cemetery in the 16th century and monks began to excavate crypts below it. In 1599 they mummified one of their number, the recently-deceased brother Silvestro of Gubbio, and placed him…
Recent Posts
- 🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
- 🧂 Sodium Reduction and Sodium Replacement: A History of Reformulation and Exploding Diseases, Including Many Diseases Unheard of Before Deadly Sodium Policies
- 🧂 The DEADLY 1500 mg Sodium Recommendation predates the WHO’s formal global sodium reduction push by nearly a decade (and it’s even worse than that)
- 🧬 What Is Beta-Glucuronidase?
- When Sugar Was Salt: Crystalline Confusion and the Covenant of Sweetness
Tags
ADAM ASPARTAME Birds Blood Bones Brain Bugs Cancer Columba Cows crystallography Death Death cults Eggs Etymology Gastrin Gold Growth hormone History Hormones Insulin Liver Mere Perplexity Metal Monkey Business Mythology Paracetamol Plants Poison Pregnancy Protein Religion Reproduction Rocks Salt Slavery Snakes Sodium the birds and the bees Thiocyanate Tobacco Tylenol Underworld Venom zinc
