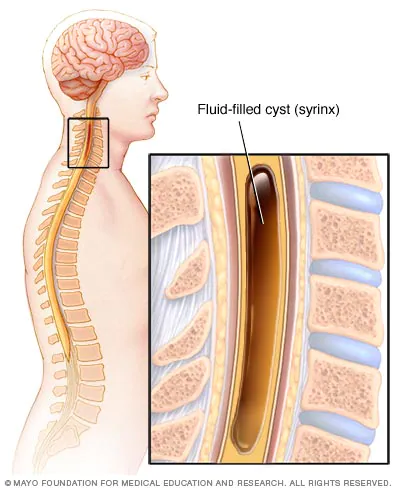
A syrinx is a fluid-filled neuroglial cavity within the spinal cord, in the brain stem, or in the nerves of the elbow
A syrinx is a rare, fluid-filled neuroglial cavity within the spinal cord (syringomyelia), in the brain stem (syringobulbia), or in the nerves of the elbow, usually in a young age. Presentation Symptoms usually begin insidiously between adolescence and…
Metoclopramide, Paracetamol/metoclopramide, Witch’s Milk, Lactating Men and Homicidal Maniacs?
Metoclopramide is a medication used for stomach and esophageal problems. It is commonly used to treat and prevent nausea and vomiting, to help with emptying of the stomach in people with delayed stomach emptying, and to help with gastroesophageal reflux disease. It is also…
Arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) and both the amino…
Somatostatin
Not to be confused with Somatocrinin or Somatomedin. Somatostatin, also known as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) or by several other names, is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G protein-coupled somatostatin receptors and inhibition of the…
Calcitonin
Calcitonin is a 32 amino acid peptide hormone secreted by PARAFOLLICULAR CELLS (also known as C cells) of the thyroid (or endostyle) in humans and other chordates in the ultimopharyngeal body. It acts to reduce blood calcium (Ca2+), opposing the effects of PARATHYROID HORMONE (PTH).…
Oxytocin
Oxytocin (Oxt or OT) is a peptide hormone and neuropeptide normally produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary. Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (41 ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. 2015. p. 358. ISBN 978-0-7020-6851-5. It plays a role in social bonding, reproduction, childbirth,…
Cholecystokinin aka pancreozymin notes
History Structure Function Gastrointestinal Digestion Satiety The effects of CCK vary between individuals. For example, in rats , CCK administration significantly reduces hunger in adult males, but is slightly less effective in younger…
Ghrelin or lenomorelin
History and name Gene, transcription products, and structure Ghrelin cells Alternative names Location Features Function and mechanism of action Blood levels Ghrelin receptor Locations of action Glucose metabolism Sleep Reproductive…
Prolactin receptor modulators
Prolactin Agonists An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action…