Chalone Rangers: The Tissue-Specific Mitotic Inhibitors You Never Knew You Needed
Chalones are the unsung heroes of cellular crowd control. These tissue-specific, water-soluble substances are like the bouncers of your body, standing at the gates of mitosis with their arms crossed, saying, “Not tonight, buddy.” They’re the biochemical equivalent of that one friend who knows
ADAM28: The Lymphocyte’s Little Helper
ADAM28 is the protein that’s bringing a whole new meaning to “immune system support”! ADAM28 is like that friend who’s always hanging out with the cool kids – in this case, the lymphocytes. This protein is exclusively expressed by lymphocytes, making it the VIP member o
ADAM8: The Inflammatory Instigator
ADAM8 is the protein that’s stirring up trouble in your immune system! ADAM8 is like that friend who always shows up when there’s drama brewing. This protein is primarily expressed in immune cells, making it a key player in inflammatory responses. Picture ADAM8 as the bouncer of the cell
ADAM10: The Cellular Scissorhands of Reproduction
Prepare to be amazed by ADAM10, the Edward Scissorhands of the cellular world! This protein isn’t just content with the usual reproductive shenanigans; it’s got its fingers in pies all over the body. Picture ADAM10 as a molecular barber, constantly snipping and trimming proteins on cell
Nerve Growth Factor
Nerve growth factor (NGF) is a neurotrophic factor and neuropeptide primarily involved in the regulation of growth, maintenance, proliferation, and survival of certain target neurons. It is perhaps the prototypical growth factor, in that it was one of the first to
Three-finger proteins and three-finger toxins
Three-finger proteins or three-finger protein domains (3FP or TFPD) are a protein superfamily consisting of small, roughly 60-80 amino acid residue protein domains with a common tertiary structure: three beta strand loops extended from
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is the development of thrombocytopenia (a low platelet count), due to the administration of various forms of heparin, an anticoagulant. HIT predisposes to thrombosis (the abnormal formation of blood clots inside a blood vessel).
When thrombosis is identified the condition is called heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and thrombosis (HITT). HIT is caused by the formation of abnormal antibodies that activate platelets, which release microparticles that activate thrombin, leading to thrombosis. If someone receiving heparin
Transferrins
Transferrins are not limited to only binding to iron but also to different metal ions.
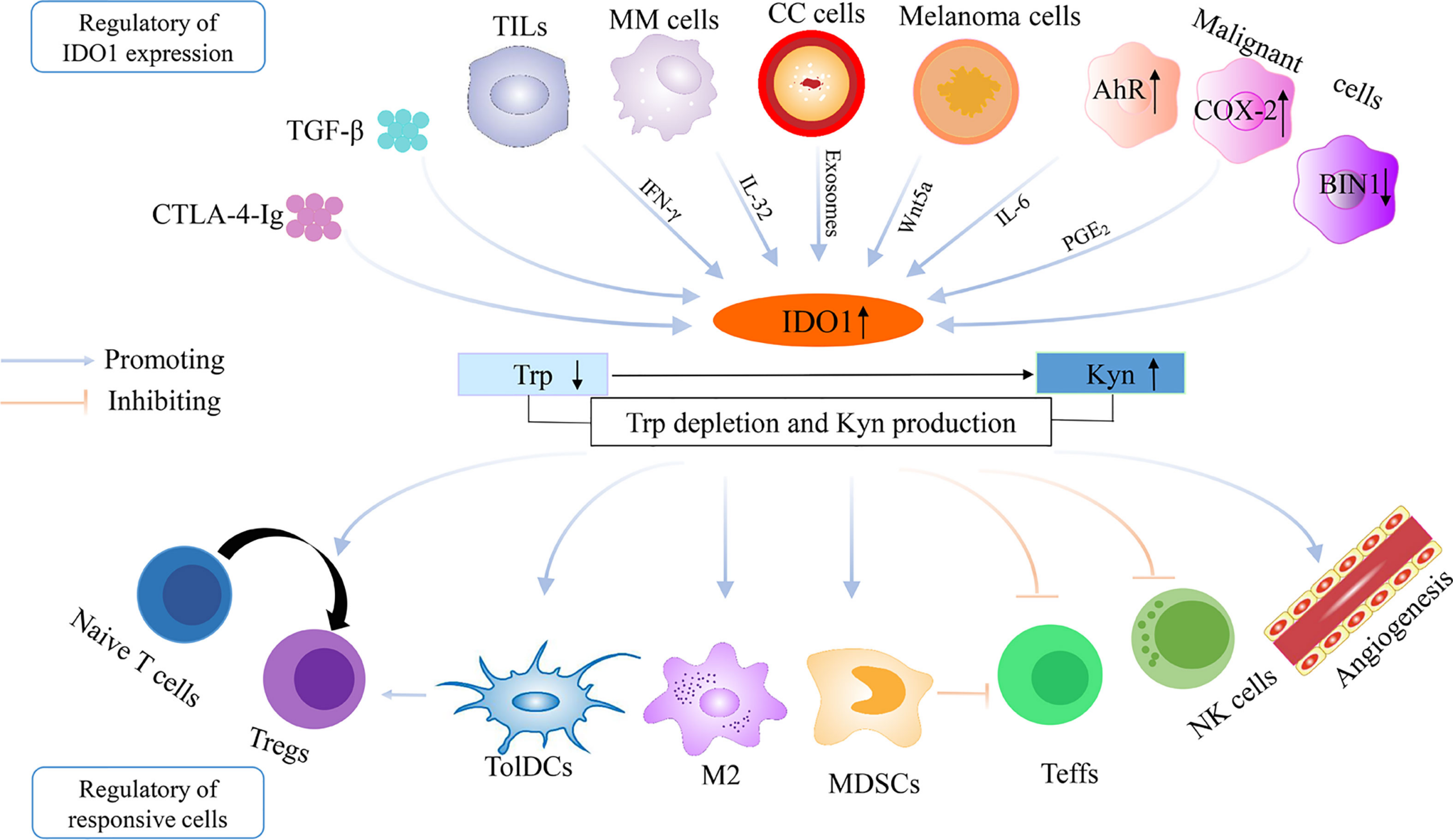
Indoleamine-pyrrole 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO or INDO) is involved in tryptophan metabolism
Indoleamine-pyrrole 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO or INDO EC 1.13.11.52) is a heme-containing enzyme physiologically expressed in a number of tissues and cells, such as the small intestine, lungs, female genital tract or placenta. In humans is
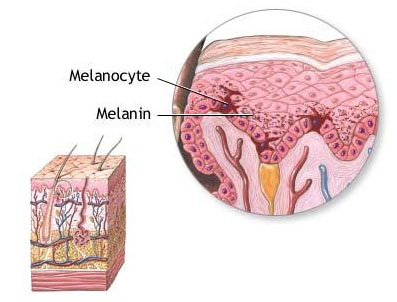
Cells in the APUD system may include melanocytes
Melanocytes are melanin-producing neural crest-derived cells located in the bottom layer (the stratum basale) of the skin’s epidermis, the middle layer of the eye (the uvea), the inner ear, vaginal epithelium, meninges, bones, and heart. Melanin is a dark pigment primarily
Xylose is the first saccharide added to the serine or threonine in the proteoglycan type O-glycosylation
Xylose is the first saccharide added to the serine or threonine in the proteoglycan type O-glycosylation, and, so, it is the first saccharide in biosynthetic pathways of most anionic polysaccharides such as heparan sulfate and chondroitin s
Cluster of Differentiation (Cluster of Designation or Classification Determinant)
The cluster of differentiation (also known as cluster of designation or classification determinant and often abbreviated as CD) is a protocol used for the identification and investigation of cell surface molecules providing targets for immunophenotyping of cells.[1] In terms of physiolog
HLA-B major histocompatibility complex, class I, B
HLA-B (major histocompatibility complex, class I, B) is a human gene that provides instructions for making a protein that plays a critical role in the immune system. HLA-B is part of a family of genes called the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) complex. The
HLA-A
Further information: Human leukocyte antigen and History and naming of human leukocyte antigens HLA-A is a group of human leukocyte antigens (HLA) that are encoded by the HLA-A locus, which is located at human chromosome 6p21.3.[1] HLA is a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigen sp