salt deficiency may mimic other conditions
Here’s a concise, evidence-informed breakdown showing how acute or chronic sodium deficiency or mismanagement (restriction, wasting, or inability to retain) may mimic, exacerbate, or parallel mechanisms seen in these conditions. Each bullet links sodium to key dysfunctions: Parkinson’s Disease C
ADAM17: The Drama Queen of the Cellular World
ADAM17 is the protein that’s not content with just one stage name! Also known as TACE (TNF-α Converting Enzyme), this molecular diva is the ultimate multi-tasker of the cellular world. Picture ADAM17 as the gossip columnist of the cell, always ready to spread the latest news. But instead of w
Asynchronous Muscles
Asynchronous muscles are muscles in which there is no one-to-one relationship between electrical stimulation and mechanical contraction. These muscles are found in 75% of flying insects and have convergently evolved 7-10 times.[1] Unlike their synchronous counterparts t
HFE H63D & VO2 max
SMOKE EM IF YOU GOT EM The HFE H63D is a single-nucleotide polymorphism in the HFE gene (c.187C>G, rs1799945), which results in the substitution of a histidine for an aspartic acid at amino acid position 63 of the HFE protein (p.His63Asp). HFE participates in the regulation of iron absorption.
Oxytocin: The Molecular Maestro of Love and Labor
Buckle up, hormone enthusiasts! We’re about to take a wild ride into the world of oxytocin, the “love hormone” that’s been playing Cupid in our bodies since the dawn of mammalian evolution. This tiny peptide packs a punch that would make even Hercules jealous! Picture this: a
Average body temperature dropped every decade since the 1800s and even more every decade since 1960
Attention, fellow humans! It’s time to chill out… literally! 🧊 Our bodies are on a cosmic cooldown, and it’s not just because we’ve all become walking popsicles addicted to air conditioning. Oh no, this is far more sinister and hilarious than that! The Great American Refri
Steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) protein and a few related things
The steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) protein is a transcription factor involved in sex determination by controlling the activity of genes related to the reproductive glands or gonads and adrenal glands. This protein is encoded by the NR5A
Reactive arthritis aka Reiter’s syndrome
Reportedly triggered by everything from food poisoning to bug bites to STDs to hormones (estrogen, relaxin) Mnemonic: Can't See, Can't Pee, Can't Climb a Tree
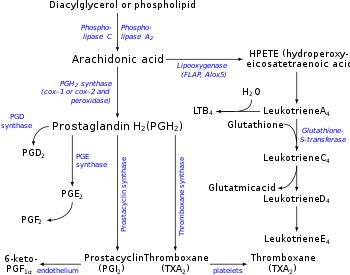
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1)
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1) or Prostaglandin E synthase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTGES gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a glutathione-dependent prostaglandin E synthase. The expression of this gene has been shown to be induced by proinfla
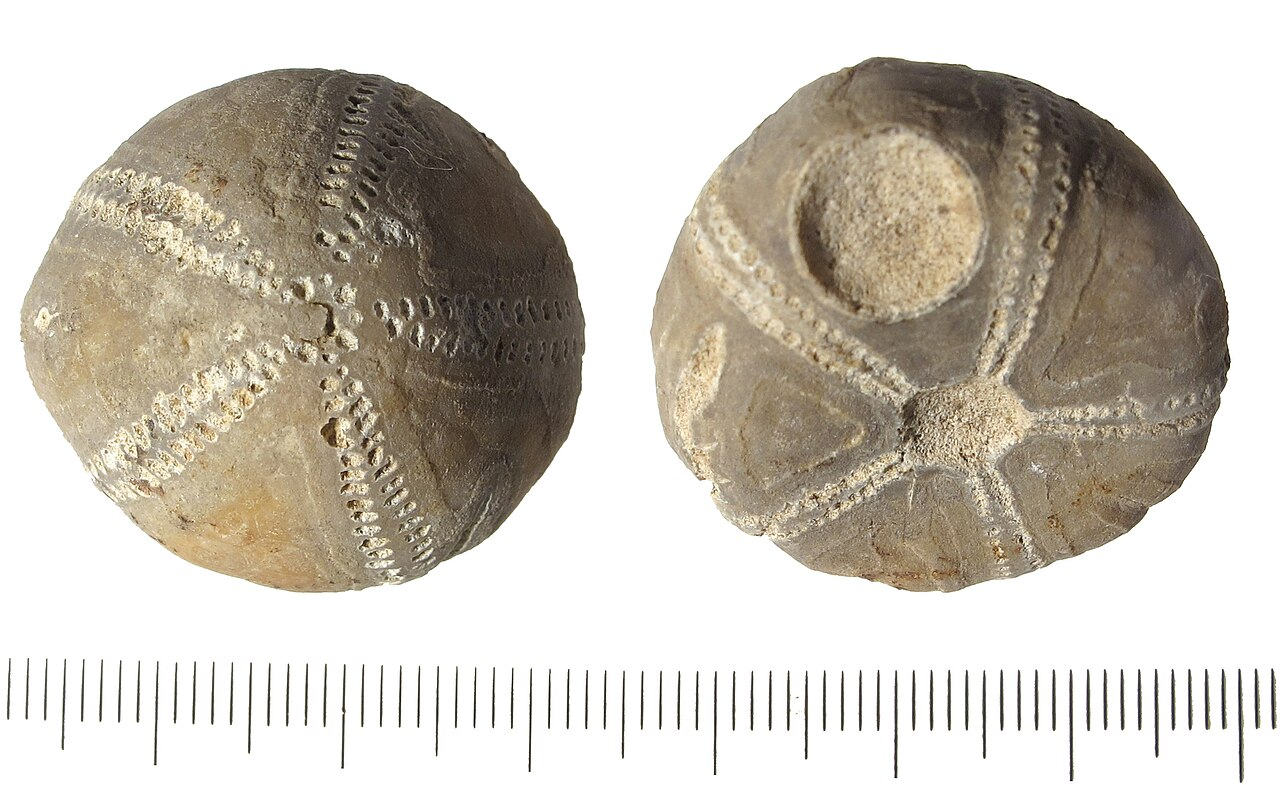
Humans have been interested in echinoid fossils (the fossilised remains of sea urchins) for millennia, considering them lucky and imbuing them with magical powers linked to their deities
A folk tradition in Denmark and southern England imagined sea urchin fossils to be thunderbolts, able to ward off harm by lightning or by witchcraft, as an apotropaic symbol. Another version supposed they were petrified eggs of snakes, able to protect against heart and liver disease, poisons, an
Osteopontin (OPN)
Osteopontin (OPN), also known as bone /sialoprotein I (BSP-1 or BNSP), early T-lymphocyte activation (ETA-1), secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1), 2ar and Rickettsia resistance (Ric), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPP1 gene (secreted phosphoprotein 1). The murine ortho
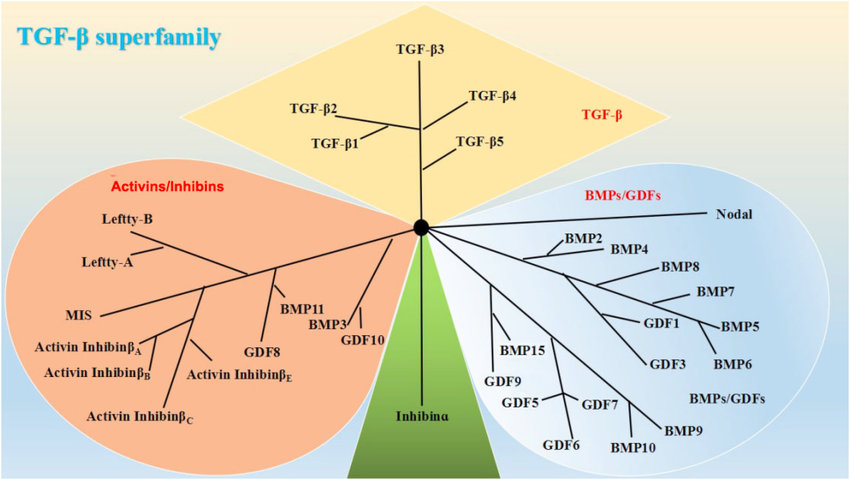
The transforming growth factor beta receptors
a family of serine/threonine kinase receptors involved in TGF beta signaling pathway
Pompe Disease
Glycogen storage disease type II, also called Pompe disease, is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder[1] which damages muscle and nerve cells throughout the body. It is caused by an accumulation of glycogen in the lysosome due to deficiency of the lysosoma
Brain natriuretic peptide 32 (BNP)
Brain natriuretic peptide 32 (BNP), also known as B-type natriuretic peptide, is a hormone secreted by cardiomyocytes in the heart ventricles in response to stretching caused by increased ventricular blood volume. BNP is one of two natriuretic peptides &
Triiodothyronine, aka T3
Triiodothyronine, also known as T3, is a thyroid hormone. It affects almost every physiological process in the body, including growth and development, metabolism, body temperature, and heart rate. Bowen, R. (2010-07-24). “Physiologic Effects of Thyroid Hormones”. Colorado State
Lipofuscin is the name given to fine yellow-brown pigment granules composed of lipid-containing residues of lysosomal digestion and considered to be one of the aging or “wear-and-tear” pigments
Lipofuscin is the name given to fine yellow-brown pigment granules composed of lipid-containing residues of lysosomal digestion.[1][2] It is considered to be one of the aging or “wear-and-tear” pigments, found in the liver, kidney, heart muscle, retina, adrenals, nerve cell