Tag: Poison
-
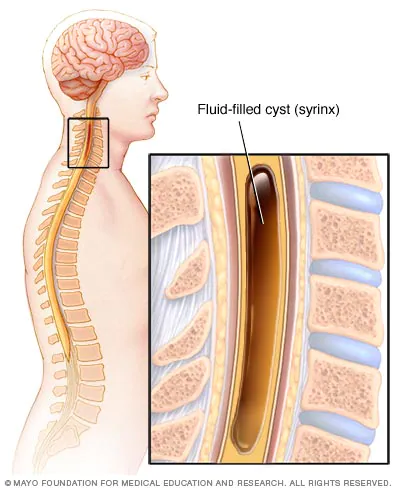
A syrinx is a fluid-filled neuroglial cavity within the spinal cord, in the brain stem, or in the nerves of the elbow
A syrinx is a rare, fluid-filled neuroglial cavity within the spinal cord (syringomyelia), in the brain stem (syringobulbia), or in the nerves of the elbow, usually in a young age. Presentation Symptoms usually begin insidiously between adolescence and age 45. Syringomyelia develops in the center of the spinal cord, causing a central cord syndrome. Pain and temperature sensory deficits occur early but may…
-
Experts warn of fatty liver disease ‘epidemic’ in young people
In Bristol University‘s study Children of the 90s, 2.5% of 4,000 people born in 1991 and 1992 were found by ultrasound scanning at the age of 18 to have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; five years later transient elastography (fibroscan) found over 20% to have the fatty deposits on the liver of steatosis, indicating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; half of those…
-
Lytico-bodig disease, Guam disease, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-parkinsonism-dementia (ALS-PDC) is a neurodegenerative disease or all of them
Lytico-bodig (also Lytigo-bodig) disease, Guam disease, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-parkinsonism-dementia (ALS-PDC) is a neurodegenerative disease of uncertain etiology endemic to the Chamorro people of the island of Guam in Micronesia. Lytigo and bodig are Chamorro language words for two different manifestations of the same condition. ALS-PDC, a term coined by Asao Hirano and colleagues in 1961, reflects its resemblance to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease. First reports of the disease surfaced in three death certificates on Guam in 1904 which made…
-
Cassava is used in a number of commercially available laundry products
Cassava is also used in a number of commercially available laundry products, especially as starch for shirts and other garments. Using cassava starch diluted in water and spraying it over fabrics before ironing helps stiffen collars.
-
Malnutrition may play a role in Tropical ataxic neuropathy (TAN) aka Strachan-Scott Syndrome and prisoners of war neuropathy
Tropical ataxic neuropathy (TAN, also known as Strachan-Scott Syndrome and prisoners of war neuropathy) is a disease or category of diseases that commonly causes disability and increases mortality. The causes of TAN are not understood; there is no generally accepted treatment, and the reported outcomes are inconsistent. The disease affects poor tropical populations; there are no good statistics on how…
-
Konzo is an epidemic paralytic disease reportedly from simultaneous malnutrition and high dietary cyanide intake
Konzo is an epidemic paralytic disease occurring among hunger-stricken rural populations in Africa where a diet dominated by insufficiently processed cassava results in simultaneous malnutrition and high dietary cyanide intake. Konzo was first described by Giovanni Trolli in 1938 who compiled the observations from eight doctors working in the Kwango area of the Belgian Congo (now Democratic Republic of the Congo). “Konzo” means “tied legs” in…
-
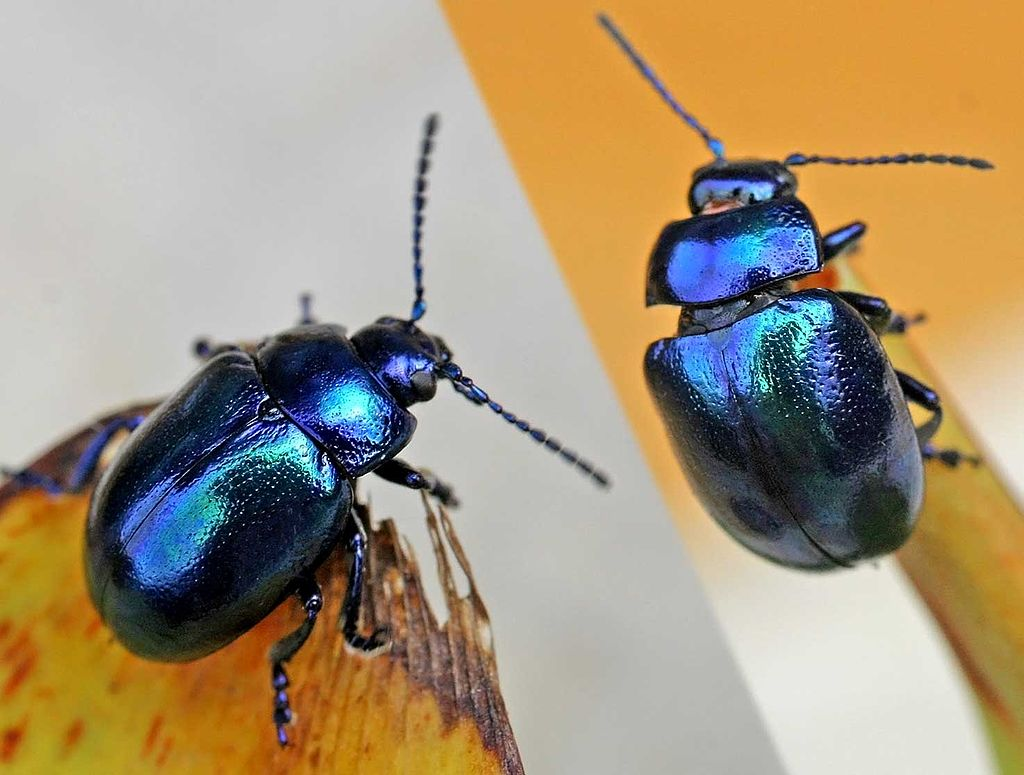

Chrysolina beetles, including Chrysolina coerulans, have cardiac glycosides (including xylose) in their defensive glands
The defensive secretions of some chrysomelid beetles belonging to the genera Chrysolina, Chrysochloa, and Dlochrysa contain complex mixtures of cardenolides. The spectral data for some of these compounds suggest that they are monohydroxylated digitoxigenin derivatives linked to a pentose (such as xylose or arabinose). Evidence indicates that the beetles do not sequester these steroid glycosides…
-

Xylitol: sweetener and laxative from hell
Xylitol, a natural sugar alcohol, has gained popularity as a low-calorie sweetener and the peddlers have attributed numerous health benefits to their product. This post is going to focus on one that doesn’t get nearly enough attention except in the countries where it was banned in things like soft drinks and elsehwere requires a diarrhea…
-
5-Nitro-2-propoxyaniline, aka P-4000 and Ultrasüss, banned artificial sweetener
5-Nitro-2-propoxyaniline, also known as P-4000 and Ultrasüss, is about 4,000 times the intensity of sucrose (hence its alternate name, P-4000). It is an orange solid that is only slightly soluble in water. It is stable in boiling water and dilute acids. 5-Nitro-2-propoxyaniline was once used as an artificial sweetener but has been banned in the United States because of its possible toxicity. In…
-
Dulcin, toxic artificial sweetener about 250 times sweeter than sugar
Dulcin is an artificial sweetener about 250 times sweeter than sugar, discovered in 1883 by the Polish chemist Józef (Joseph) Berlinerblau (27 August 1859 – 1935). It was first mass-produced about seven years later. Although it was discovered only five years after saccharin, it never enjoyed the latter compound’s market success. Nevertheless, it was an important sweetener of the early 20th…
-
Mithridatism
Mithridatism is the practice of protecting oneself against a poison by gradually self-administering non-lethal amounts. The word is derived from Mithridates VI, the King of Pontus, who so feared being poisoned that he regularly ingested small doses, aiming to develop immunity. Not to be confused with Mithraism. Background Mithridates VI‘s father, Mithridates V, was assassinated by poisoning by a conspiracy among his attendants. After…
-

Toxin (etymology)
toxin (n.) “organic poison,” especially one produced by bacteria in an animal body, 1886, from toxic + -in (2). toxic (adj.) 1660s, from French toxique and directly from Late Latin toxicus “poisoned,” from Latin toxicum “poison,” from Greek toxikon (pharmakon) “(poison) for use on arrows,” from toxikon, neuter of toxikos “pertaining to arrows or archery,” and thus to a bow, from toxon “bow,” probably from a Scythian word that also was borrowed into Latin…
-
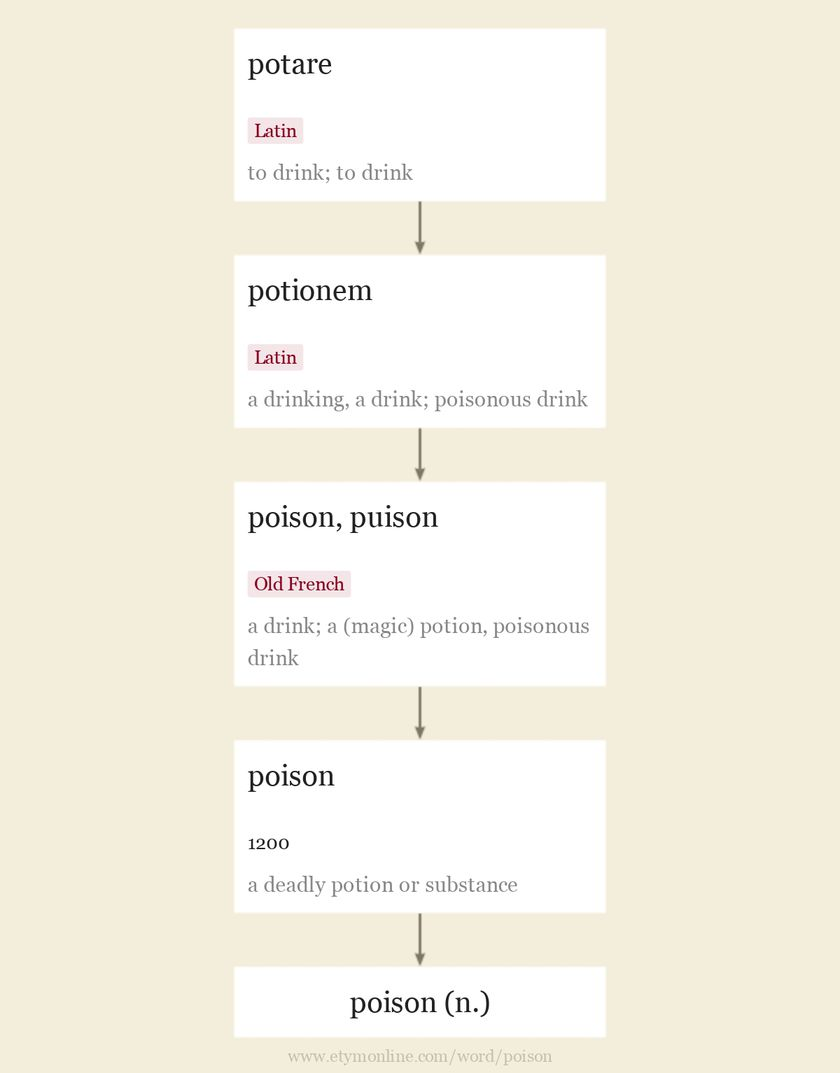
Poison (etymology)
poison (n.) c. 1200, poisoun, “a deadly potion or substance,” also figuratively, “spiritually corrupting ideas; evil intentions,” from Old French poison, puison (12c., Modern French poison) “a drink,” especially a medical drink, later “a (magic) potion, poisonous drink” (14c.), from Latin potionem (nominative potio) “a drinking, a drink,” also “poisonous drink” (Cicero), from potare “to drink” (from PIE root *po(i)- “to drink”). A doublet of potion. For similar form…
-
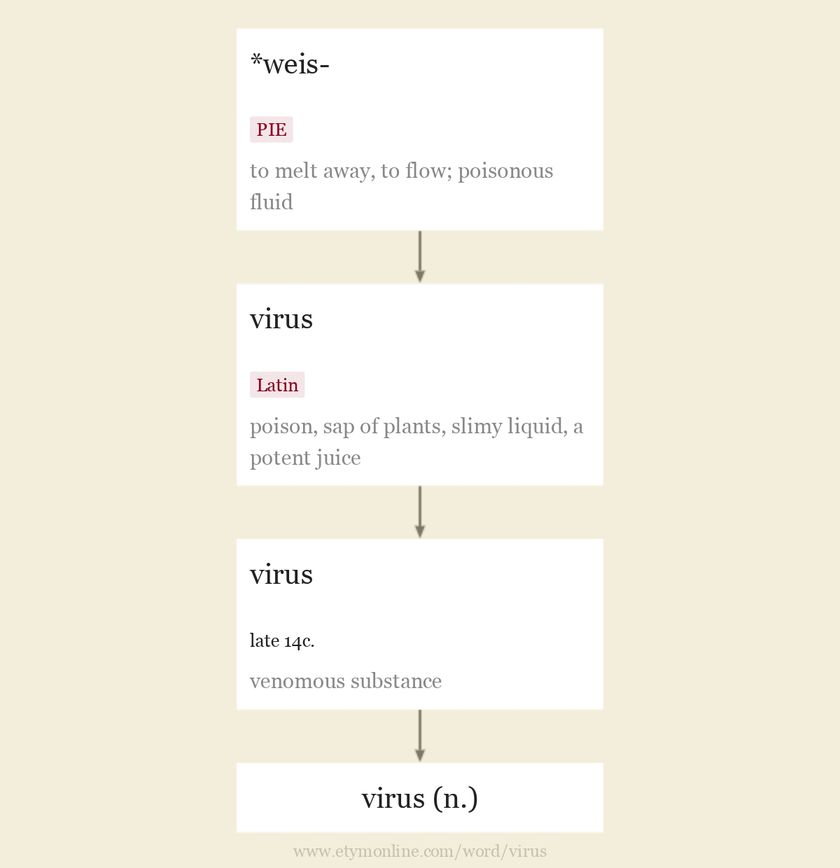
Virus (etymology)
virus (n.) late 14c., “poisonous substance” (a sense now archaic), from Latin virus “poison, sap of plants, slimy liquid, a potent juice,” from Proto-Italic *weis-o-(s-) “poison,” which is probably from a PIE root *ueis-, perhaps originally meaning “to melt away, to flow,” used of foul or malodorous fluids, but with specialization in some languages to “poisonous fluid” (source also of Sanskrit visam “venom, poison,” visah “poisonous;”…
-

Etymology of Pharmacy
pharmacy (n.) late 14c., farmacie, “a medicine that rids the body of an excess of humors (except blood);” also “treatment with medicine; theory of treatment with medicine,” from Old French farmacie “a purgative” (13c.) and directly from Medieval Latin pharmacia, from Greek pharmakeia “a healing or harmful medicine, a healing or poisonous herb; a drug, poisonous potion; magic (potion), dye, raw material…
-

What Is Nitrophenol? (besides something mentioned in ‘Scientific Opinion on the re‐evaluation of aspartame as a food additive’)
Nitrophenols are compounds of the formula HOC6H5−x(NO2)x. The conjugate bases are called nitrophenolates. Nitrophenols are more acidic than phenol itself. Wikipedia Mono-nitrophenols with the formula HOC6H4NO2. Three isomeric nitrophenols exist: o-Nitrophenol (2-nitrophenol; OH and NO2 groups are neighboring; CAS number: 88-75-5), a yellow crystalline solid (m.p. 46 °C). m-Nitrophenol (3-nitrophenol, CAS number: 554-84-7), a yellow solid (m.p. 97 °C) and precursor to the…
NOTES
- 🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
- 🧂 Sodium Reduction and Sodium Replacement: A History of Reformulation and Exploding Diseases, Including Many Diseases Unheard of Before Deadly Sodium Policies
- 🧂 The DEADLY 1500 mg Sodium Recommendation predates the WHO’s formal global sodium reduction push by nearly a decade (and it’s even worse than that)
- 🧬 What Is Beta-Glucuronidase?
- When Sugar Was Salt: Crystalline Confusion and the Covenant of Sweetness
Tags
ADAM ASPARTAME Birds Blood Bones Brain Bugs Cancer Columba Cows crystallography Death Death cults Eggs Etymology Gastrin Gold Growth hormone History Hormones Insulin Liver Mere Perplexity Metal Monkey Business Mythology Paracetamol Plants Poison Pregnancy Protein Religion Reproduction Rocks Salt Slavery Snakes Sodium the birds and the bees Thiocyanate Tobacco Tylenol Underworld Venom zinc

