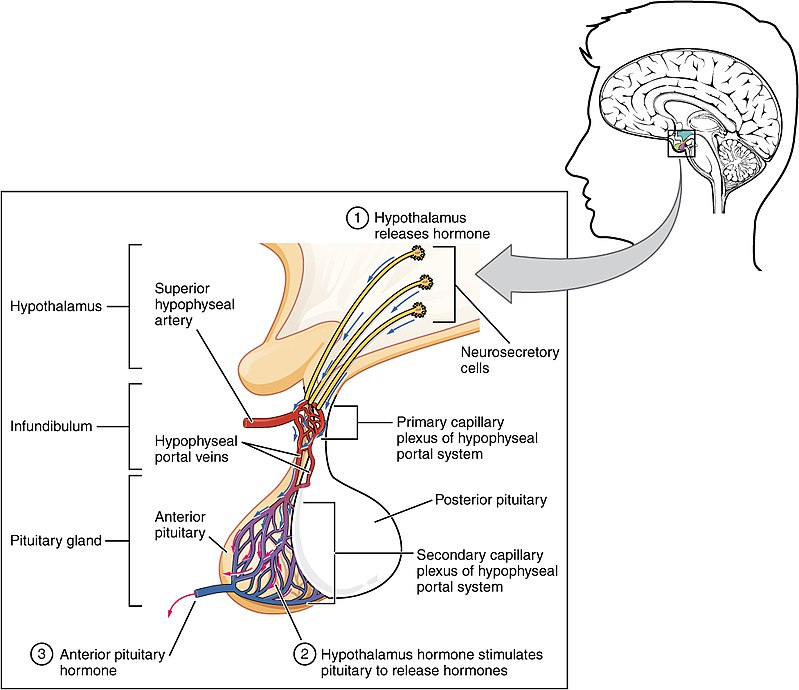
Adenohypophysis regulates several physiological processes, including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation
A major organ of the endocrine system, the anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis or pars anterior) is the glandular, anterior lobe that together with the posterior lobe (posterior pituitary, or the neurohypophysis) makes
The lactating birds and the bees (gastrin, pepsin, etc)
Crop milk is a secretion from the lining of the crop of parent birds that is regurgitated to young birds. It is found among all pigeons and doves where it is referred to as pigeon milk. An analog to crop milk is also secreted from the esophagus of flamingos and the male emperor penguin. D
Columbidae anatomy and physiology notes
Overall, the anatomy of Columbidae is characterized by short legs, short bills with a fleshy cere, and small heads on large, compact bodies. Like some other birds, the Columbidae have no gall bladders. Some medieval naturalists concluded they have no bile (gall), which in the medieval theory
Metoclopramide, Paracetamol/metoclopramide, Witch’s Milk, Lactating Men and Homicidal Maniacs?
Metoclopramide is a medication used for stomach and esophageal problems. It is commonly used to treat and prevent nausea and vomiting, to help with emptying of the stomach in people with delayed stomach emptying, and to help with gastr
Calcitriol
Medical use Adverse effects Mechanism of action Calcitriol increases blood calcium levels ([Ca2+]) by: Biosynthesis and its regulation Interactive pathway map Metabolism History Names External links Hormones Vitamins (A11) Drugs used for psoriasis (D05) Vitamin D receptor modulators P
Calcitonin
Calcitonin is a 32 amino acid peptide hormone secreted by PARAFOLLICULAR CELLS (also known as C cells) of the thyroid (or endostyle) in humans and other chordates in the ultimopharyngeal body. It acts to reduce blood calcium (Ca2+), opposing the effects of PARATHYROID HORMONE (PTH). I
Melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) aka PMCH
Melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH), also known as pro-melanin stimulating hormone (PMCH), is a cyclic 19-amino acid orexigenic hypothalamicpeptide originally isolated from the pituitary gland of teleost fish, where it controls skin pigmentation. Barson JR, Mo
Oxytocin
Oxytocin (Oxt or OT) is a peptide hormone and neuropeptide normally produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary. Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (41 ed.). Elsevier Health Scienc
Prolactin receptor modulators
Prolactin Agonists An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agoni
Prolactin (PRL)
In mammals, prolactin is associated with milk production; in fish it is thought to be related to the control of water and salt balance. Prolactin also acts in a cytokine-like manner and as an important regulator of the immune system. It has important cell cycle-related functions as a growth-, diffe
Haldol: The Grim Reaper’s Sidekick
Haloperidol, better known as Haldol, is not just a drug—it’s a cultural artifact of medicine’s darker corners. It has worn many hats: psychiatric savior, hospice workhorse, veterinary tranquilizer, and even a lurking specter in the shadowy world of death cocktails. This report dives deep into
Human placental lactogen (hPL)
Human placental lactogen (hPL), also called human chorionic somatomammotropin (HCS), is a polypeptideplacental hormone, the human form of placental lactogen (chorionic somatomammotropin). Its structure and function are similar to those of human growth hor