Tag: APUD
-
The pineal gland as an APUD organ
It is only in recent years that the pineal gland has emerged from being thought of as non-functional and unimportant. The rise from obscurity has been the result of the interest of investigators of multidisciplinary origins; such approaches, whilst clearly advancing understanding, also tend to leave knowledge fragmentary. In the last decade, a new neuroendocrine…
-
Pineal gland notes
The pineal gland, conarium, or epiphysis cerebri, is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. The pineal gland produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone which modulates sleep patterns in both circadian and seasonal cycles. The shape of the gland resembles a pine cone, which gives it its name. The pineal gland is located in the epithalamus, near the center of the brain, between the two hemispheres, tucked in a groove where the two halves…
-
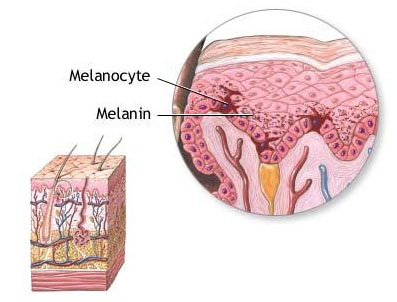
Cells in the APUD system may include melanocytes
Melanocytes are melanin-producing neural crest-derived cells located in the bottom layer (the stratum basale) of the skin’s epidermis, the middle layer of the eye (the uvea), the inner ear, vaginal epithelium, meninges, bones, and heart. Melanin is a dark pigment primarily responsible for skin color. Once synthesized, melanin is contained in special organelles called melanosomes which can be transported to nearby keratinocytes to induce pigmentation. Thus darker skin tones have more melanosomes present than lighter skin tones. Functionally, melanin serves as protection…
-
Cells in the APUD system may include Juxtaglomerular cells (JG cells), the renin producing cells in the kidney
Juxtaglomerular cells (JG cells), also known as juxtaglomerular granular cells are cells in the kidney that synthesize, store, and secrete the enzyme renin. They are specialized smooth muscle cells mainly in the walls of the afferent arterioles (and some in the efferent arterioles) that deliver blood to the glomerulus. In synthesizing renin, they play a critical role in the renin–angiotensin system and thus in autoregulation of the kidney. Juxtaglomerular cells secrete renin in…
-
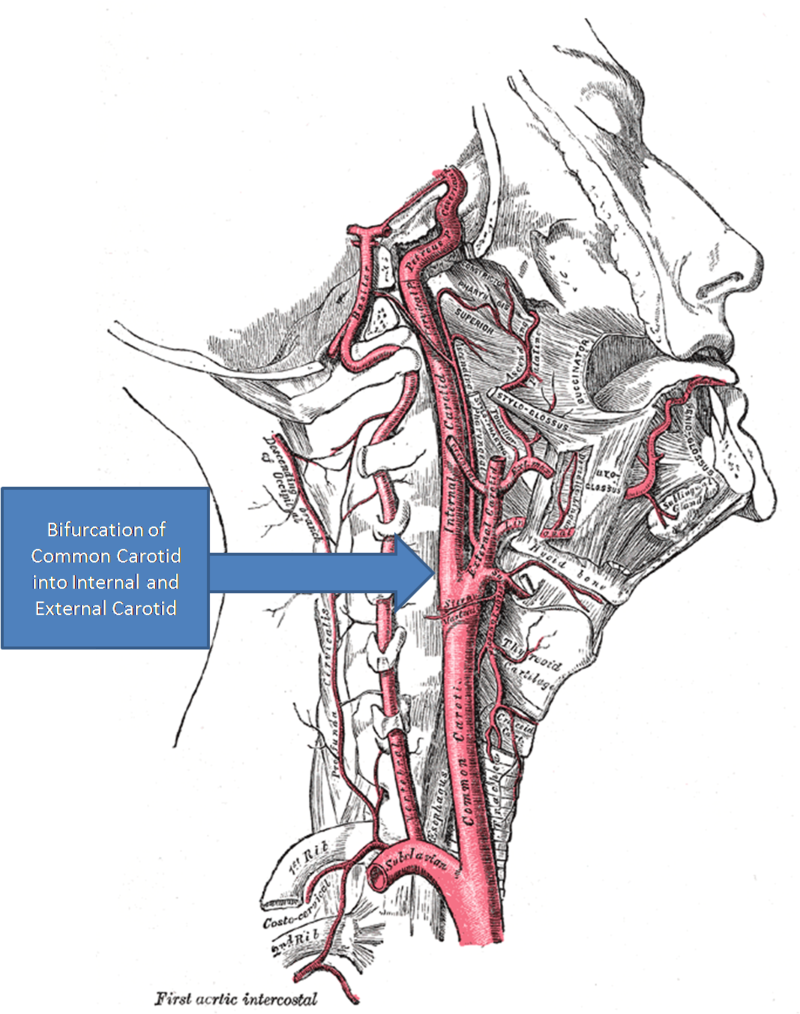
Carotid body glomus cells mediate essential reflex responses to arterial blood hypoxia
Glomus cells are the cell type mainly located in the carotid bodies and aortic bodies. Glomus type I cells are peripheral chemoreceptors which sense the oxygen, carbon dioxide and pH levels of the blood. When there is a decrease in the blood’s pH, a decrease in oxygen (pO2), or an increase in carbon dioxide (pCO2), the carotid bodies and the aortic bodies signal the dorsal…
-
Parafollicular cells aka C cells secrete calcitonin and several neuroendocrine peptides
Parafollicular cells, also called C cells, are neuroendocrine cells in the thyroid. The primary function of these cells is to secrete calcitonin. They are located adjacent to the thyroid follicles and reside in the connective tissue. These cells are large and have a pale stain compared with the follicular cells. In teleost and avian species these cells occupy a structure outside the thyroid…
-
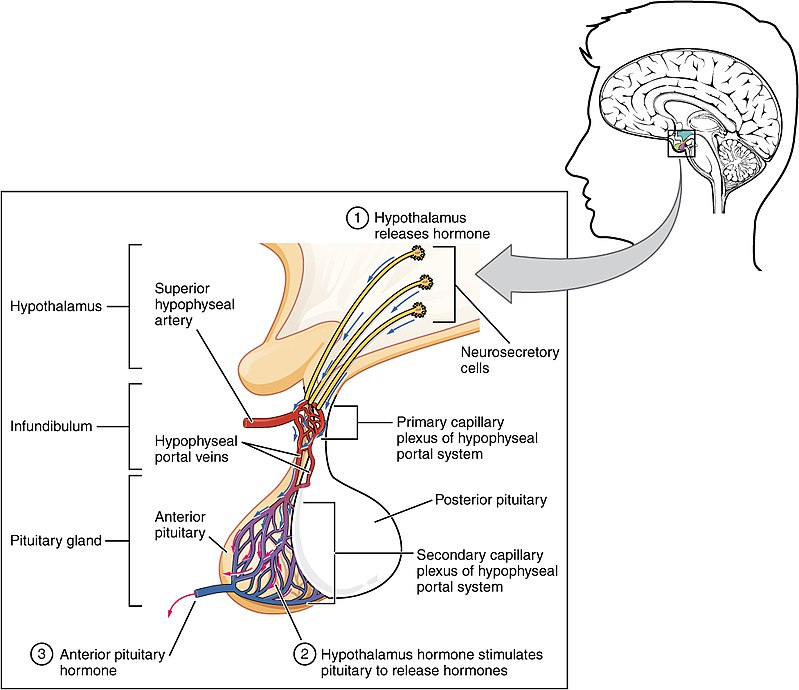
Adenohypophysis regulates several physiological processes, including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation
A major organ of the endocrine system, the anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis or pars anterior) is the glandular, anterior lobe that together with the posterior lobe (posterior pituitary, or the neurohypophysis) makes up the pituitary gland (hypophysis). The anterior pituitary regulates several physiological processes, including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation. Proper functioning of the anterior pituitary and of the organs it regulates can often be ascertained via blood tests that measure hormone levels. Structure The pituitary gland sits in a…
-
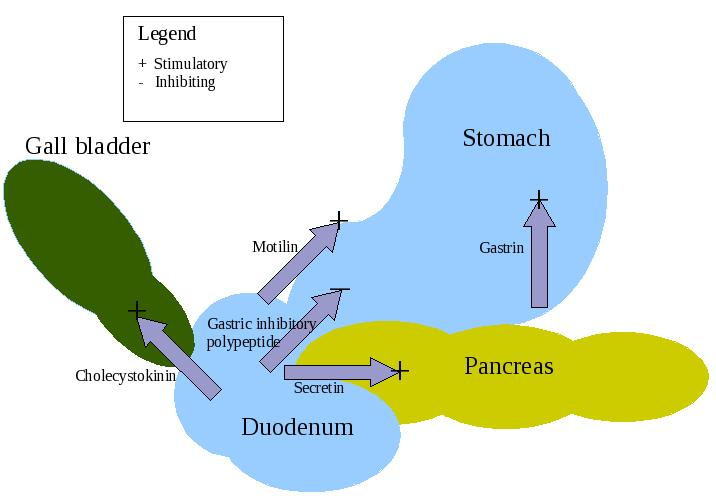
APUD cells (DNES cells)
APUD cells (DNES cells) constitute a group of apparently unrelated endocrine cells, which were named by the scientist A.G.E. Pearse, who developed the APUD concept in the 1960s based on calcitonin-secreting parafollicular C cells of dog thyroid. These cells share the common function of secreting a low molecular weight polypeptide hormone. There are several different types which secrete the hormones secretin, cholecystokinin and several others.…
Recent Posts
- 🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
- 🧂 Sodium Reduction and Sodium Replacement: A History of Reformulation and Exploding Diseases, Including Many Diseases Unheard of Before Deadly Sodium Policies
- 🧂 The DEADLY 1500 mg Sodium Recommendation predates the WHO’s formal global sodium reduction push by nearly a decade (and it’s even worse than that)
- 🧬 What Is Beta-Glucuronidase?
- When Sugar Was Salt: Crystalline Confusion and the Covenant of Sweetness
Tags
ADAM ASPARTAME Birds Blood Bones Brain Bugs Cancer Columba Cows crystallography Death Death cults Eggs Etymology Gastrin Gold Growth hormone History Hormones Insulin Liver Mere Perplexity Metal Monkey Business Mythology Paracetamol Plants Poison Pregnancy Protein Religion Reproduction Rocks Salt Slavery Snakes Sodium the birds and the bees Thiocyanate Tobacco Tylenol Underworld Venom zinc
