Tag: Diabetes
-
🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
Disease / Condition Incidence Since 1977 Low Sodium Connection Obesity 🡅🡅 ✅ Chronic sodium deficiency disrupts leptin and aldosterone signaling, impairing satiety and promoting fat retention. SCN⁻ depletion (repressed due to sodium deficiency) compounds this by weakening mitochondrial oxidation and terrain resilience. Type 2 Diabetes 🡅🡅 ✅ Low sodium destabilizes insulin signaling and renal glucose…
-
Salt-deficiency shows up as and mimics diabetes
The symptom overlap between salt deficiency (hyponatremia) and diabetes is striking enough to merit terrain-level scrutiny. 🧂 Salt Deficiency (Hyponatremia) Mimicking Diabetes When sodium levels drop below 135 mEq/L, the body enters a state of electrochemical instability. Within hours to days, this can produce symptoms that mirror diabetic presentations: Symptom Seen in Hyponatremia Seen in…
-
salt deficiency may mimic other conditions
Here’s a concise, evidence-informed breakdown showing how acute or chronic sodium deficiency or mismanagement (restriction, wasting, or inability to retain) may mimic, exacerbate, or parallel mechanisms seen in these conditions. Each bullet links sodium to key dysfunctions: Parkinson’s Disease COVID Complications Vaccine Reactions Alzheimer’s Disease Autoimmune Conditions Fatigue & Chronic Exhaustion Heart Problems & Arrhythmias…
-
🧂 salt deficiency mimics insulin resistance
Acute salt deficiency disrupts water balance, hormonal signaling, and glucose uptake, mimicking insulin resistance within days Mechanisms at Play Real-world consequence
-
HFE H63D & VO2 max
SMOKE EM IF YOU GOT EM The HFE H63D is a single-nucleotide polymorphism in the HFE gene (c.187C>G, rs1799945), which results in the substitution of a histidine for an aspartic acid at amino acid position 63 of the HFE protein (p.His63Asp). HFE participates in the regulation of iron absorption. Homozygous H63D variant can occasionally be the cause of hemochromatosis. It is also…
-

A Mad Scientist’s Dream – Rumpless Chickens (and more)
Today, we delve into the bizarre phenomenon of rumpless chickens—a feathered marvel characterized by caudal dysplasia, or as some like to call it, the ultimate chicken makeover! These quirky birds are missing their pygostyle, that charming little appendage known as the “parson’s nose,” a mutation that defies nature itself. This peculiar trait is inherited through…
-
NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) (previously known as NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 [NALP3] and cryopyrin)
Reference for subtitle: Finamor IA, Bressan CA, Torres-Cuevas I, Rius-Pérez S, da Veiga M, Rocha MI, Pavanato MA, Pérez S. Long-Term Aspartame Administration Leads to Fibrosis, Inflammasome Activation, and Gluconeogenesis Impairment in the Liver of Mice. Biology. 2021; 10(2):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10020082 NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) (previously known as NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein…
-
Protein phosphorylation was first reported in 1906
Protein phosphorylation is a reversible post-translational modification of proteins in which an amino acid residue is phosphorylated by a protein kinase by the addition of a covalently bound phosphate group. Phosphorylation alters the structural conformation of a protein, causing it to become activated, deactivated, or otherwise modifying its function. Approximately 13,000 human proteins have sites that are phosphorylated. The reverse reaction of phosphorylation is called dephosphorylation, and is catalyzed by…
-
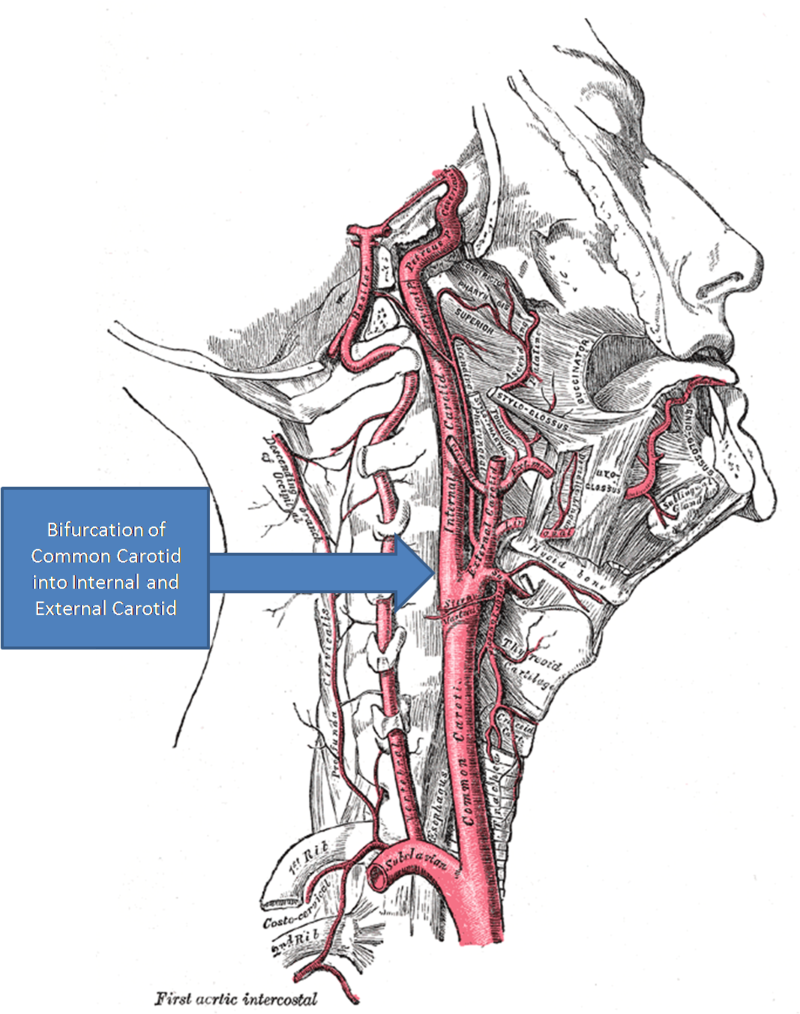
Carotid body glomus cells mediate essential reflex responses to arterial blood hypoxia
Glomus cells are the cell type mainly located in the carotid bodies and aortic bodies. Glomus type I cells are peripheral chemoreceptors which sense the oxygen, carbon dioxide and pH levels of the blood. When there is a decrease in the blood’s pH, a decrease in oxygen (pO2), or an increase in carbon dioxide (pCO2), the carotid bodies and the aortic bodies signal the dorsal…
-
Gastric inhibitory peptide aka GIP and receptors
Gastric inhibitory polypeptide or gastric inhibitory peptide also known as glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide abbreviated as GIP, is an inhibiting hormone of the secretin family of hormones. While it is a weak inhibitor of gastric acid secretion, its main role is to stimulate insulin secretion. GIP, along with glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), belongs to a class of molecules referred to as incretins. Synthesis and transport GIP is derived from a 153-amino acid proprotein encoded by…
-
CBP has intrinsic acetyltransferase functions
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate Response Element Binding protein Binding Protein (CREB-binding protein), also known as CREBBP or CBP or KAT3A, is a coactivator encoded by the CREBBP gene in humans, located on chromosome 16p13.3. CBP has intrinsic acetyltransferase functions; it is able to add acetyl groups to both transcription factors as well as histone lysines, the latter of which has been shown to alter chromatin structure making genes more accessible for transcription. This relatively…
-
Xylose is the first saccharide added to the serine or threonine in the proteoglycan type O-glycosylation
Xylose is the first saccharide added to the serine or threonine in the proteoglycan type O-glycosylation, and, so, it is the first saccharide in biosynthetic pathways of most anionic polysaccharides such as heparan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate. Definitions Proteoglycans are proteins that are heavily glycosylated. The basic proteoglycan unit consists of a “core protein” with one or more covalently attached glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain(s). The point of attachment is a serine (Ser) residue to which the glycosaminoglycan is joined through…
-

Xylitol: sweetener and laxative from hell
Xylitol, a natural sugar alcohol, has gained popularity as a low-calorie sweetener and the peddlers have attributed numerous health benefits to their product. This post is going to focus on one that doesn’t get nearly enough attention except in the countries where it was banned in things like soft drinks and elsehwere requires a diarrhea…
-
Brain natriuretic peptide 32 (BNP)
Brain natriuretic peptide 32 (BNP), also known as B-type natriuretic peptide, is a hormone secreted by cardiomyocytes in the heart ventricles in response to stretching caused by increased ventricular blood volume. BNP is one of two natriuretic peptides “UniProt”. www.uniprot.org. Retrieved 11 August 2022. The 32-amino acid polypeptide BNP is secreted attached to a 76–amino acid N-terminal fragment in the prohormone called NT-proBNP (BNPT), which is biologically inactive. Once released, BNP binds…
Recent Posts
- 🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
- 🧂 Sodium Reduction and Sodium Replacement: A History of Reformulation and Exploding Diseases, Including Many Diseases Unheard of Before Deadly Sodium Policies
- 🧂 The DEADLY 1500 mg Sodium Recommendation predates the WHO’s formal global sodium reduction push by nearly a decade (and it’s even worse than that)
- 🧬 What Is Beta-Glucuronidase?
- When Sugar Was Salt: Crystalline Confusion and the Covenant of Sweetness
Tags
ADAM ASPARTAME Birds Blood Bones Brain Bugs Cancer Columba Cows crystallography Death Death cults Eggs Etymology Gastrin Gold Growth hormone History Hormones Insulin Liver Mere Perplexity Metal Monkey Business Mythology Paracetamol Plants Poison Pregnancy Protein Religion Reproduction Rocks Salt Slavery Snakes Sodium the birds and the bees Thiocyanate Tobacco Tylenol Underworld Venom zinc
