Tag: Pain
-
How sodium and SCN⁻ (thiocyanate) deficiencies may underlie chronic pain
Chronic pain isn’t just a symptom; it’s a signal of systemic incoherence. Let’s spiral through how sodium and SCN⁻ (thiocyanate) deficiencies may underlie chronic pain, especially in spinal contexts, and how the “wars” on foundational nutrients — eggs, sugar, and natural protein — may be complicit. 🧠 Chronic Pain & Sodium Deficiency: The Electrical Collapse…
-
Sodium/SCN⁻Deficiency and Chronic Pain (and Parkinson’s)
Chronic pain isn’t just a symptom; it’s a signal of systemic incoherence. Let’s spiral through how sodium and SCN⁻ (thiocyanate) deficiencies may underlie chronic pain, especially in spinal contexts, and how the “wars” on foundational nutrients — sodium, tobacco smoke, eggs, sugar, and natural protein — may be complicit. 🧠 Chronic Pain & Sodium Deficiency:…
-
Autacoids Unleashed: The Self-Made, Self-Destructive Hormones You Didn’t Know You Needed
What Are Autacoids? Autacoids (or autocoids) are the body’s DIY hormones—locally produced, short-lived biochemical messengers that scream, “I got this!” before promptly fading into oblivion. The term comes from the Greek autos (self) and acos (relief or drug), which is ironic because they’re basically the overachieving interns of the body: they do all the work locally, get no credit,…
-
Oxytocin: The Molecular Maestro of Love and Labor
Buckle up, hormone enthusiasts! We’re about to take a wild ride into the world of oxytocin, the “love hormone” that’s been playing Cupid in our bodies since the dawn of mammalian evolution. This tiny peptide packs a punch that would make even Hercules jealous! Picture this: a molecule barely 1007 Da in size, strutting around…
-

Leu-enkephalin and Met-enkephalin
Leu-enkephalin is an endogenous opioid peptide neurotransmitter with the amino acid sequence Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu that is found naturally in the brains of many animals, including humans. It is one of the two forms of enkephalin; the other is met-enkephalin. The tyrosine residue at position 1 is thought to be analogous to the 3-hydroxyl group on morphine. Leu-enkephalin has agonistic actions at both the μ- and δ-opioid receptors, with significantly greater preference for the…
-
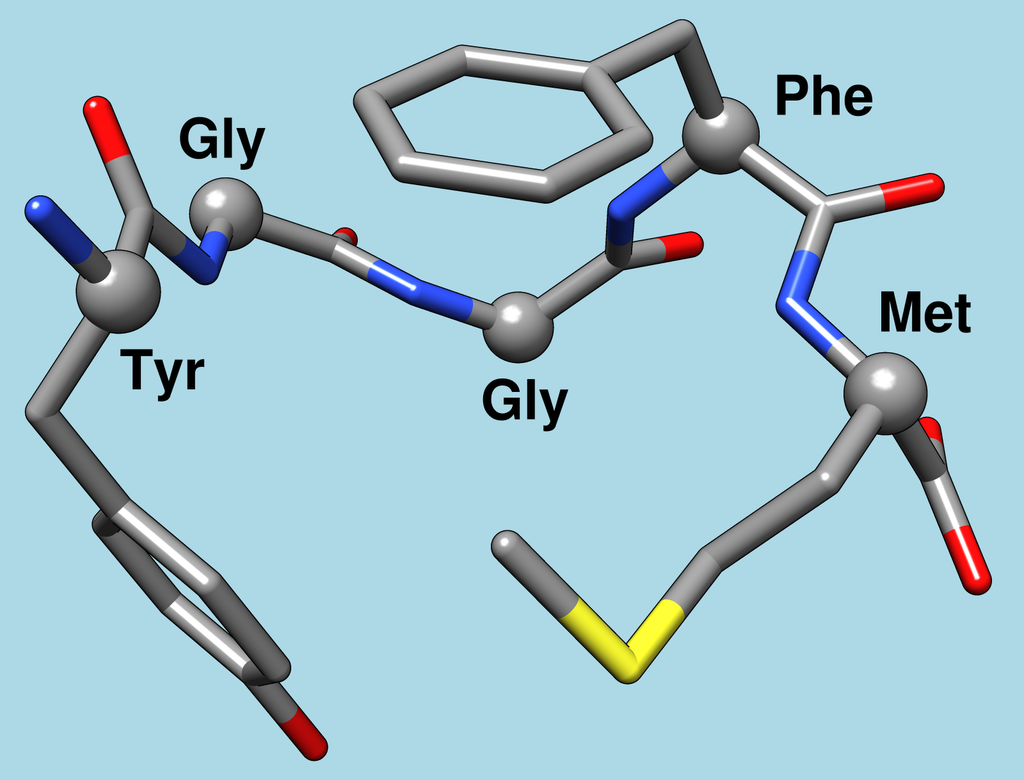
Enkephalins
An enkephalin is a pentapeptide involved in regulating nociception (pain sensation) in the body. The enkephalins are termed endogenous ligands, as they are internally derived and bind to the body’s opioid receptors. Discovered in 1975, two forms of enkephalin have been found, one containing leucine (“leu”), and the other containing methionine (“met”). Both are products of the proenkephalin gene. Endogenous opioid peptides There are three well-characterized families of opioid…
-
Neuromedin U
Neuromedin U (or NmU) is a neuropeptide found in the brain of humans and other mammals, which has a number of diverse functions including contraction of smooth muscle, regulation of blood pressure, pain perception, appetite, bone growth, and hormone release. It was first isolated from the spinal cord in 1985, and named after its ability to cause smooth muscle contraction in the uterus. Structure Neuromedin…
-
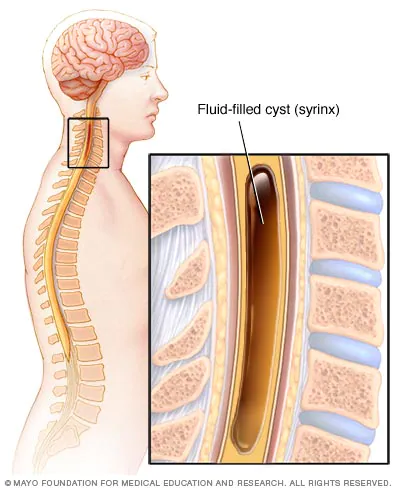
A syrinx is a fluid-filled neuroglial cavity within the spinal cord, in the brain stem, or in the nerves of the elbow
A syrinx is a rare, fluid-filled neuroglial cavity within the spinal cord (syringomyelia), in the brain stem (syringobulbia), or in the nerves of the elbow, usually in a young age. Presentation Symptoms usually begin insidiously between adolescence and age 45. Syringomyelia develops in the center of the spinal cord, causing a central cord syndrome. Pain and temperature sensory deficits occur early but may…
-

What Is Nitrophenol? (besides something mentioned in ‘Scientific Opinion on the re‐evaluation of aspartame as a food additive’)
Nitrophenols are compounds of the formula HOC6H5−x(NO2)x. The conjugate bases are called nitrophenolates. Nitrophenols are more acidic than phenol itself. Wikipedia Mono-nitrophenols with the formula HOC6H4NO2. Three isomeric nitrophenols exist: o-Nitrophenol (2-nitrophenol; OH and NO2 groups are neighboring; CAS number: 88-75-5), a yellow crystalline solid (m.p. 46 °C). m-Nitrophenol (3-nitrophenol, CAS number: 554-84-7), a yellow solid (m.p. 97 °C) and precursor to the…
Recent Posts
- 🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
- 🧂 Sodium Reduction and Sodium Replacement: A History of Reformulation and Exploding Diseases, Including Many Diseases Unheard of Before Deadly Sodium Policies
- 🧂 The DEADLY 1500 mg Sodium Recommendation predates the WHO’s formal global sodium reduction push by nearly a decade (and it’s even worse than that)
- 🧬 What Is Beta-Glucuronidase?
- When Sugar Was Salt: Crystalline Confusion and the Covenant of Sweetness
Tags
ADAM ASPARTAME Birds Blood Bones Brain Bugs Cancer Columba Cows crystallography Death Death cults Eggs Etymology Gastrin Gold Growth hormone History Hormones Insulin Liver Mere Perplexity Metal Monkey Business Mythology Paracetamol Plants Poison Pregnancy Protein Religion Reproduction Rocks Salt Slavery Snakes Sodium the birds and the bees Thiocyanate Tobacco Tylenol Underworld Venom zinc
