🧬 Disease Table with Low Sodium Connection
Disease / Condition Incidence Since 1977 Low Sodium Connection Obesity 🡅🡅 ✅ Chronic sodium deficiency disrupts leptin and aldosterone signaling, impairing satiety and promoting fat retention. SCN⁻ depletion (repressed due…
HFE H63D & VO2 max
SMOKE EM IF YOU GOT EM The HFE H63D is a single-nucleotide polymorphism in the HFE gene (c.187C>G, rs1799945), which results in the substitution of a histidine for an aspartic acid at amino acid position 63…
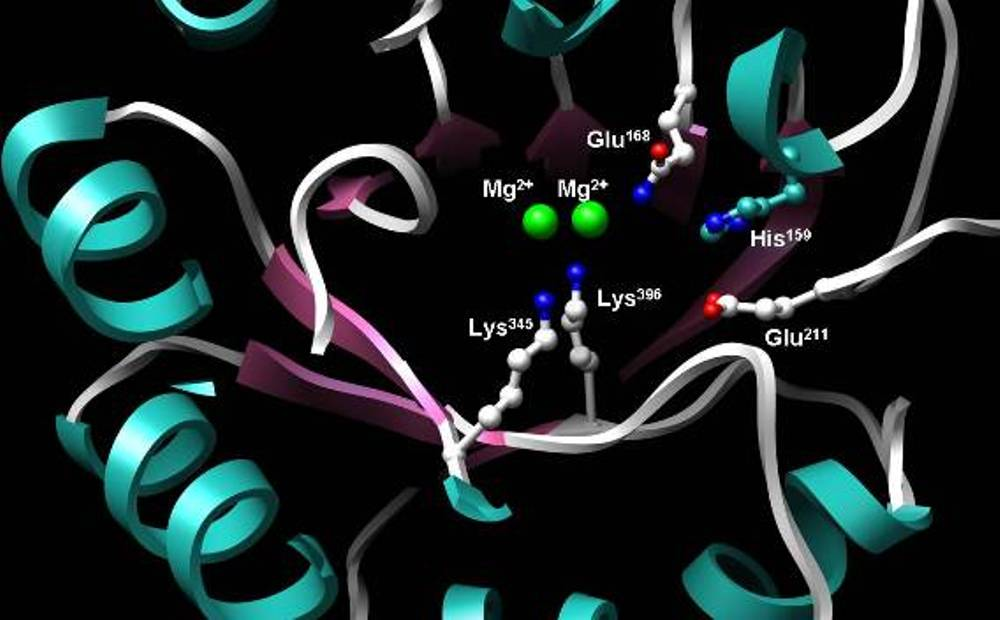
Deficiency of Adenosine deaminase 2 (DADA2)
Deficiency of Adenosine deaminase 2 (DADA2) is a monogenic disease associated with systemic inflammation and vasculopathy that affects a wide variety of organs in different patients. As a result, it is hard to characterize a patient with…