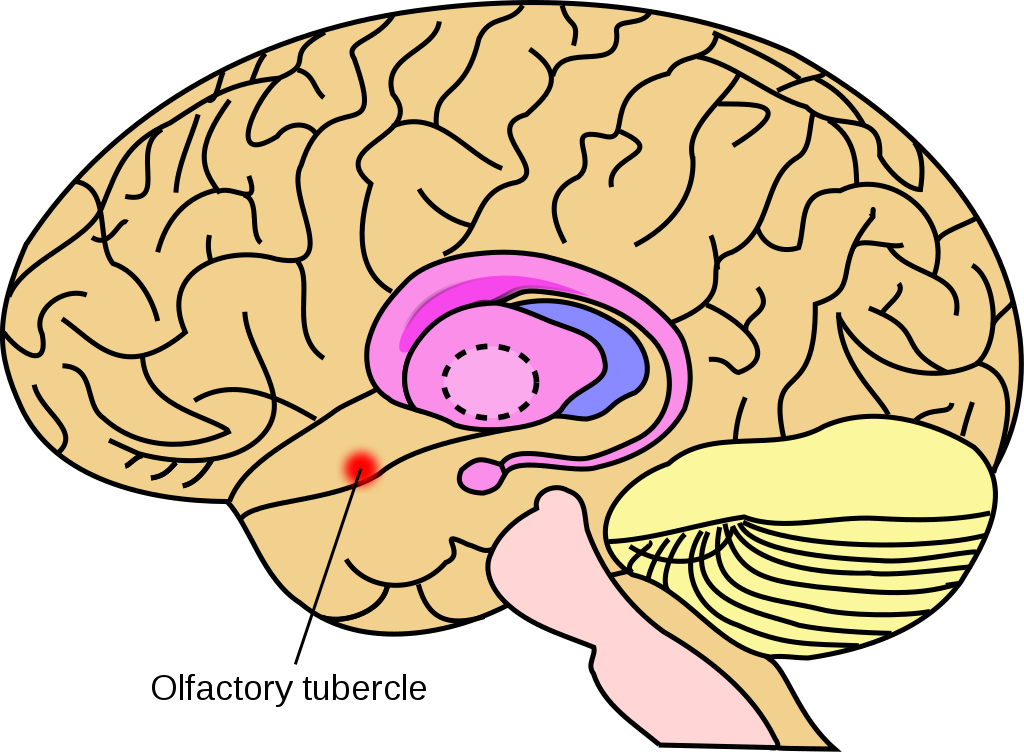
Olfactory tubercle (OT) aka tuberculum olfactorium
The olfactory tubercle (OT), also known as the tuberculum olfactorium, is a multi-sensory processing center that is contained within the olfactory cortex and ventral striatum and plays a role in reward cognition. The OT has also been shown to play a role in locomotor and attentional be
Sound-induced convulsions in the hamster associated with magnesium deficiency (1947)
Exposure of 16 hamsters maintained on an Mg deficient diet, 10 animals placed on a control diet immediately after a first convulsive attack, 10 Mg-deficient animals given Mg supplements after each induced convulsion, and 12 control animals maintained on adequate purified diet, to sound tests, indica
Studies on the nutritional basis of abnormal behavior in albino rats; the effect of pyridoxine deficiency upon sound-induced magnesium tetany (1945)
After a magnesium deficient diet for 5 to 8 days, young rats showed vasodilatation, hyperirritability, and latent tetany. Brief exposures to the sound of a resonated buzzer elicited severe tonic-clonic convulsions. When such a diet was continued for 10 to 23 days, sensitivity increased with death re
Sonification
Sonification is the use of non-speech audio to convey information or perceptualize data. Auditory perception has advantages in temporal, spatial, amplitude, and frequency resolution that open possibilities as an alternative or complement to visualization techniques. For example, the rate of
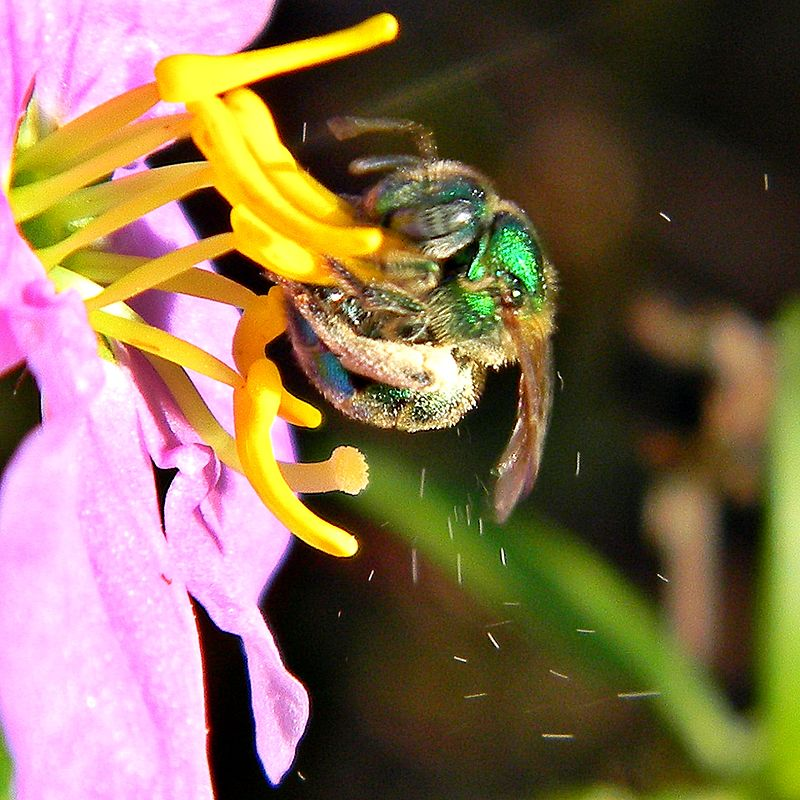
Buzz Pollination or Sonication
Buzz pollination or sonication is a technique used by some bees, such as solitary bees to release pollen which is more or less firmly held by the anthers. The anthers of buzz-pollinated plant species are typically tubular, with an opening at only one end, and
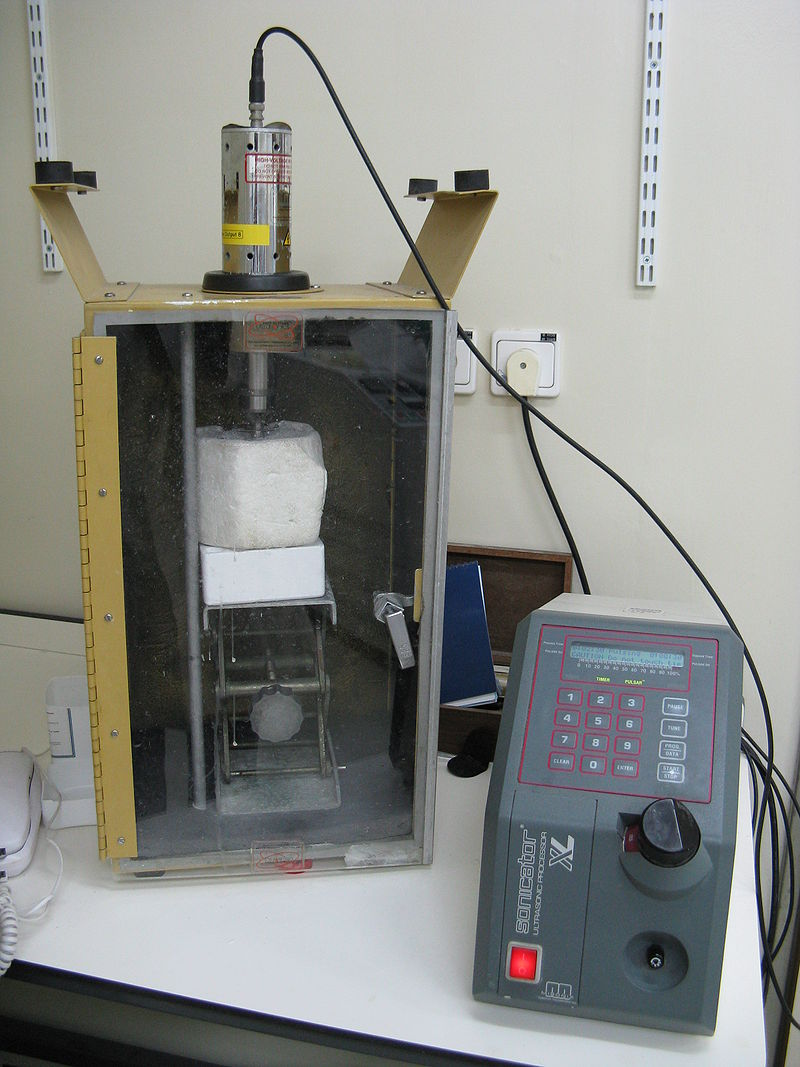
Sonication
Sonication is the act of applying sound energy to agitate particles in a sample, for various purposes such as the extraction of multiple compounds from plants, microalgae and seaweeds. Ultrasonic frequencies (> 20 kHz) are usually used, leading to the process also being known as ultrasonication
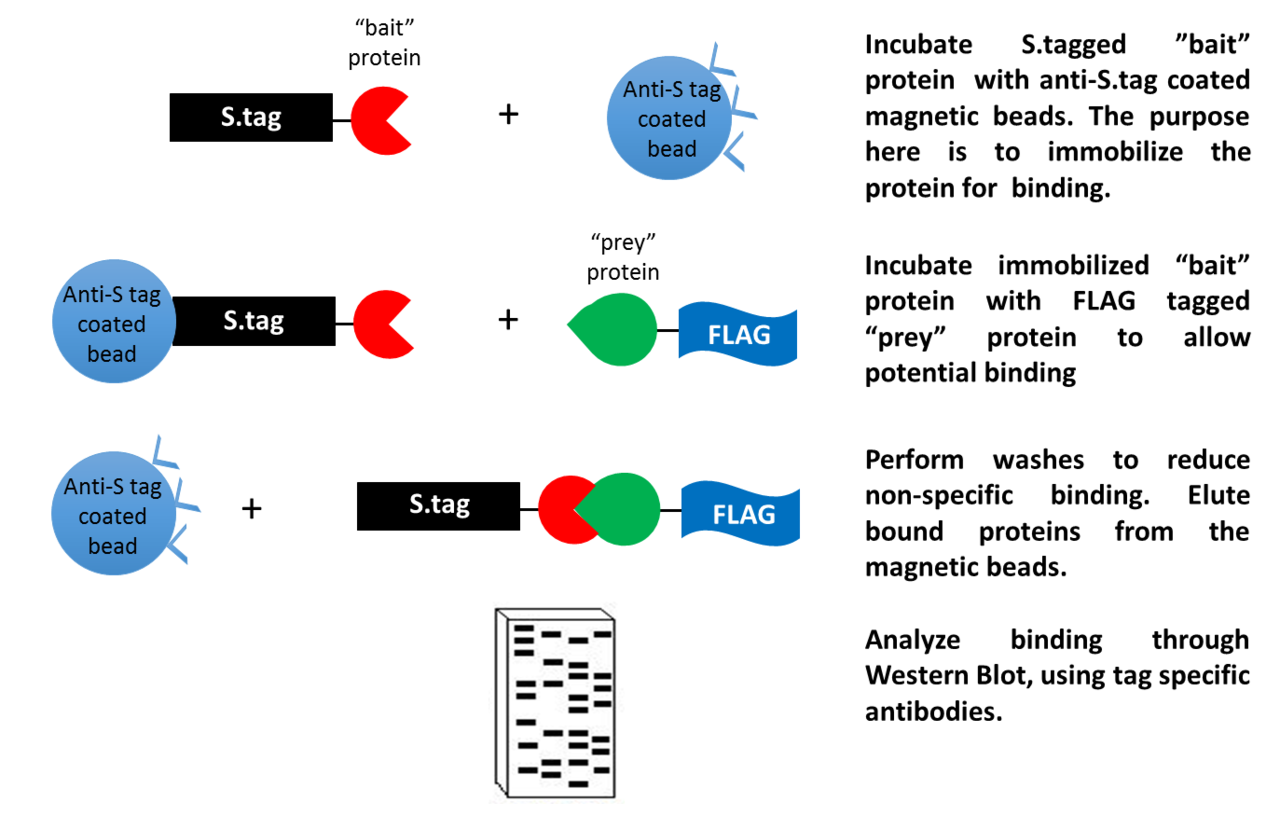
What is Immunoprecipitation (IP)?
Immunoprecipitation (IP) is a technique used to enrich protein antigens from a complex mixture using specific antibodies. To carry out an IP, antibodies must be coupled to a solid substrate, such as agarose resin or magnetic beads, to allow for purification of the target antigens. Immunoprecipitatio