Chalone Rangers: The Tissue-Specific Mitotic Inhibitors You Never Knew You Needed
Chalones are the unsung heroes of cellular crowd control. These tissue-specific, water-soluble substances are like the bouncers of your body, standing at the gates of mitosis with their arms crossed, saying, “Not tonight, buddy.” They’re the biochemical equivalent of that one friend who knows
Autacoids Unleashed: The Self-Made, Self-Destructive Hormones You Didn’t Know You Needed
What Are Autacoids? Autacoids (or autocoids) are the body’s DIY hormones—locally produced, short-lived biochemical messengers that scream, “I got this!” before promptly fading into oblivion. The term comes from the Greek autos (self) and acos (relief or drug), which is ir
Snake Venom: The Hormone Hijacker 🐍
Imagine a villainous mastermind that can infiltrate your body’s hormonal headquarters, manipulating the delicate balance of estrogen and other hormones. Welcome to the world of snake venom, where the stakes are high and the effects are unpredictable. Estrogen’s Uninvited Guest: When Snak
Eraso Y. Biotypology, endocrinology, and sterilization: the practice of eugenics in the treatment of Argentinian women during the 1930s. Bull Hist Med. 2007 Winter;81(4):793-822. doi: 10.1353/bhm.2007.0130. PMID: 18084107; PMCID: PMC2629848.
SUMMARYThis article looks at medical approaches to women’s fertility in Argentina in the 1930s and explores the ways in which eugenics encouraged the reproduction of the fit and attempted to avoid the reproduction of the unfit. The analysis concentrates on three main aspects: biotypology (the scie
the hormone hustle
We’re about to embark on a time-traveling, mind-bending journey through the evolution of normalization, biopolitics, and the wild world of hormones. From Foucault’s philosophical bombshells to Nicola Pende’s hormone-fueled science experiments, this is a story that will leave y
Beccalossi C. Sexology, sexual development, and hormone treatments in Southern Europe and Latin America, c.1920-40. Hist Human Sci. 2023 Dec;36(5):94-121. doi: 10.1177/09526951231213028. Epub 2023 Dec 6. PMID: 38077463; PMCID: PMC10700059.
AbstractDisplacing the physiological model that had held sway in 19th-century medical thinking, early 20th-century medical scientists working on hormones promoted a new understanding of the body, psychological reactions, and the sexual instinct, arguing that each were fundamentally malleable. Hormon
Beccalossi C. Italian sexology, Nicola Pende’s biotypology and hormone treatments in the 1920s. Hist Med Sante. 2017 Winter;12:73-97. doi: 10.4000/hms.1173. Epub 2018 May 28. PMID: 31501760; PMCID: PMC6733708.
AbstractThis article analyses a selection of Nicola Pende’s studies from the 1920s on ‘endocrinological abnormalities’ associated with impotence, a lack of virility in men, a lack of femininity in women, and homosexuality. By analysing endocrinological sexual theories and treatments, it aims t
BECCALOSSI C. Optimizing and normalizing the population through hormone therapies in Italian science, c.1926–1950. The British Journal for the History of Science. 2020;53(1):67-88. doi:10.1017/S0007087419000906
Abstract This essay explores how hormone treatments were used to optimize and normalize individuals under Italian Fascism. It does so by taking the activities of the Biotypological Orthogenetic Institute − an Italian eugenics and endocrinological centre founded by Nicola Pende in 1926 − as the p
Buggy Love Potion: The Science of Insect Sex Hormones
Listen up, you sexy six-legged sirens and alluring arthropods! 🐞💋 Get ready to have your mind blown and your exoskeleton rocked. Insect sex hormones: They’re real, they’re spectacular, and they’re changing the game of love in the miniature world! From ecdysone’s double
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) aka abrineurin
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), or abrineurin, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the BDNF gene. BDNF is a member of the neurotrophin family of growth factors, which are related to the canonical nerve growth factor (NGF), a family which also includes NT-3 and NT-4/N
Neurotrophin-3 and Neurotrophin-4
Neurotrophin-4 (NT-4), also known as neurotrophin-5 (NT-5), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NTF4 gene. It is a neurotrophic factor that signals predominantly through the TrkB receptor tyrosine kinase. NT-4 was first discovered and isolated from xenopus and viper in the ye
Juvenile hormone (and Methoprene)
Juvenile hormones (JHs) are a group of acyclic sesquiterpenoids that regulate many aspects of insect physiology. The first discovery of a JH was by Vincent Wigglesworth. JHs regulate development, reproduction, diapause, and polyphenisms. The chemical formula for juvenile hormone is C18H30O3.
The PVN Powerhouse: How the Paraventricular Nucleus Rules Hormone Secretion
Hold onto your hypothalamus, folks! We’re about to dive into the wild world of the Paraventricular Nucleus (PVN), where tiny cells pack a mighty hormonal punch! Picture this: deep in the brain’s control center, the hypothalamus, sits the PVN – a cluster of cells that’s like t
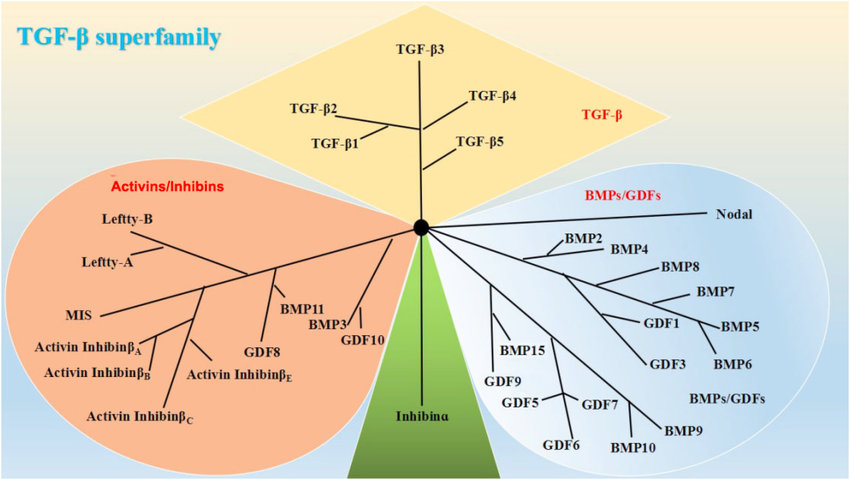
The transforming growth factor beta receptors
a family of serine/threonine kinase receptors involved in TGF beta signaling pathway
The adrenal medulla is the principal site of the conversion of the amino acid tyrosine into the catecholamines; epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine
The adrenal medulla (Latin: medulla glandulae suprarenalis) is part of the adrenal gland. It is located at the center of the gland, being surrounded by the adrenal cortex. It is the innermost part of the adrenal gland, consisting of chromaffin cells that secrete catecholamines, including