Dermatan sulfate (and a few other things)
Dermatan sulfate is a glycosaminoglycan (formerly called a mucopolysaccharide) found mostly in skin, but also in blood vessels, heart valves, tendons, and lungs. It is also referred to as chondroitin sulfate B, although it is no longer classified as
Chondroitin sulfate
CHONDROITIN SULFATE is a sulfated glycosaminoglycan (GAG) composed of a chain of alternating sugars (N-acetylgalactosamine and glucuronic acid). It is usually found attached to proteins as part of a proteoglycan. A chondroitin chain can have over 100 individual sugars, each of which can be su
Steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) protein and a few related things
The steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) protein is a transcription factor involved in sex determination by controlling the activity of genes related to the reproductive glands or gonads and adrenal glands. This protein is encoded by the NR5A
Subtilisin
Subtilisin is a protease (a protein-digesting enzyme) initially obtained from Bacillus subtilis. Subtilisins belong to subtilases, a group of serine proteases that – like all serine proteases – initiate the nucleophilic attack on the peptide (amide) bond through a serine residue a
Structure of DNA repair protein XRCC4 aka X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 4
XRCC4 protein is a TETRAMER that resembles the shape of a DUMBBELL containing two globular ends separated by a long, thin stalk. The tetramer is composed of two dimers, and each dimer is made up of two similar subunits. The first subunit (L) contains amino acid residues 1 – 203 and has a longer
Staphylokinase (SAK) aka staphylococcal fibrinolysin or Müller’s factor
Staphylokinase (SAK; also known as staphylococcal fibrinolysin or Müller’s factor) is a protein produced by Staphylococcus aureus. It contains 136 amino acid residues and has a molecular mass of 15kDa. Synthesis of staphylokinase occurs in late exponential phase. It is similar to strep
Elastase
In molecular biology, elastase is an enzyme from the class of proteases (peptidases) that break down proteins. In particular, it is a serine protease. Forms and classification Eight human genes exist for elastase: Family Gene symbol Protein name EC number Approved Previous Appro
Agrin is a large chimeric proteoglycan, a heparan sulfate and chondroitin proteoglycan, whose best-characterised role is in the development of the neuromuscular junction during embryogenesis
Agrin was originally found in the electric organ of Tarpedo california and in the basal lamina at the neuromuscular junction as a protein that directs the aggregation of acetylcholine receptors (AChR) and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) at synaptic
Protein phosphorylation was first reported in 1906
Protein phosphorylation is a reversible post-translational modification of proteins in which an amino acid residue is phosphorylated by a protein kinase by the addition of a covalently bound phosphate group. Phosphorylation alters the structural conformation of a protein, causing it to
Phosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion.[1] This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology.[2] Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes.
Sericin is a protein created by Bombyx mori (silkworms) in the production of silk
Silk is a fibre produced by the silkworm in production of its cocoon. It consists mainly of two proteins, fibroin and sericin. Silk consists of 70–80% fibroin and 20–30% sericin; fibroin being the structural center of the silk, and sericin being the gum coating the fibres and allo
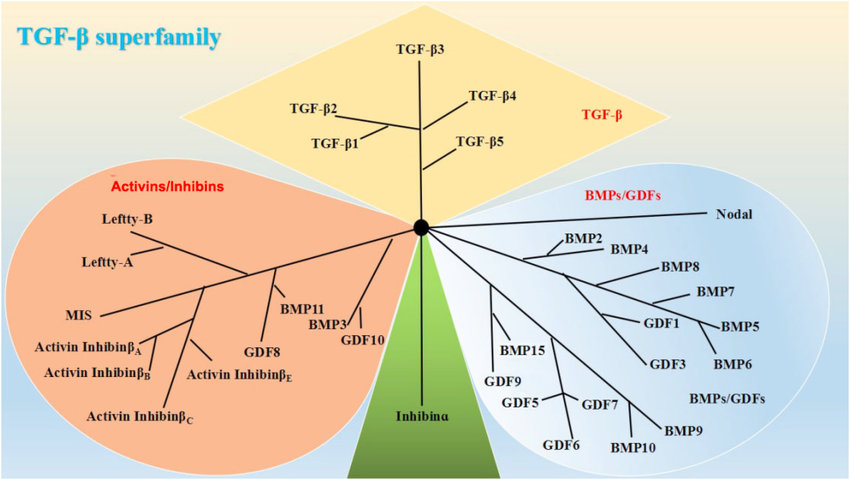
The transforming growth factor beta receptors
a family of serine/threonine kinase receptors involved in TGF beta signaling pathway
Fischer-Fantuzzi L, Vesco C. Deletion of 43 amino acids in the NH2-terminal half of the large tumor antigen of simian virus 40 results in a non-karyophilic protein capable of transforming established cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985
Abstract We have characterized a simian virus 40 (SV40) mutant, derived from the viral DNA insertion present in simian cell transformants, which carries a deletion affecting the NH2-terminal region of the SV40 large tumor antigen. This mutant protein is 6% smaller than normal, has lost the typical n
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH+3 form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), a
β-Methylamino-L-alanine, or BMAA
β-Methylamino-L-alanine, or BMAA, is a non-proteinogenic amino acid produced by cyanobacteria. BMAA is a neurotoxin and its potential role in various neurodegenerative disorders is the subject of scientific research. Structure and properties BMAA is a de