Tag: Phenol
-
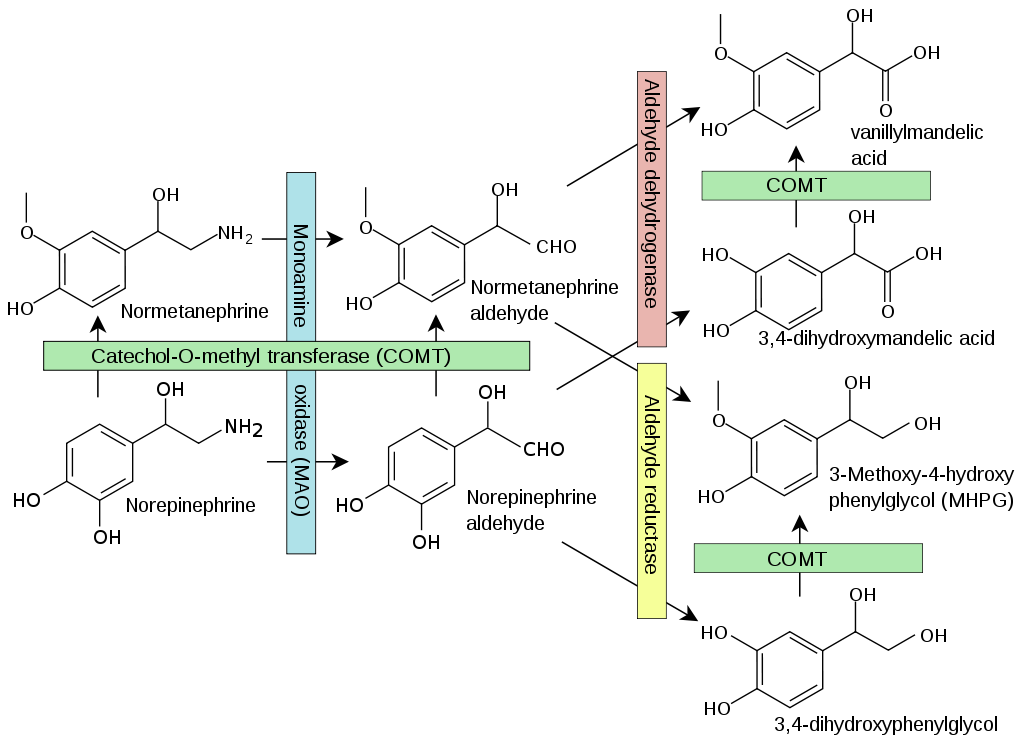
Homovanillic acid (HVC) and Vanillylmandelic acid (VMA)
Homovanillic acid (HVA) is a major catecholamine metabolite that is produced by a consecutive action of monoamine oxidase and catechol-O-methyltransferase on dopamine. Homovanillic acid is used as a reagent to detect oxidative enzymes, and is associated with dopamine levels in the brain. In psychiatry and neuroscience, brain and cerebrospinal fluid levels of HVA are measured as a marker of metabolic stress caused by 2-deoxy-D-glucose. HVA presence supports a diagnosis of neuroblastoma and malignant pheochromocytoma. Fasting plasma levels of HVA are known to be…
-

Cryptanaerobacter phenolicus transforms phenol into benzoate via 4-hydroxybenzoate
Benzoic acid occurs naturally in many plants and serves as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of many secondary metabolites. Salts of benzoic acid are used as food preservatives. Benzoic acid is an important precursor for the industrial synthesis of many other organic substances. The salts and esters of benzoic acid are known as benzoates. Benzoic acid occurs naturally as do its esters in many plant…
-
Rhodococcus phenolicus is a bacterium able to degrade phenol as sole carbon source
Rhodococcus phenolicus is a bacterium species in the genus Rhodococcus. Phenolicus comes from New Latin noun phenol –olis, phenol; Latin masculine gender suff. –icus, suffix used in adjectives with the sense of belonging to; New Latin masculine gender adjective phenolicus, belonging to phenol. This species is able to degrade phenol as sole carbon source. External links Categories:
-

Piceol is a phenolic compound found in the needles and in mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruces and more
Piceol is a phenolic compound found in the needles and in mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruces (Picea abies). Picein is the glucoside of piceol. Pungenin is a also phenolic compound found in the needles of Blue Spruce (Picea pungens). It is the glucoside of 3,4-dihydroxyacetophenone. The compound serves a feeding deterrent against Spruce Budworm larvae. This may be a little redundant as the base information is already included on the Baccharis page…
-
4-Aminophenol – what a molecule!
This is a humble organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4OH, but don’t let its unassuming structure fool you. This is not just any crystalline powder; this is a chemical that moonlights as a pharmaceutical ingredient, a hair dye precursor, and—wait for it—a black-and-white film developer. If molecules had résumés, 4-Aminophenol’s would read like someone who’s worked…
-

Phenol injections – originally used by the Nazis as part of the Aktion T4 euthanasia program – were used as a means of individual execution by Nazi Germany during the Second World War.
The toxic effect of phenol on the central nervous system, causes sudden collapse and loss of consciousness in both humans and animals; a state of cramping precedes these symptoms because of the motor activity controlled by the central nervous system.[“Phenol”. Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Vol. 25. Wiley-VCH. 2003. pp. 589–604.] Injections of phenol were used as a…
NOTES
- 🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
- 🧂 Sodium Reduction and Sodium Replacement: A History of Reformulation and Exploding Diseases, Including Many Diseases Unheard of Before Deadly Sodium Policies
- 🧂 The DEADLY 1500 mg Sodium Recommendation predates the WHO’s formal global sodium reduction push by nearly a decade (and it’s even worse than that)
- 🧬 What Is Beta-Glucuronidase?
- When Sugar Was Salt: Crystalline Confusion and the Covenant of Sweetness
Tags
ADAM ASPARTAME Birds Blood Bones Brain Bugs Cancer Columba Cows crystallography Death Death cults Eggs Etymology Gastrin Gold Growth hormone History Hormones Insulin Liver Mere Perplexity Metal Monkey Business Mythology Paracetamol Plants Poison Pregnancy Protein Religion Reproduction Rocks Salt Slavery Snakes Sodium the birds and the bees Thiocyanate Tobacco Tylenol Underworld Venom zinc

