🧂 Salt as the Gatekeeper Matrix
Domain Mechanism of Water Control Key Cell/System Salt Role PF4–CXCR4 Connection Biological Osmotic gradients across cell membranes Keratinocytes, melanocytes Na⁺ gradients drive cellular hydration and membrane potential High sodium upregulates…
Thunderstones in European Folklore
In Scandinavia thunderstones were frequently worshiped as family gods who kept off spells and witchcraft. Beer was poured over them as an offering, and they were sometimes anointed with butter. In Switzerland the owner of a thunderstone whirls…
Albanians believed the supreme powers of thunderstones were formed during lightning strikes
Albanians believed in the supreme powers of thunderstones (kokrra e rrufesë or guri i rejës), which were believed to be formed during lightning strikes and to fall from the sky. Thunderstones were preserved in family life…
“Ye therefore, who seek in science a means to satisfy your passions, pause in this fatal way: you will find nothing but madness or death.”
This is the meaning of the vulgar tradition that the devil ends sooner or later by strangling sorcerers. Eliphas Levi, Transcendental Magic Also… “We have said that impassioned ecstasy may…
The Garden of Earthly Delights, Hieronymus Bosch
The Garden of Earthly Delights is the modern title[a] given to a triptych oil painting on oak panel painted by the Early Netherlandish master Hieronymus Bosch, between 1490 and 1510, when Bosch was between 40 and 60 years old. It has been…
Goldfinch in art
The bird that repeatedly, almost obsessively, turns up in Renaissance religious painting is the European Goldfinch Carduelis carduelis, almost always in the hands of the Infant Jesus, and symbolising variously the…
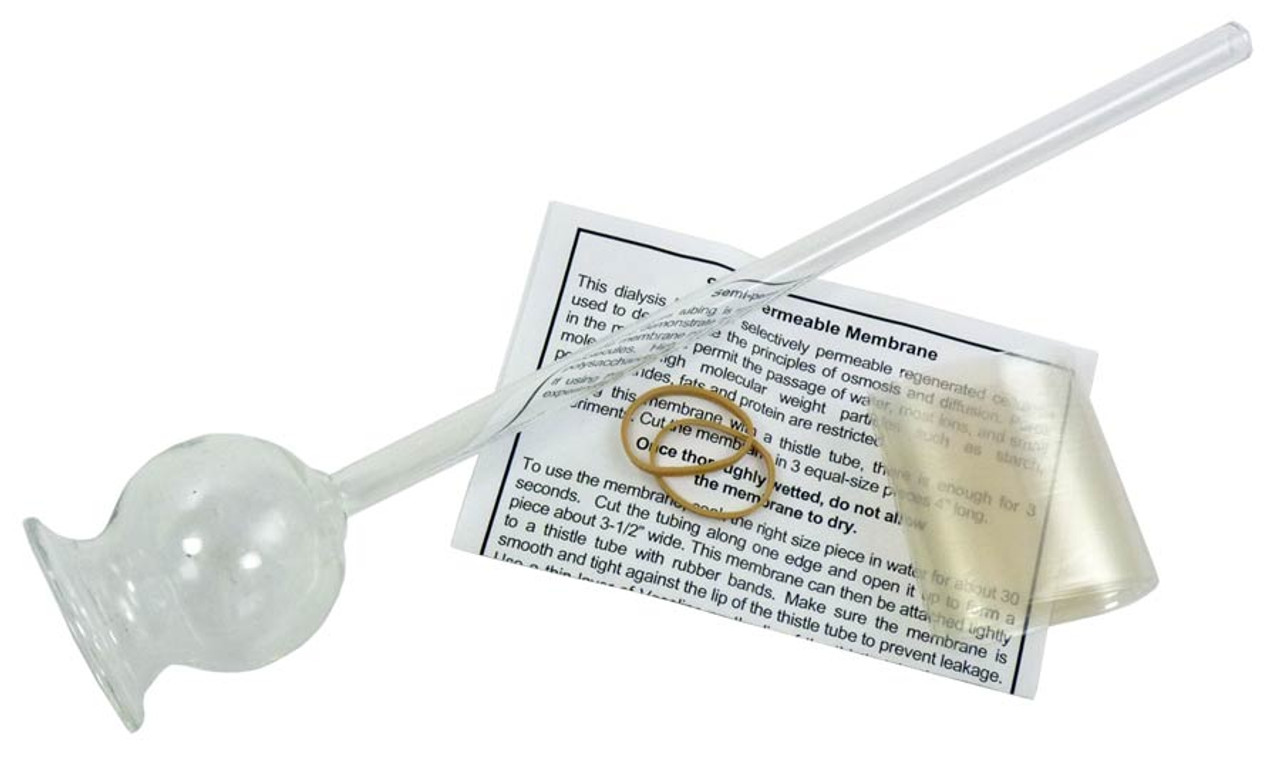
Thistle tubes, thistle feeders, distelfinks and goldfinches
A thistle tube is a piece of laboratory glassware consisting of a shaft of tube, with a reservoir and funnel-like section at the top. Thistle tubes are typically used by chemists to add liquid to an existing system or…
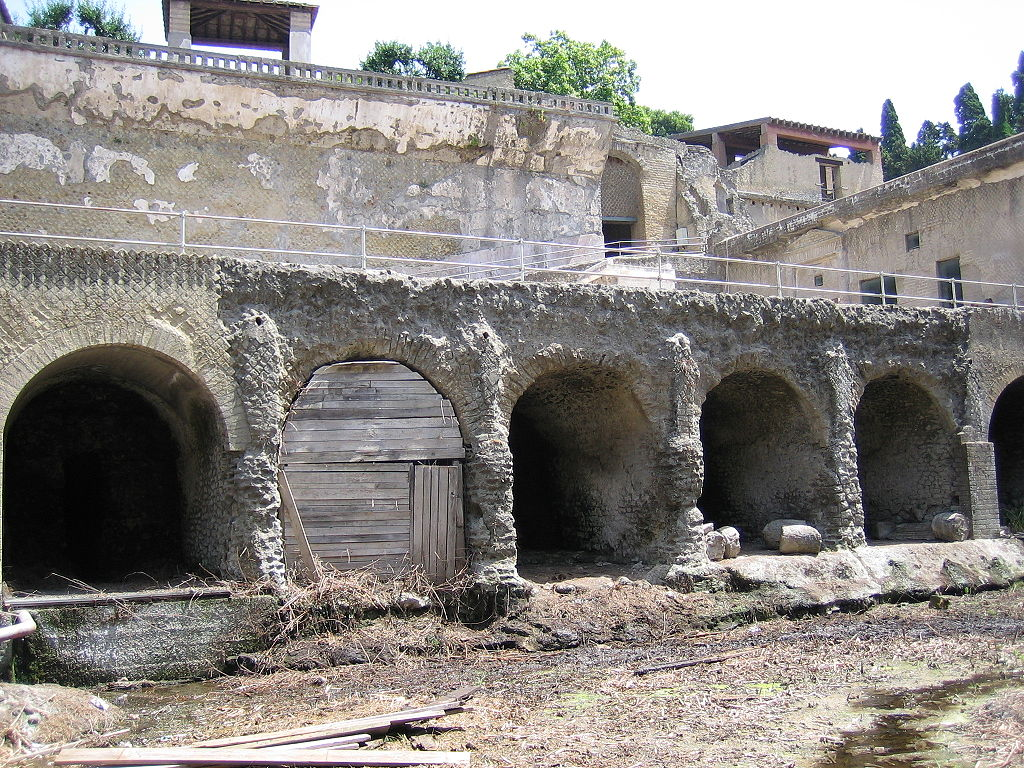
Herculaneum was an ancient Roman town buried under volcanic ash and pumice in the Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD.
Herculaneum (Neapolitan and Italian: Ercolano) was an ancient Roman town, located in the modern-day comune of Ercolano, Campania, Italy. Herculaneum was buried under volcanic ash and pumice in the Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. Like the nearby city of Pompeii,…
Manes or Di Manes
In ancient Roman religion, the Manes or Di Manes are chthonic deities sometimes thought to represent souls of deceased loved ones. They were associated with the Lares, Lemures, Genii, and Di Penates as deities (di) that pertained to domestic, local, and…
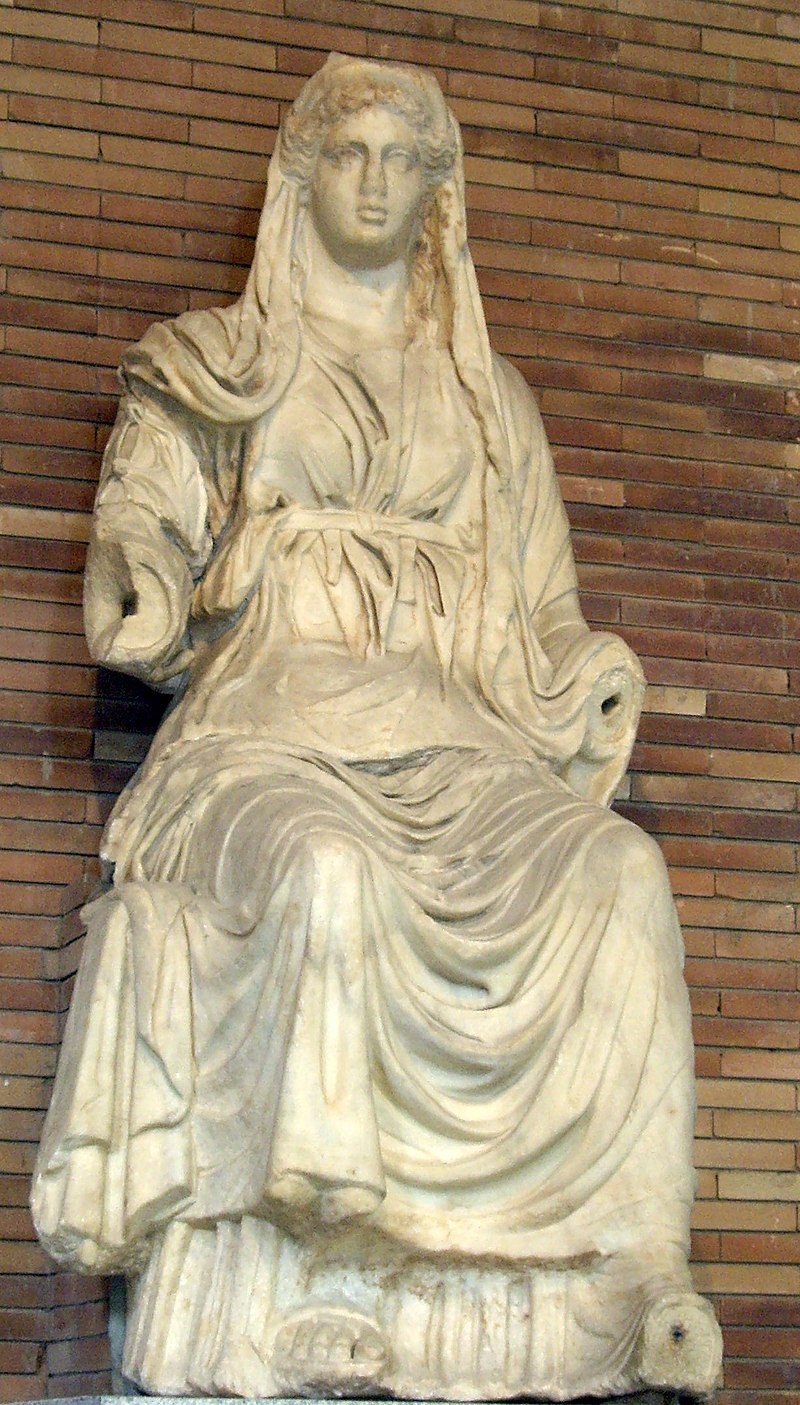
Ceres, Roman goddess
In ancient Roman religion, Ceres was a goddess of agriculture, grain crops, fertility and motherly relationships. She was originally the central deity in Rome’s so-called plebeian or Aventine Triad, then was paired with her daughter Proserpina in what Romans described as “the…
Stone lanterns
Stone lanterns (灯籠/灯篭/灯楼, Chinese: dēnglóng; Japanese: tōrō, meaning ‘light basket’, ‘light tower’)[a] are a type of traditional East Asian lantern made of stone, wood, or metal. Originating in China, stone lanterns spread to Japan,…