Chalone Rangers: The Tissue-Specific Mitotic Inhibitors You Never Knew You Needed
Chalones are the unsung heroes of cellular crowd control. These tissue-specific, water-soluble substances are like the bouncers of your body, standing at the gates of mitosis with their arms crossed, saying, “Not tonight, buddy.” They’re the biochemical equivalent of that one friend who knows
HFE H63D & VO2 max
SMOKE EM IF YOU GOT EM The HFE H63D is a single-nucleotide polymorphism in the HFE gene (c.187C>G, rs1799945), which results in the substitution of a histidine for an aspartic acid at amino acid position 63 of the HFE protein (p.His63Asp). HFE participates in the regulation of iron absorption.
The adrenal medulla is the principal site of the conversion of the amino acid tyrosine into the catecholamines; epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine
The adrenal medulla (Latin: medulla glandulae suprarenalis) is part of the adrenal gland. It is located at the center of the gland, being surrounded by the adrenal cortex. It is the innermost part of the adrenal gland, consisting of chromaffin cells that secrete catecholamines, including
Adrenochrome
Adrenochrome is a chemical compound produced by the oxidation of adrenaline (epinephrine). It was the subject of limited research from the 1950s through to the 1970s as a potential cause of schizophrenia. While it has no current medical application, the related derivative compound, carbaz
Medical uses of adrenaline
Main article: Epinephrine (medication) As a medication, it is used to treat several conditions, including allergic reaction anaphylaxis, cardiac arrest, and superficial bleeding. Inhaled adrenaline may be used to improve the symptoms of croup. It may also be used for asthma when other tr
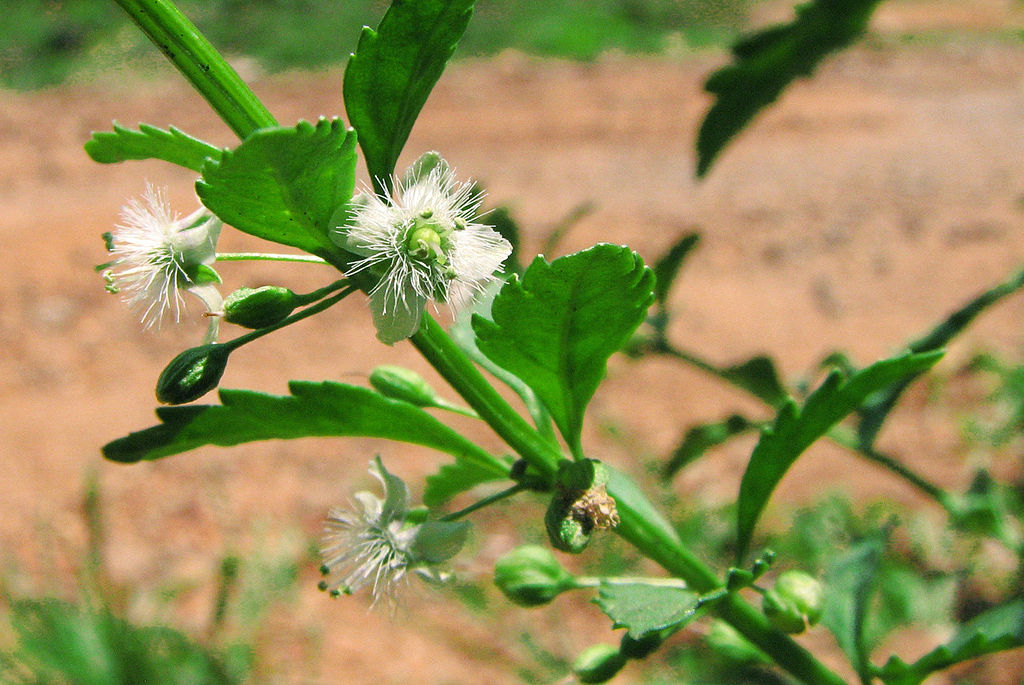
Adrenaline has been isolated from the plant Scoparia dulcis found in Northern Vietnam
Scoparia dulcis is a species of flowering plant in the plantain family. Plantaginaceae, the plantain family, is a large, diverse family of flowering plants in the order Lamiales that includes common flowers such as snapdragon and foxglove. It is unrelated to the banana-like fruit also ca
Adrenaline, aka epinephrine, is a hormone and medication involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration)
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and by a small number of neurons in the medulla o
An example of a process involving p300 and CBP is G protein signaling
Function in G protein signaling Some G proteins stimulate adenylate cyclase that results in elevation of cAMP. cAMP stimulates PKA, which consists of four subunits, two regulatory and two catalytic. Binding of cAMP to the regulatory subunits causes release of the catalytic subunits. These subuni