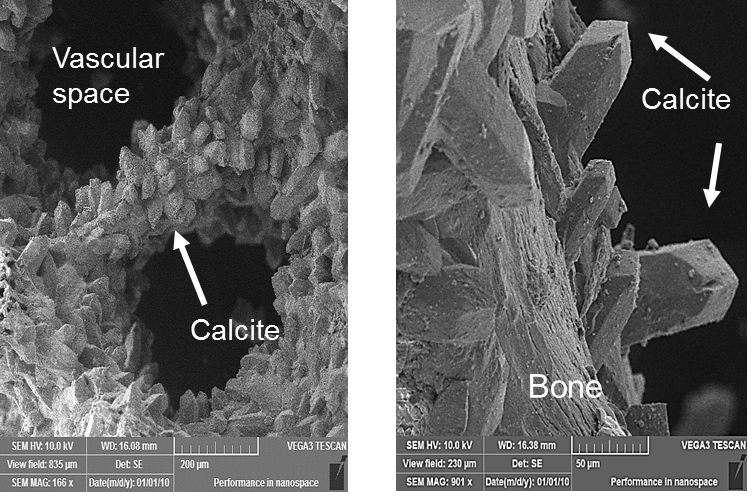
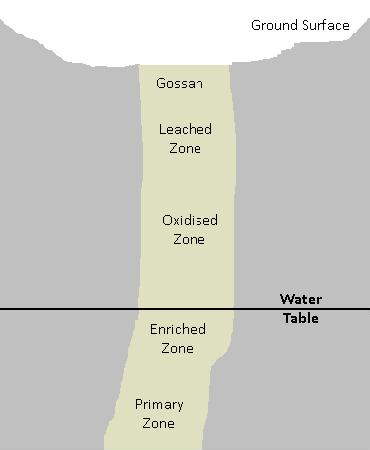
Diagenesis (the Petrologic principle)
Diagenesis is the process that describes physical and chemical changes in sediments first caused by water-rock interactions, microbial activity, and compaction after their deposition. Increased pressure and temperature only start to play a role as sediments become…
Autochthon and allochthon
An autochthon in structural geology is a large block or mass of rock which is in the place of its original formation relative to its basement or foundation rock. It can be described as rooted to…