Neuromedins
-
Neuromedin U
Neuromedin U (or NmU) is a neuropeptide found in the brain of humans and other mammals, which has a number of diverse functions including contraction of smooth muscle, regulation of blood pressure, pain perception,… Read more.
-
Neuromedin S
Neuromedin S is a 36-amino acid neuropeptide found in the brain of humans and other mammals. It is produced in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus and is related to neuromedin U. It is thought to be involved… Read more.
-
Neuromedin N
Neuromedin N is a neuropeptide derived from the same precursor polypeptide as neurotensin, and with similar but subtly distinct expression and effects. References Peptides: neuropeptides Categories: Read more.
-
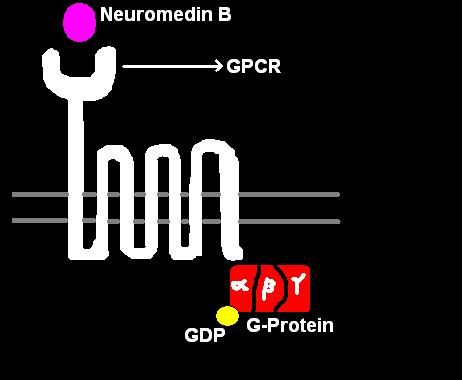
Neuromedin B
Neuromedin B (NMB) is a bombesin-related peptide in mammals. It was originally purified from pig spinal cord, and later shown to be present in human central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract. Sequence The sequence of the C-terminal… Read more.