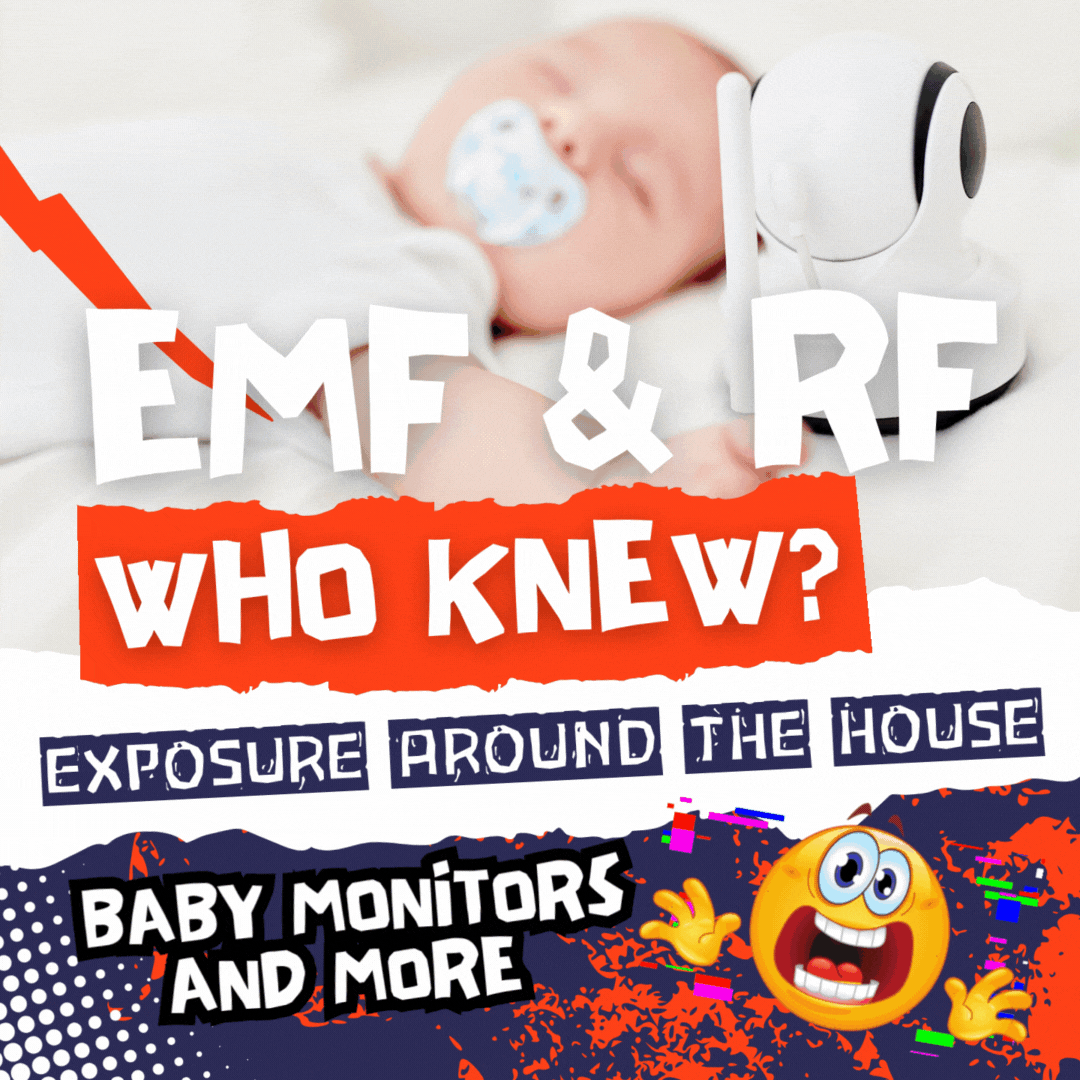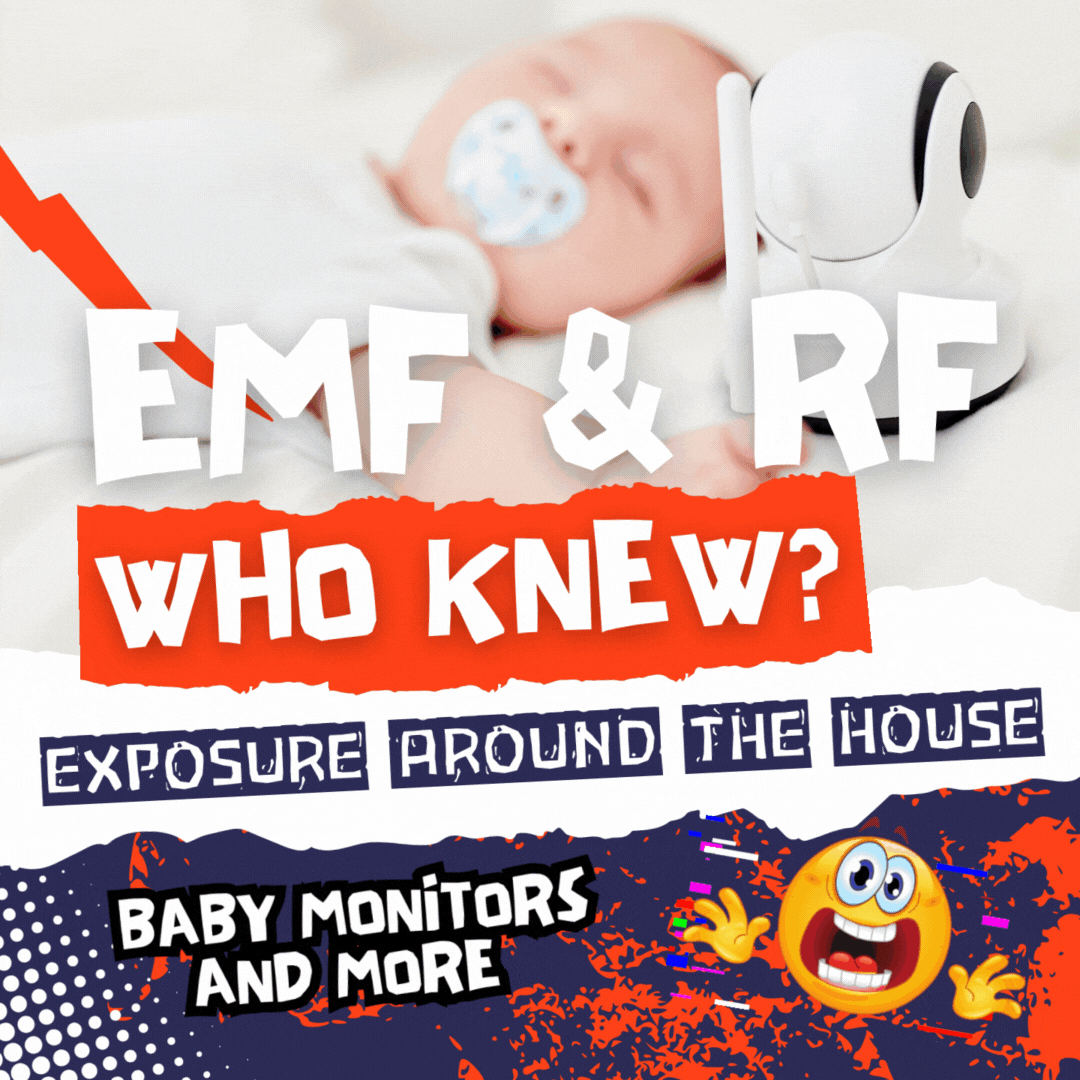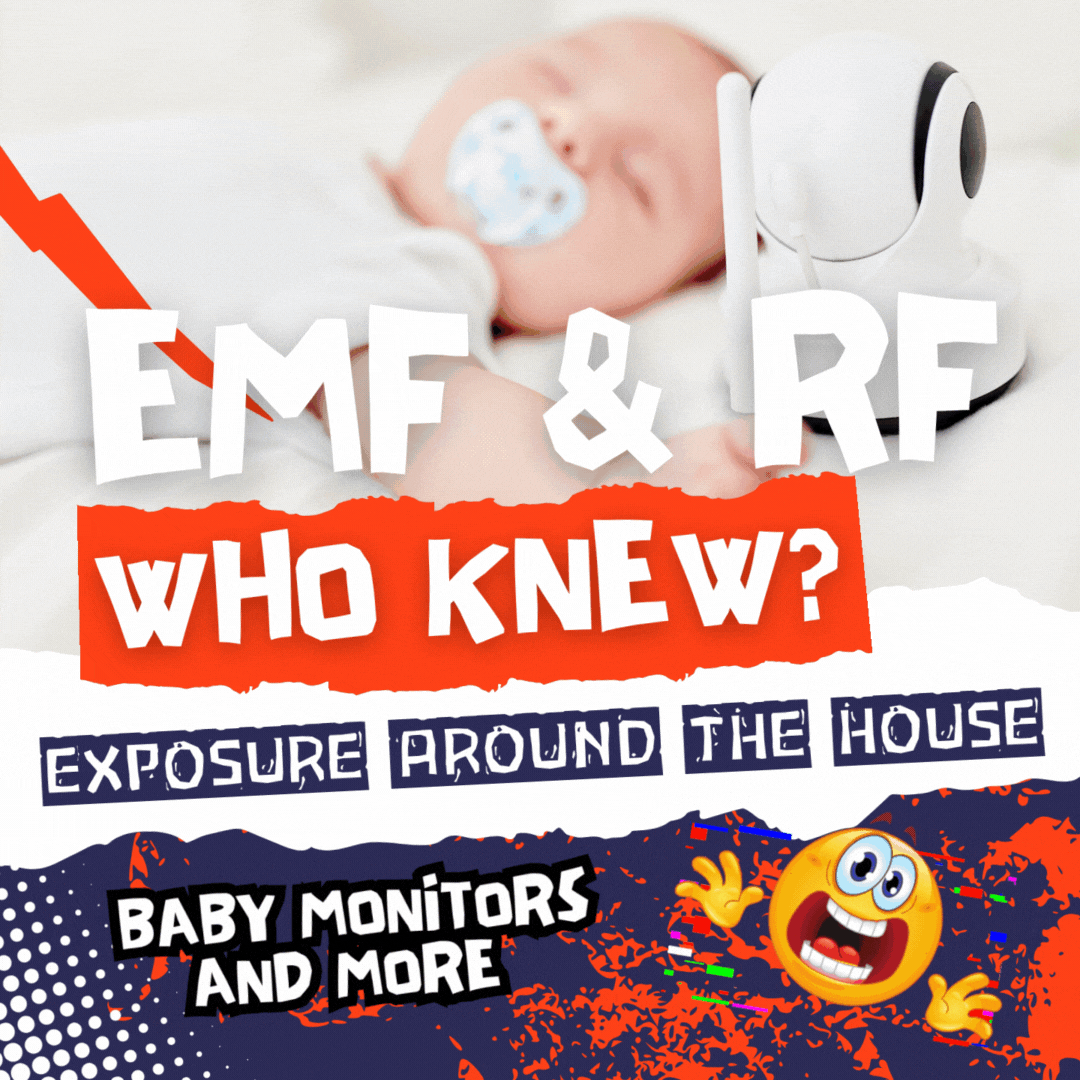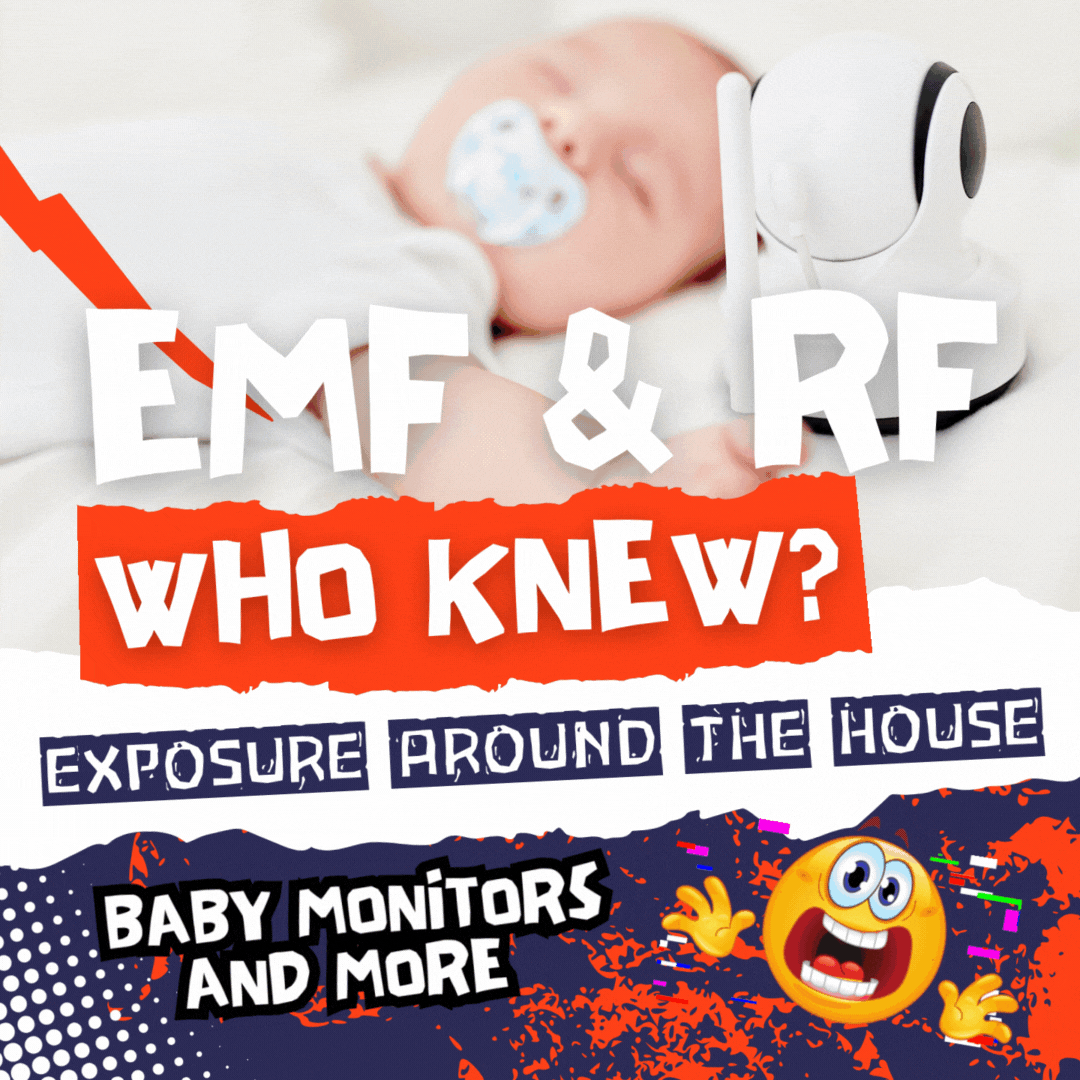
Leech Etymology
leech (n.1) “bloodsucking aquatic worm,” from Old English læce (Kentish lyce), of unknown origin (with a cognate in Middle Dutch lake). Commonly regarded as a transferred use of leech (n.2), but according to OED the Old English…
Leeches at Wellcome Collection
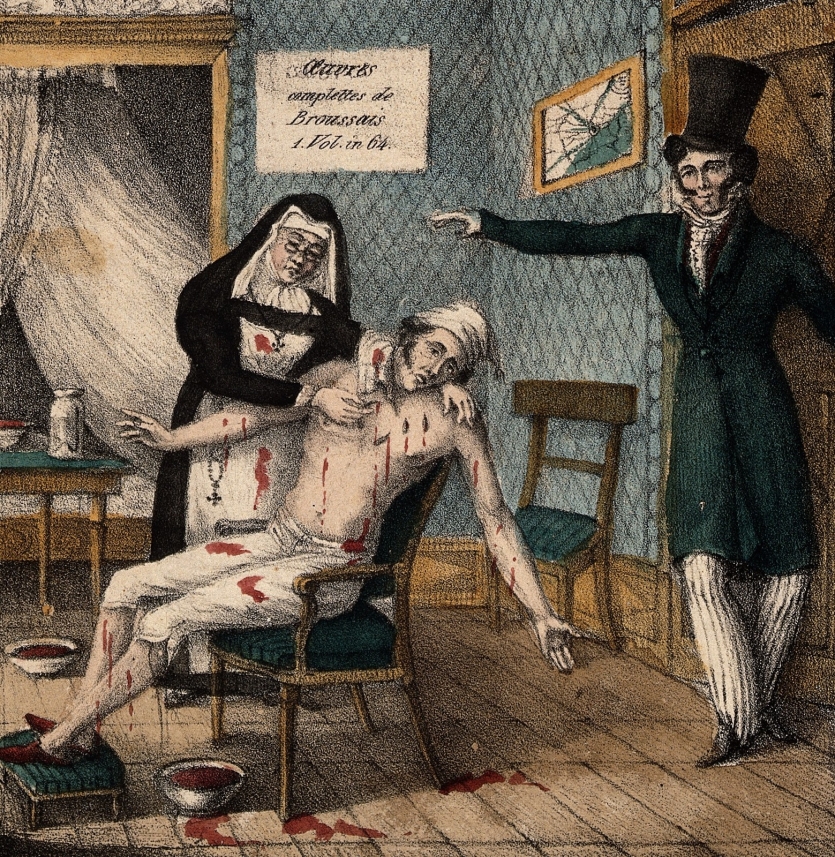
61 Results for “Leeches” A fierce battle between the supporters of John Brown (Bruno), in favour of treatment with stimulants, and those of F.J.V. Broussais, in favour of bloodletting. Pen…
Arsenic and Old Leeches
In 1816 Dr. James Rawlins Johnson published his Treatise on the Medicinal Leech. Besides the aforementioned methods of leech use, he studied the leech itself with exacting care. He tested to…
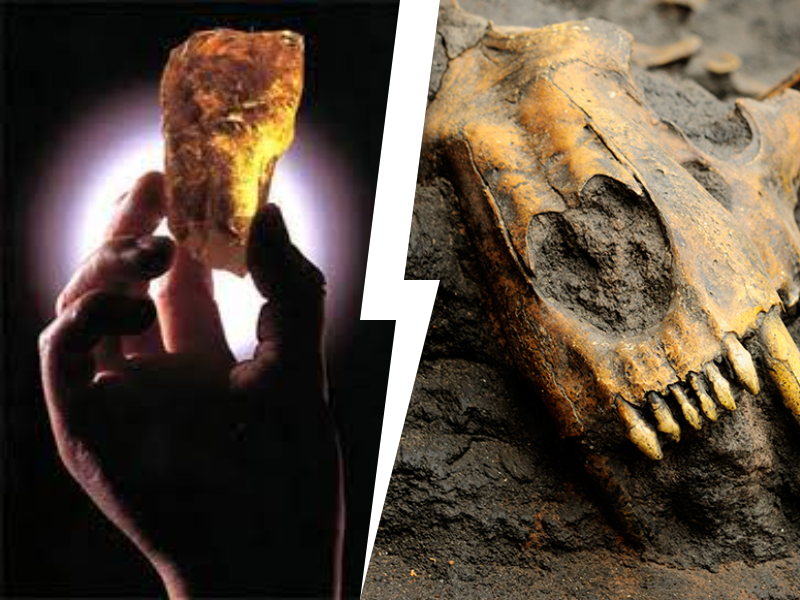
Crouching Hu Po, Hidden Long Gu?
What is Hu Po succinum or amber? When it comes to amber, also known as succinum in Latin and Hu Po in Mandarin, everyone seems know it well that this is a…
The tale known as “The Poison Dress” or “Embalmed Alive” features a dress that has in some way been poisoned
The tale known as “The Poison Dress” or “Embalmed Alive“[1] features a dress that has in some way been poisoned. This is a recurring theme throughout legends and folktales of various cultures, including ancient Greece, Mughal…
4-Nitrophenol mentioned in ‘Scientific Opinion on the re‐evaluation of aspartame (E 951) as a food additive’ (2013)
3.2.6.2. Studies on the effect of aspartame administration on xenobiotic metabolising enzymesAn early study (E15, 1972) indicated that the oral administration of aspartame to male Charles River rats (2000-4000 mg/kg)…
Aspartame was discovered by James M. Schlatter (1930 – 2019)
Lead chemist and developer of Aspartame used to make NutraSweet and Equal artificial sweeteners
Torunn Atteraas Garin (1947 – 2002)
Norwegian chemical engineer who helped develop aspartame sweetener as a sugar substitute while working for General Foods (1971-85)


 🔥 Salt Snatchers and The Cosmic Stick-Up of Your Soul’s Swagger (with receipts)
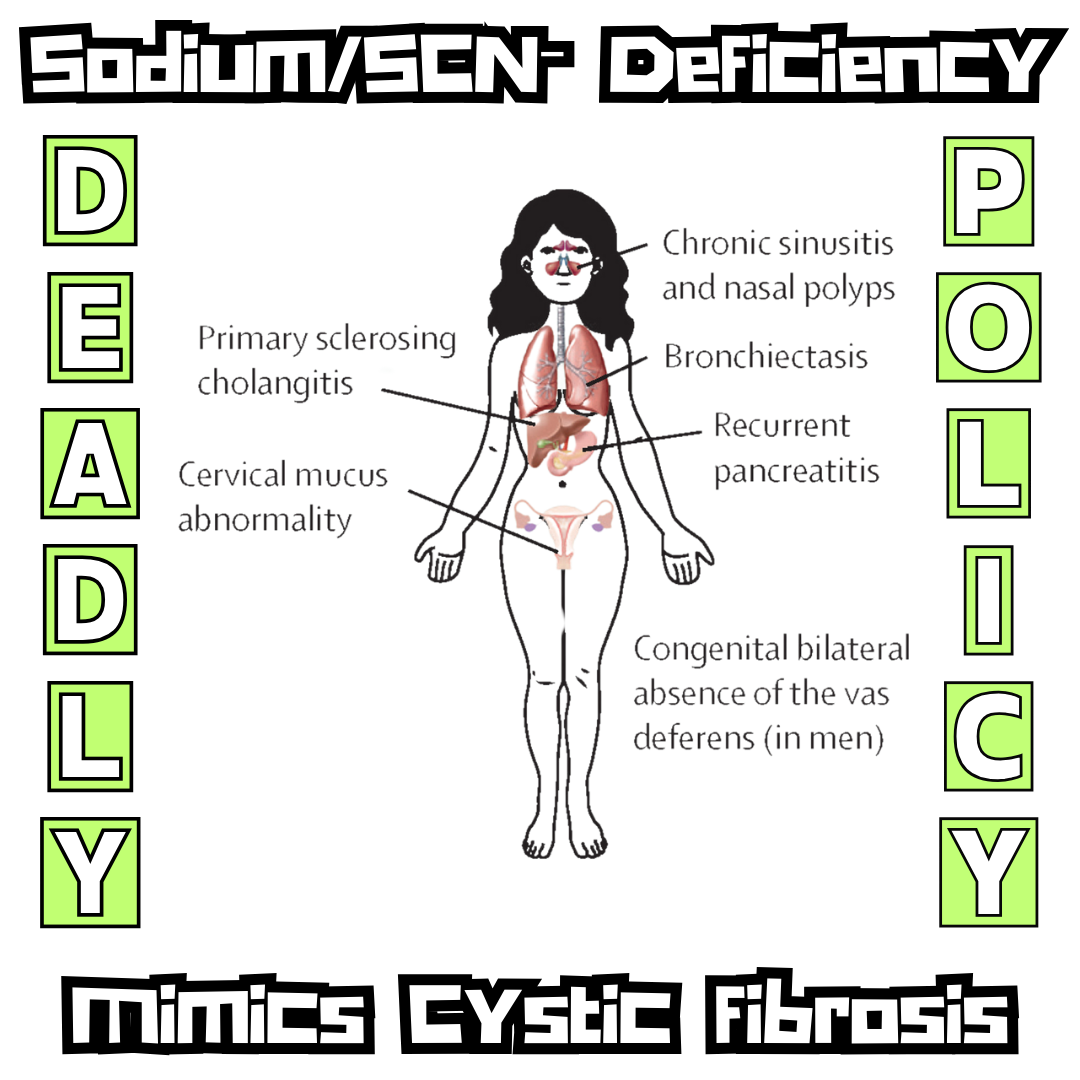
🔥 Salt Snatchers and The Cosmic Stick-Up of Your Soul’s Swagger (with receipts) ⚡⚡Voltage Famine: Sodium, SCN⁻, and the Biochemical Coup
⚡⚡Voltage Famine: Sodium, SCN⁻, and the Biochemical Coup 🧂 Sodium & SCN⁻: The Stratified Terrain of School Meals
🧂 Sodium & SCN⁻: The Stratified Terrain of School Meals 👁️ Sodium & SCN⁻ as Ocular Guardians
👁️ Sodium & SCN⁻ as Ocular Guardians 🧬 How PTH and Vitamin D Pills Mask Sodium Deficiency
🧬 How PTH and Vitamin D Pills Mask Sodium Deficiency 🧂 Salt-Linked Town Suffixes (and stuff)
🧂 Salt-Linked Town Suffixes (and stuff) 🐄📜 The Culling Threshold: Rapeseed Meal, Livestock Illness, Birth of Canola
🐄📜 The Culling Threshold: Rapeseed Meal, Livestock Illness, Birth of Canola