The Holy Innocents’ Cemetery is a defunct cemetery in Paris that was used from the Middle Ages until the late 18th century
In 1780, the former Holy Innocents’ Cemetery in Paris was closed because of overuse. In 1786, the bodies were exhumed and the bones were moved to the Catacombs.[ “Paris’ Les Innocents cemetery”. Retrieved February 6, 2011.] Many bodies had…
Etymology of Pharmacy
pharmacy (n.) late 14c., farmacie, “a medicine that rids the body of an excess of humors (except blood);” also “treatment with medicine; theory of treatment with medicine,” from Old French farmacie “a purgative” (13c.)…
Organ Donation Back In The Day
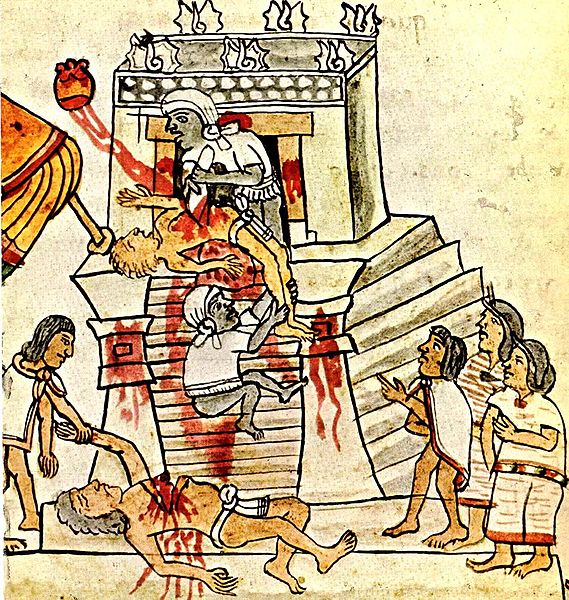
The Aztecs were particularly noted for practicing human sacrifice on a large scale; an offering to Huitzilopochtli would be made to restore the blood he lost, as the sun was engaged in a daily…
What Is Carnoy’s Solution?
Carnoy’s solution is a fixative composed of 60% ethanol, 30% chloroform and 10% glacial acetic acid, 1 gram of ferric chloride.[1][2] Carnoy’s solution is also the name of a different fixation composed of ethanol and glacial acetic acid…
Histones
In biology, histones are highly basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei. They act as spools around which DNA winds to create structural units called nucleosomes.[1][2] Nucleosomes in turn are wrapped into 30-nanometer fibers that form tightly packed chromatin. Histones…
Heterochromatin
Heterochromatin is a tightly packed form of DNA or condensed DNA, which comes in multiple varieties. These varieties lie on a continuum between the two extremes of constitutive heterochromatin and facultative heterochromatin. Both play a role in…
Leydig cells aka interstitial cells of the testes and interstitial cells of Leydig
Leydig cells, also known as interstitial cells of the testes and interstitial cells of Leydig, are found adjacent to the seminiferous tubules in the testicle and produce testosterone in the presence of luteinizing hormone (LH).[1][2] They are polyhedral in shape and have…


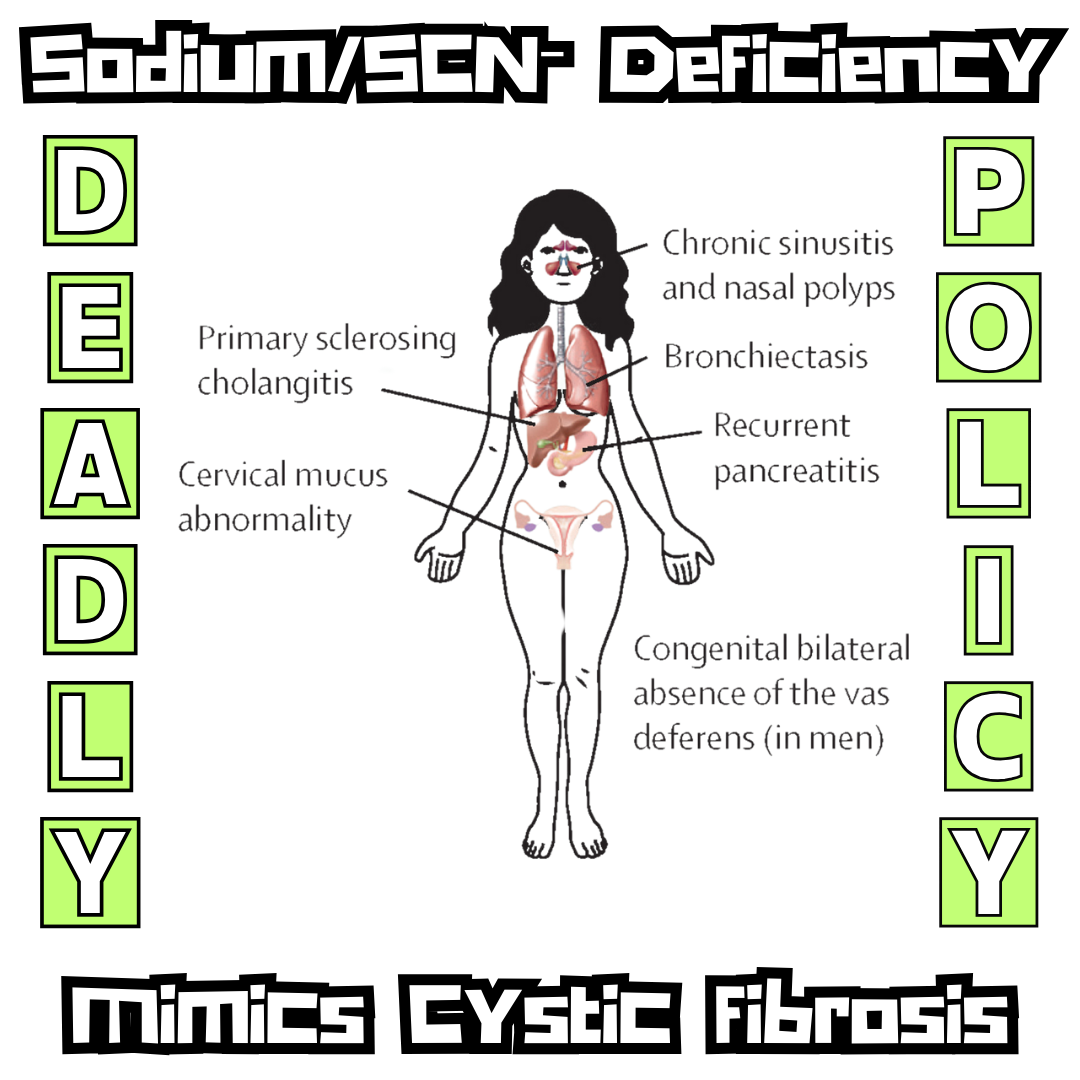
 🔥 Salt Snatchers and The Cosmic Stick-Up of Your Soul’s Swagger (with receipts)
🔥 Salt Snatchers and The Cosmic Stick-Up of Your Soul’s Swagger (with receipts) ⚡⚡Voltage Famine: Sodium, SCN⁻, and the Biochemical Coup
⚡⚡Voltage Famine: Sodium, SCN⁻, and the Biochemical Coup 🧂 Sodium & SCN⁻: The Stratified Terrain of School Meals
🧂 Sodium & SCN⁻: The Stratified Terrain of School Meals 👁️ Sodium & SCN⁻ as Ocular Guardians
👁️ Sodium & SCN⁻ as Ocular Guardians 🧬 How PTH and Vitamin D Pills Mask Sodium Deficiency
🧬 How PTH and Vitamin D Pills Mask Sodium Deficiency 🧂 Salt-Linked Town Suffixes (and stuff)
🧂 Salt-Linked Town Suffixes (and stuff) 🐄📜 The Culling Threshold: Rapeseed Meal, Livestock Illness, Birth of Canola
🐄📜 The Culling Threshold: Rapeseed Meal, Livestock Illness, Birth of Canola