ADAM8: The Inflammatory Instigator
ADAM8 is the protein that’s stirring up trouble in your immune system! ADAM8 is like that friend who always shows

ADAM8 is the protein that’s stirring up trouble in your immune system! ADAM8 is like that friend who always shows
Reportedly triggered by everything from food poisoning to bug bites to STDs to hormones (estrogen, relaxin) Mnemonic: Can’t See, Can’t Pee, Can’t Climb a Tree
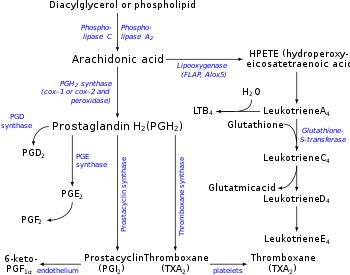
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1) or Prostaglandin E synthase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTGES gene. The protein encoded by this gene
Clusterin (apolipoprotein J) is a 75-80 kDa disulfide-linked heterodimeric protein associated with the clearance of cellular debris and apoptosis. In humans, clusterin is encoded by
An ectodomain is the domain of a membrane protein that extends into the extracellular space (the space outside a cell). Ectodomains are usually the parts of proteins that initiate contact
Osteopontin (OPN), also known as bone /sialoprotein I (BSP-1 or BNSP), early T-lymphocyte activation (ETA-1), secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1), 2ar and Rickettsia resistance (Ric), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPP1 gene (secreted phosphoprotein

Ceruloplasmin (or caeruloplasmin) is a ferroxidase enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CP gene. Ceruloplasmin is the major copper-carrying protein in the blood, and in addition
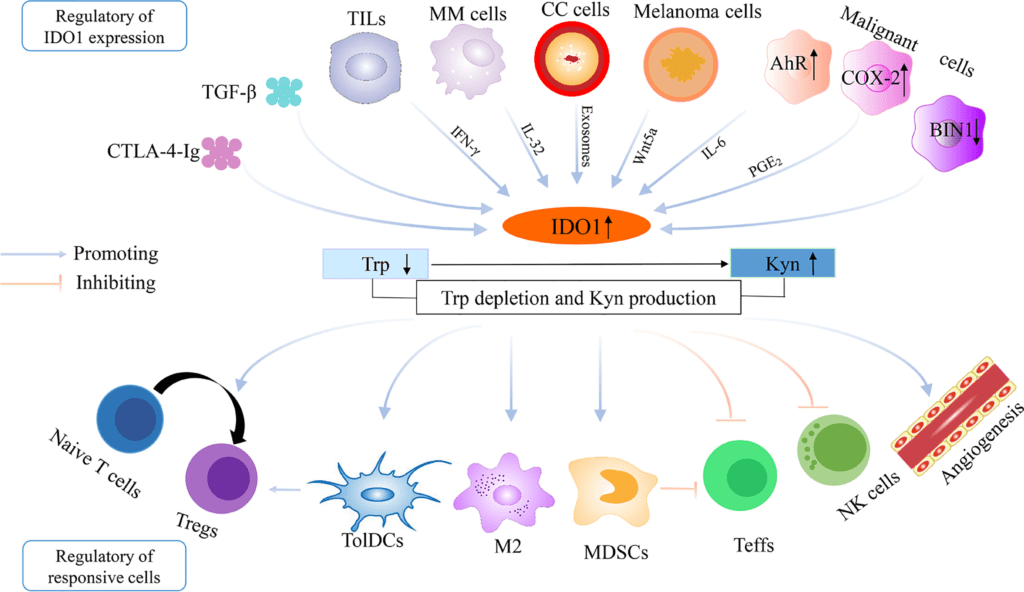
Indoleamine-pyrrole 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO or INDO EC 1.13.11.52) is a heme-containing enzyme physiologically expressed in a number of tissues and cells, such as the small intestine, lungs, female genital tract or placenta. In humans
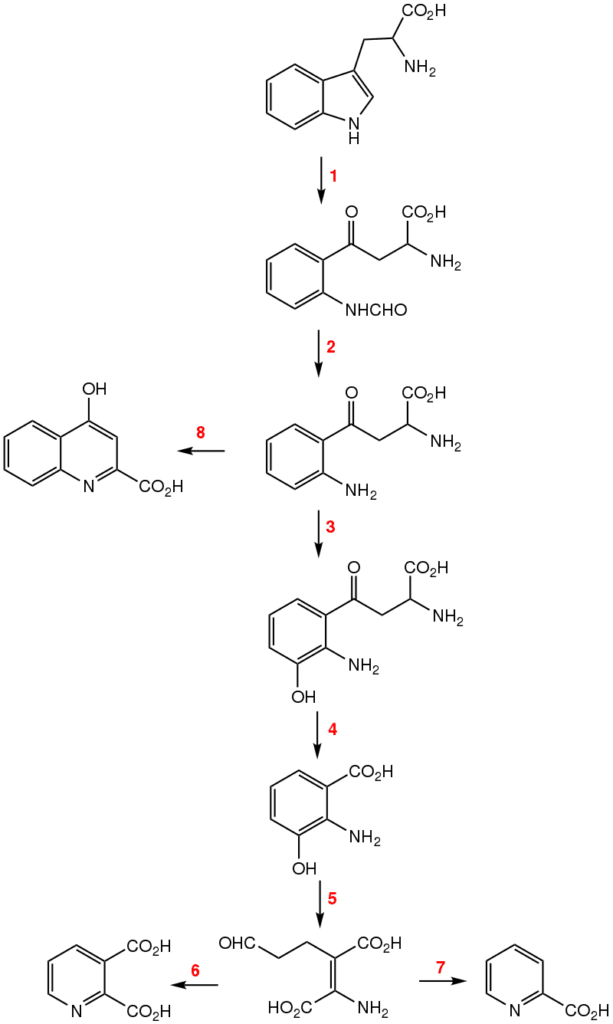
Ommochrome (or visual pigment) refers to several biological pigments that occur in the eyes of crustaceans and insects. The eye color is determined by the ommochromes. Ommochromes are also
The prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids “Eicosanoid Synthesis and Metabolism: Prostaglandins, Thromboxanes, Leukotrienes, Lipoxins”. themedicalbiochemistrypage.org. Retrieved 2018-09-21. having diverse hormone-like effects in animals.